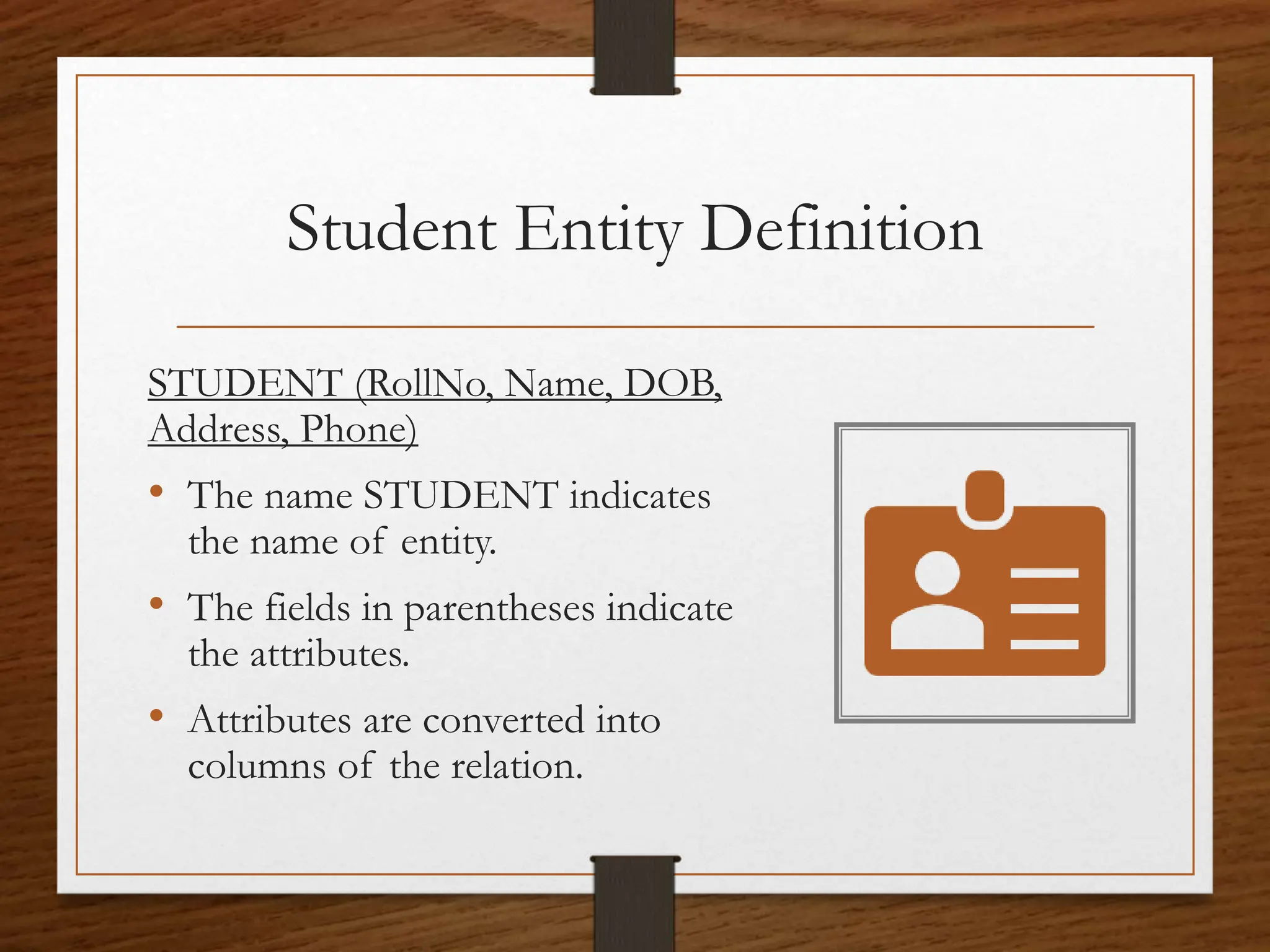
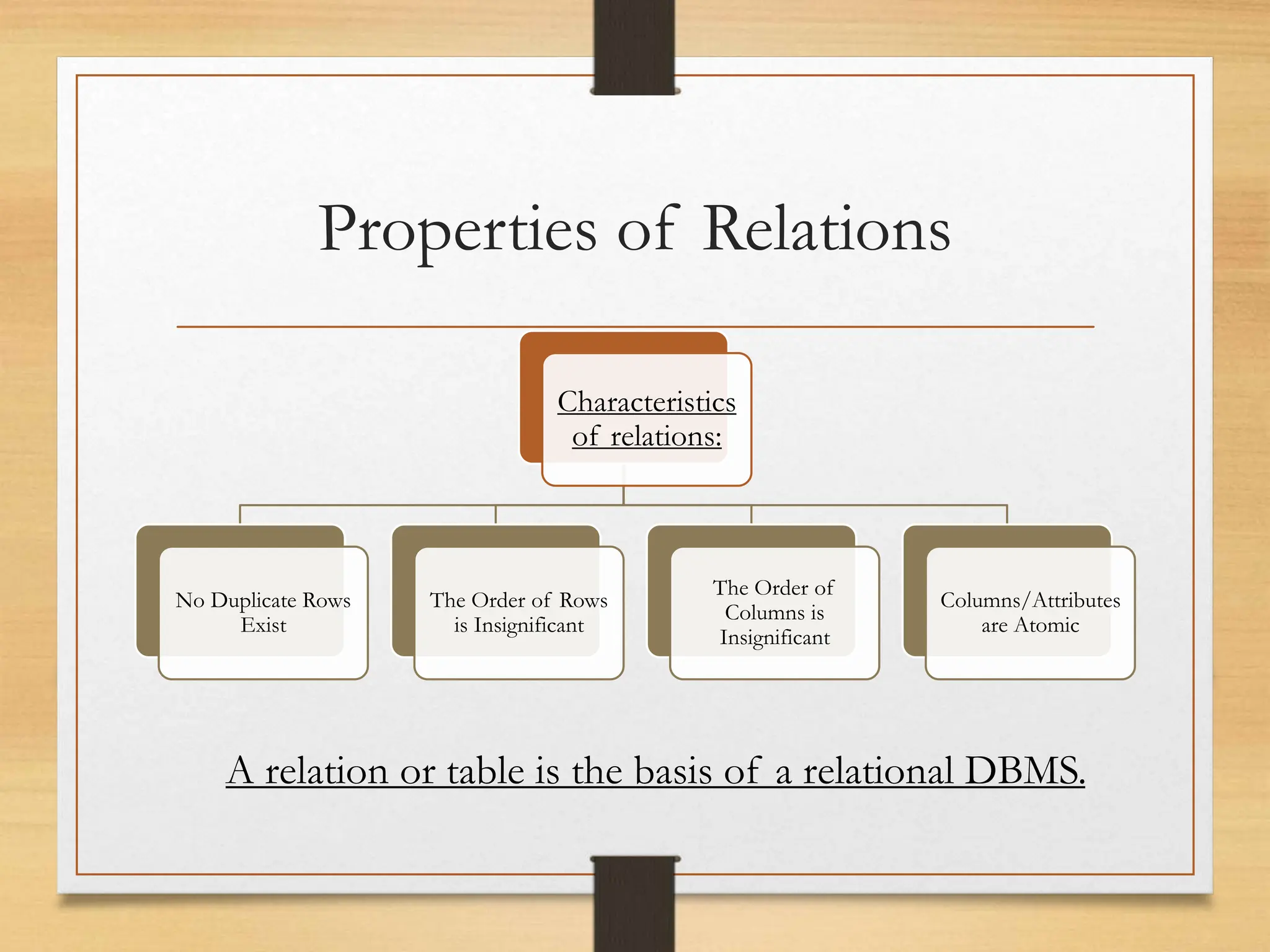
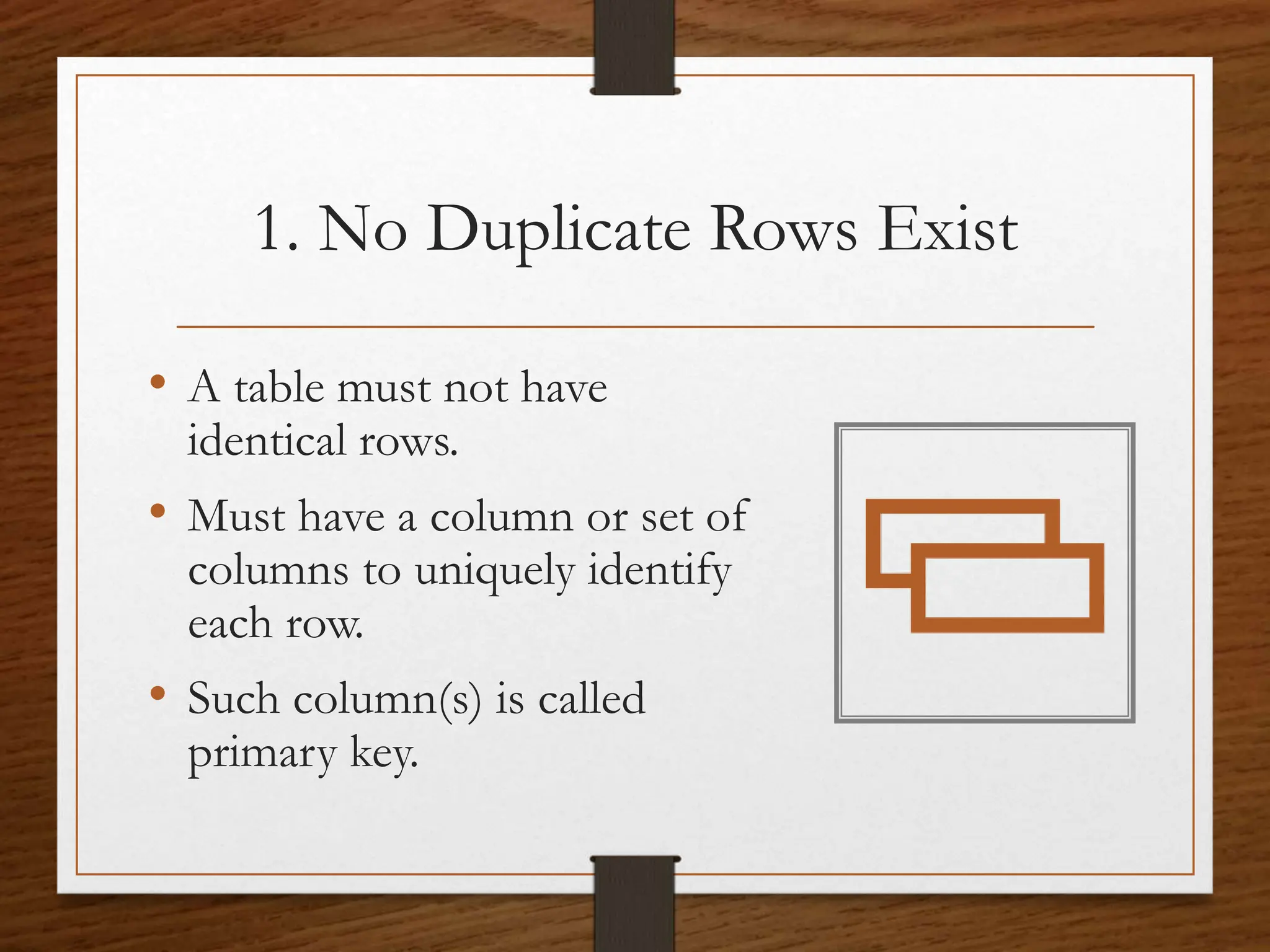
The document explains the concept of tables and relations in a Database Management System (DBMS), focusing on their formation, properties, and characteristics. It outlines the essential features of relations, including the significance of primary keys, and introduces the concept of views, which act as virtual tables to enhance data security and flexibility. An example of creating a SQL view to filter student records is also provided.