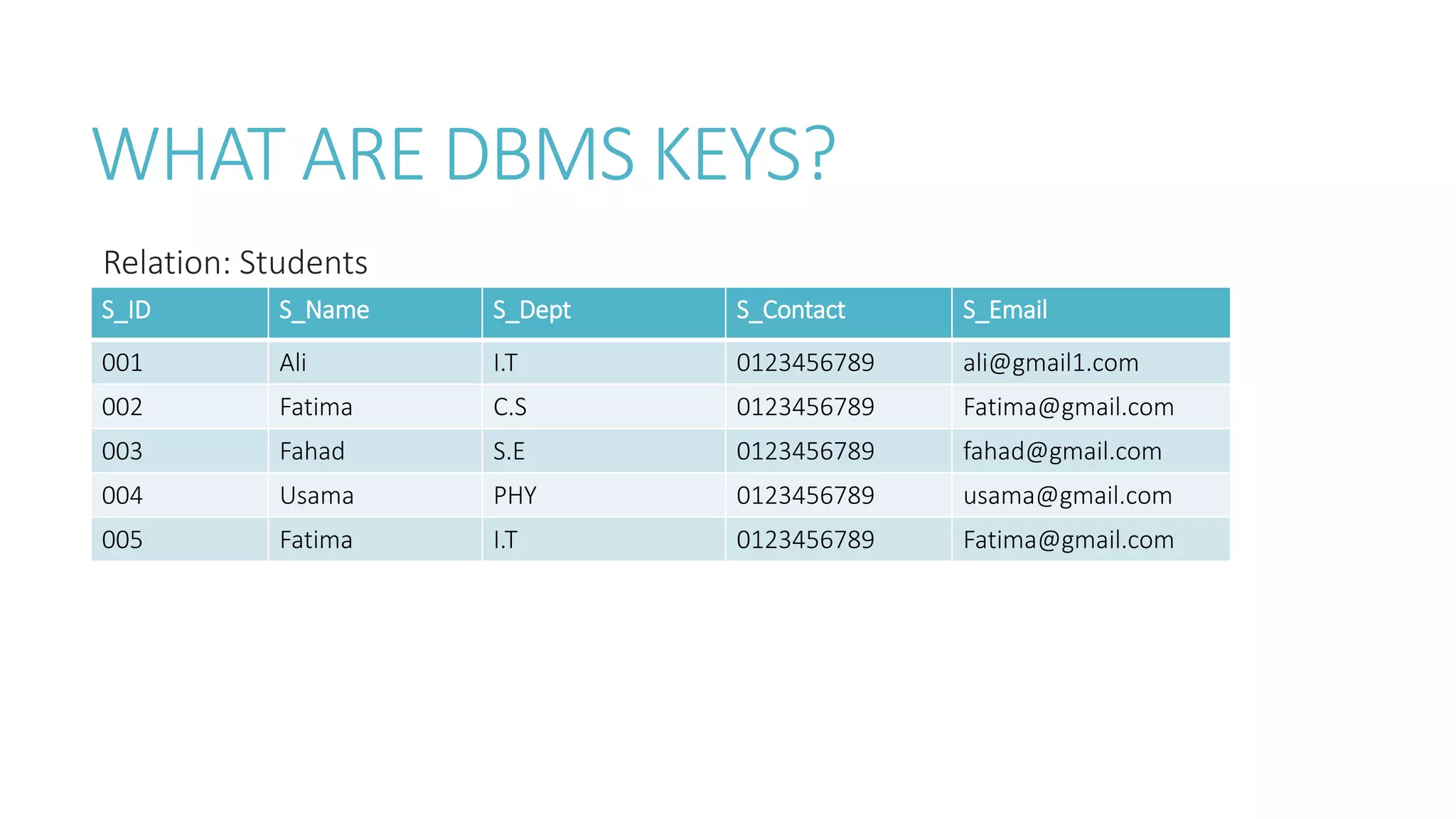
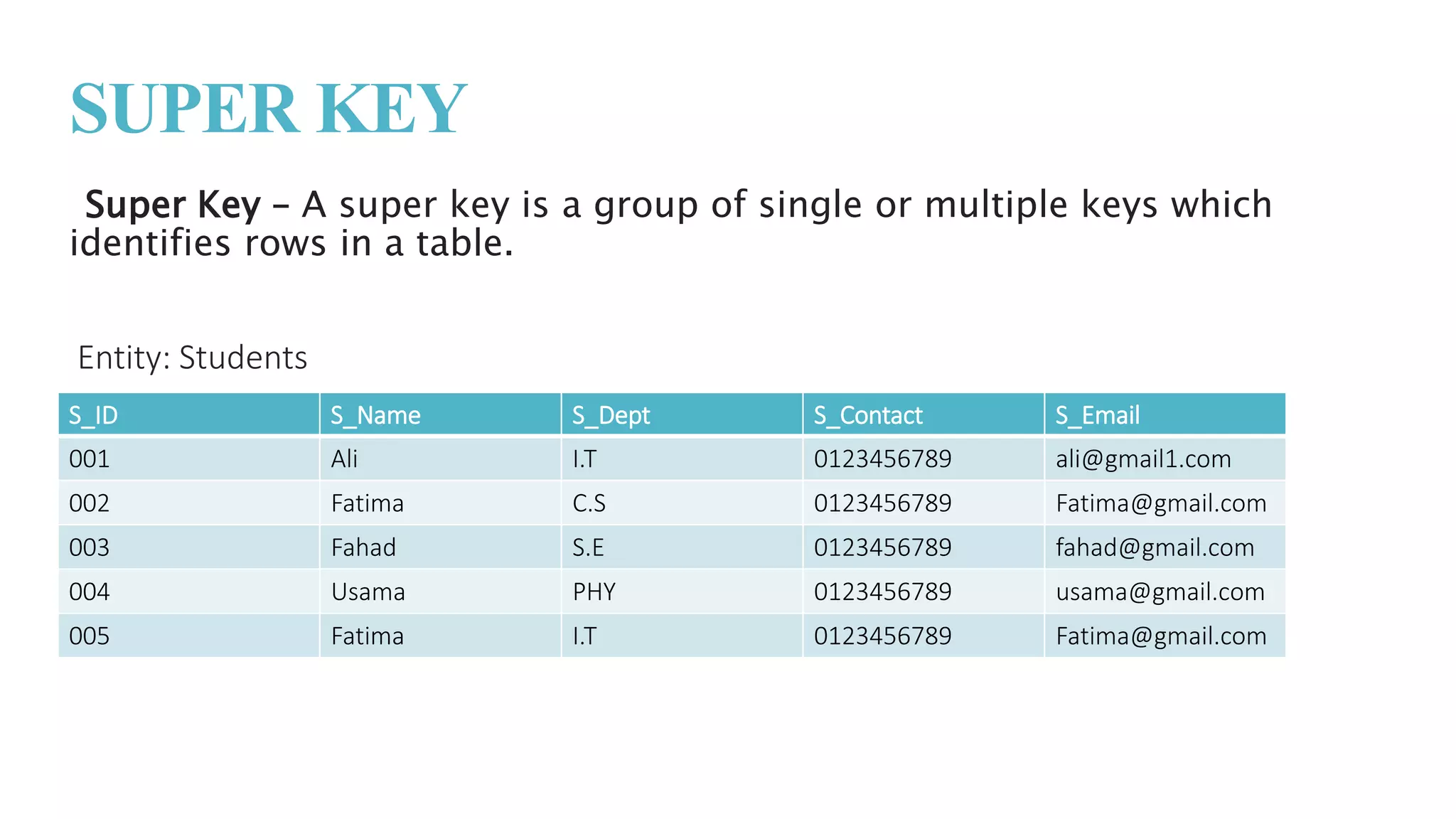
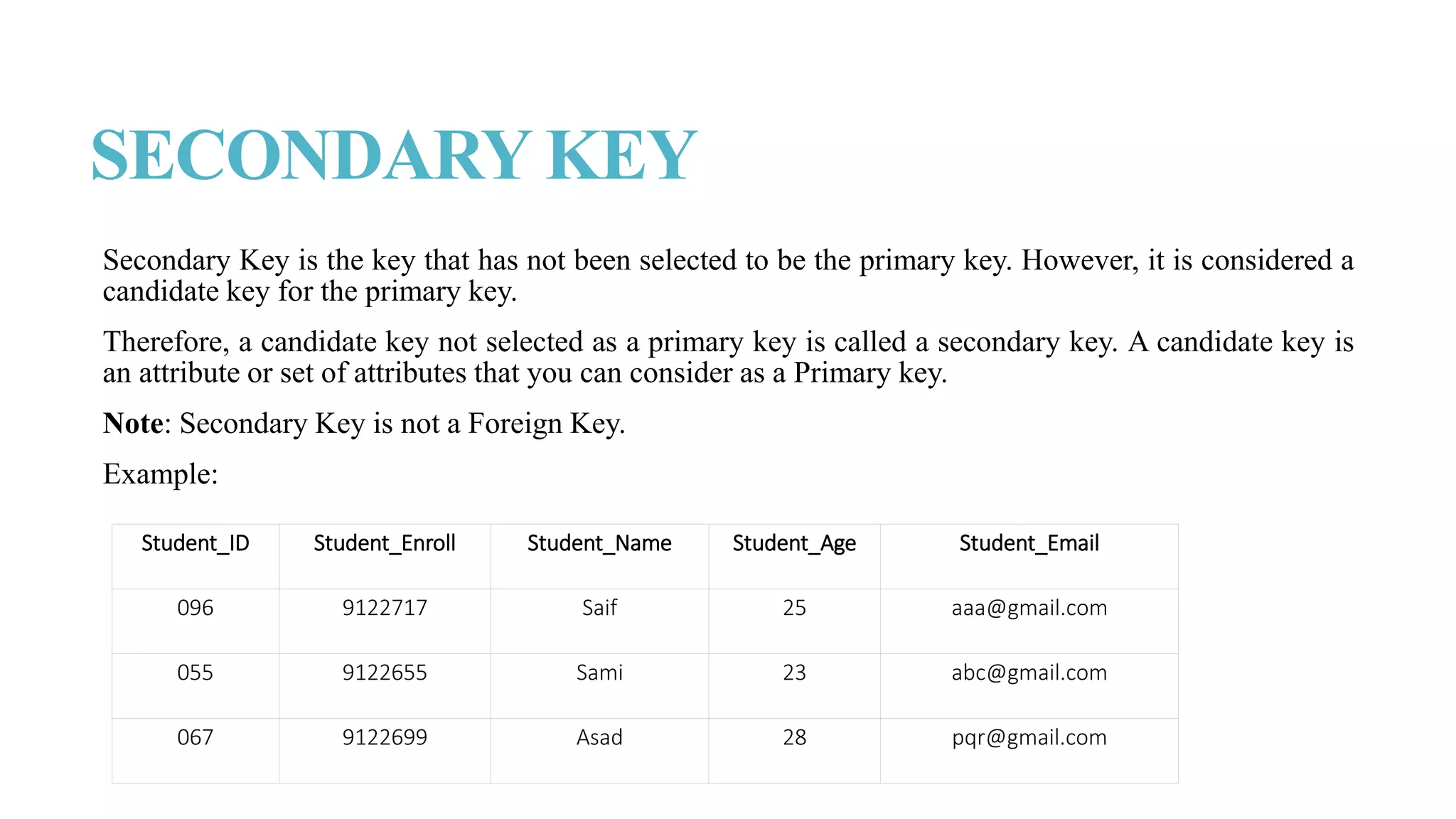
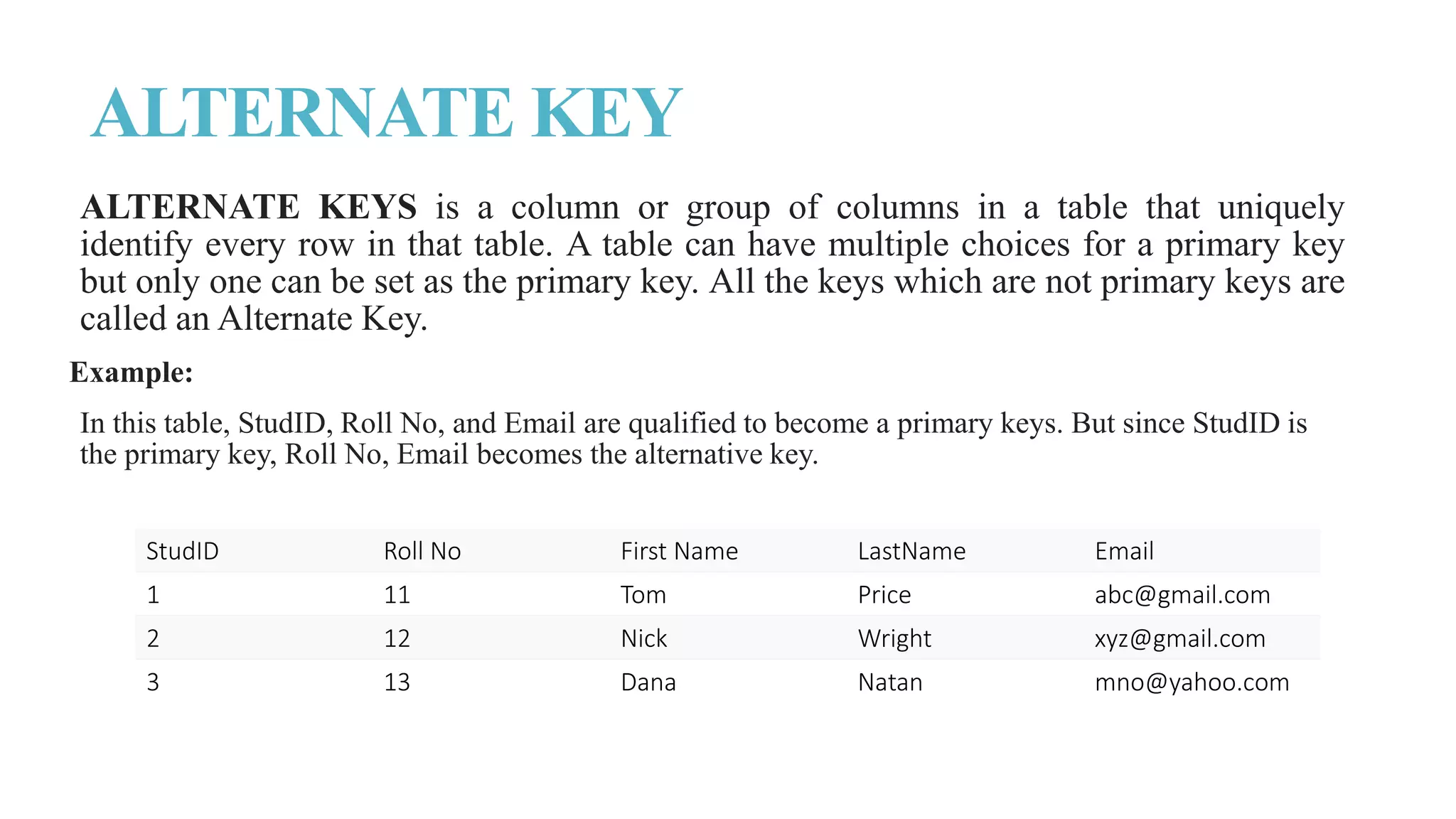
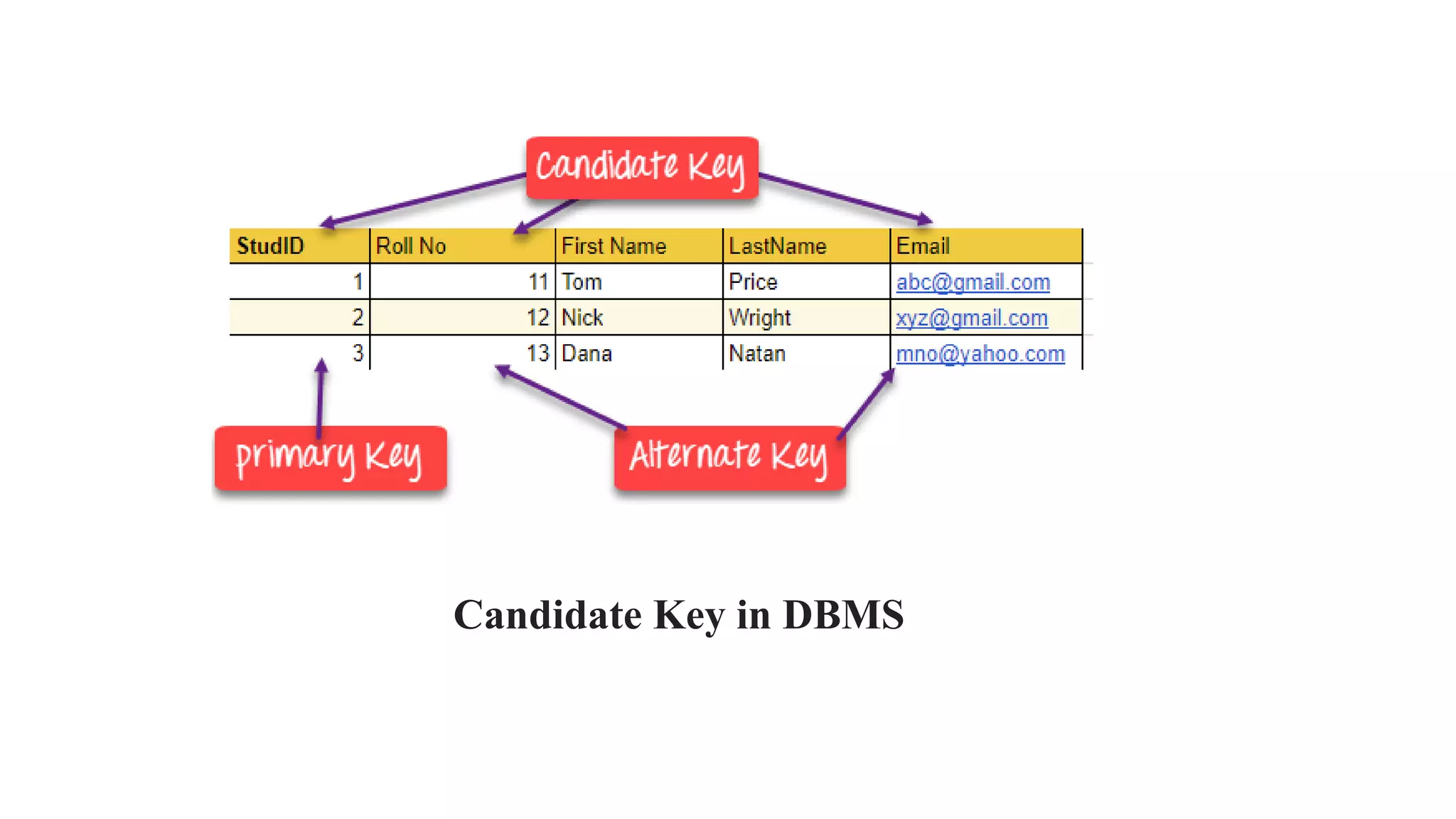
The document discusses different types of keys used in database management systems (DBMS) to uniquely identify and relate data between tables. It defines keys such as primary keys, foreign keys, candidate keys, surrogate keys, composite keys and others. For example, it states that a primary key uniquely identifies each row in a table and cannot be duplicate, while a foreign key creates a relationship between two tables by referencing the primary key of another table.