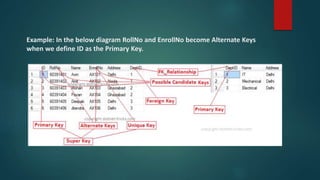
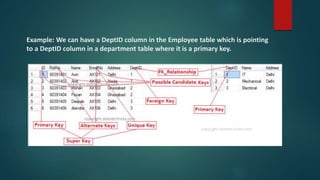
DBMS keys help uniquely identify and relate data between database tables. The seven types of keys are: super key, candidate key, primary key, alternate key, unique key, foreign key, and composite key. A primary key uniquely identifies each row/record in a table and cannot be null. Foreign keys link tables by matching to a primary key, ensuring referential integrity of the data.