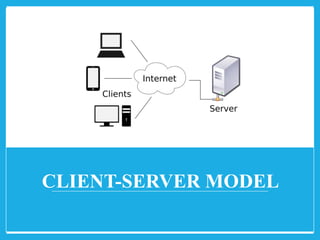
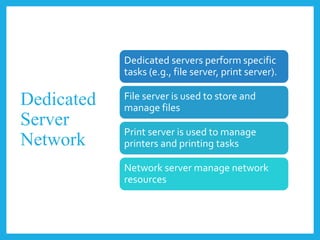
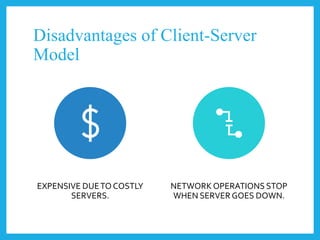
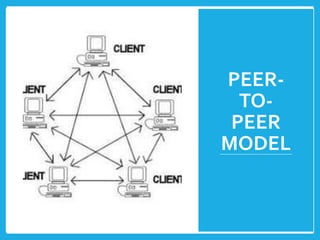
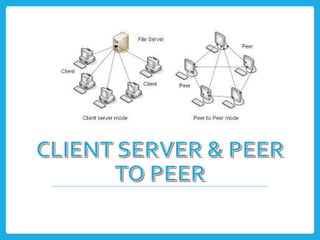
The document explores different computer network models, specifically the client-server, peer-to-peer, and hybrid models. It outlines the structure, advantages, and disadvantages of each model, noting that the client-server model uses a dedicated server for resource management, while the peer-to-peer model lacks a central server. The hybrid model incorporates features from both, leveraging their respective benefits.