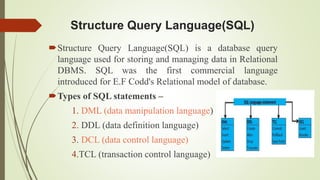
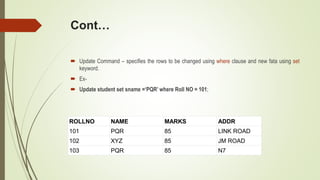
The document provides an overview of SQL, focusing on Data Manipulation Language (DML) and Data Control Language (DCL). It explains various SQL commands such as SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE, detailing their syntax and usage for managing database records. Additionally, it describes DCL commands like GRANT and REVOKE for controlling user access to the database.













![Grant command
GRANT command gives user's access privileges to the
database.
This command allows specified users to perform specific
tasks.
Syntax:
GRANT <privilege list>
ON <relation name or view name>
TO <user/role list>;
Example : GRANT Command
GRANT ALL ON employee
TO ABC;
[WITH GRANT OPTION]
In the above example, user 'ABC' has been given permission to view and modify the records in the
'employee' table.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pragyadmlddl-191015221008/85/SQL-commands-16-320.jpg)




