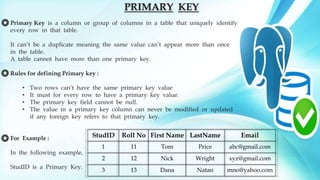
The document discusses different types of keys in database management systems (DBMS). It defines keys as attributes that help uniquely identify rows in database tables. The main types of keys discussed are primary keys, foreign keys, candidate keys, alternate keys, composite keys, and super keys. Primary keys uniquely identify each row and cannot contain null values or duplicates. Foreign keys link rows between tables. Candidate keys could serve as primary keys but only one is chosen. Alternate and composite keys provide other unique identifiers. Super keys may contain non-key attributes. Keys help maintain data integrity and relationships between tables in a DBMS.