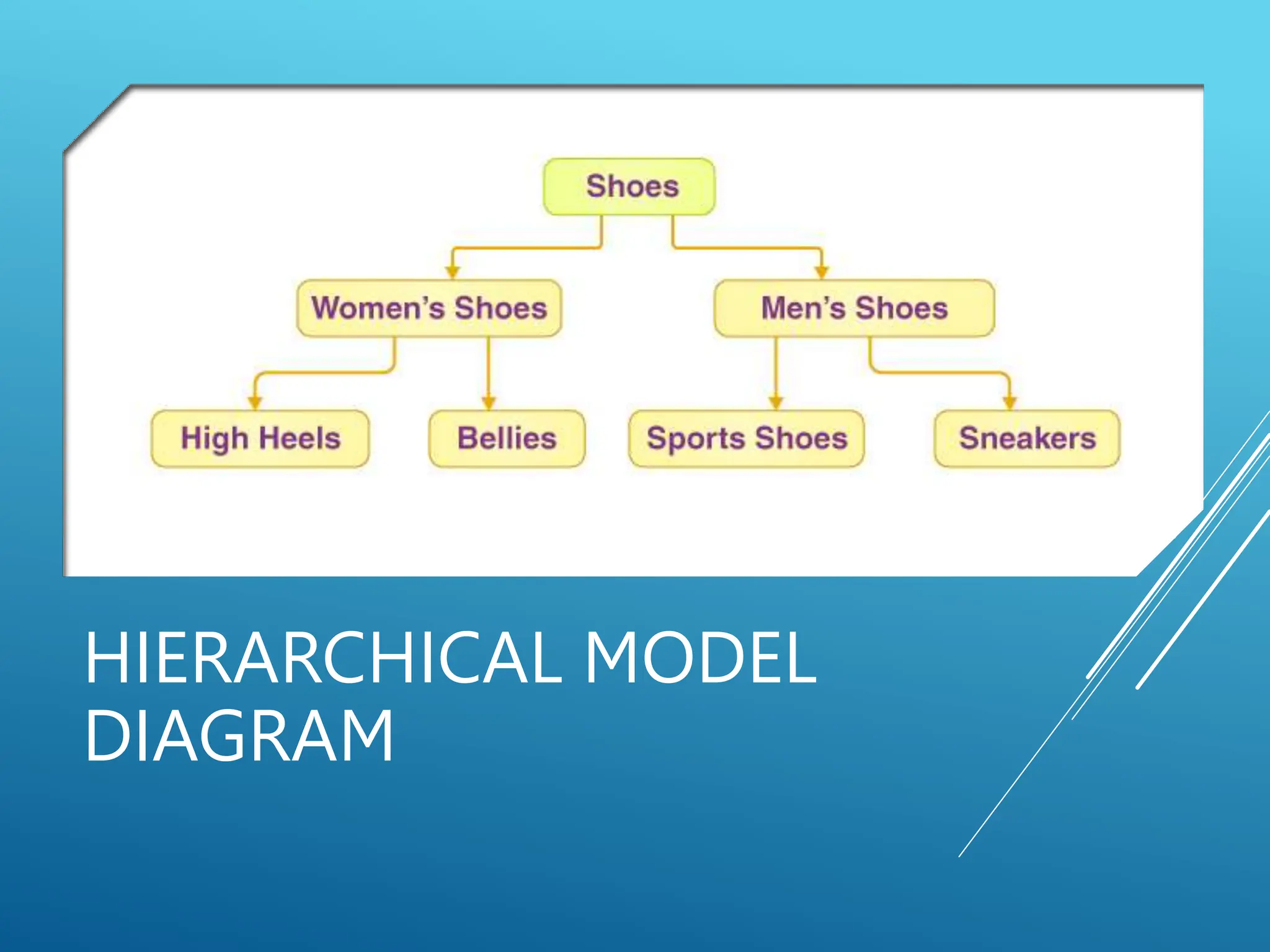
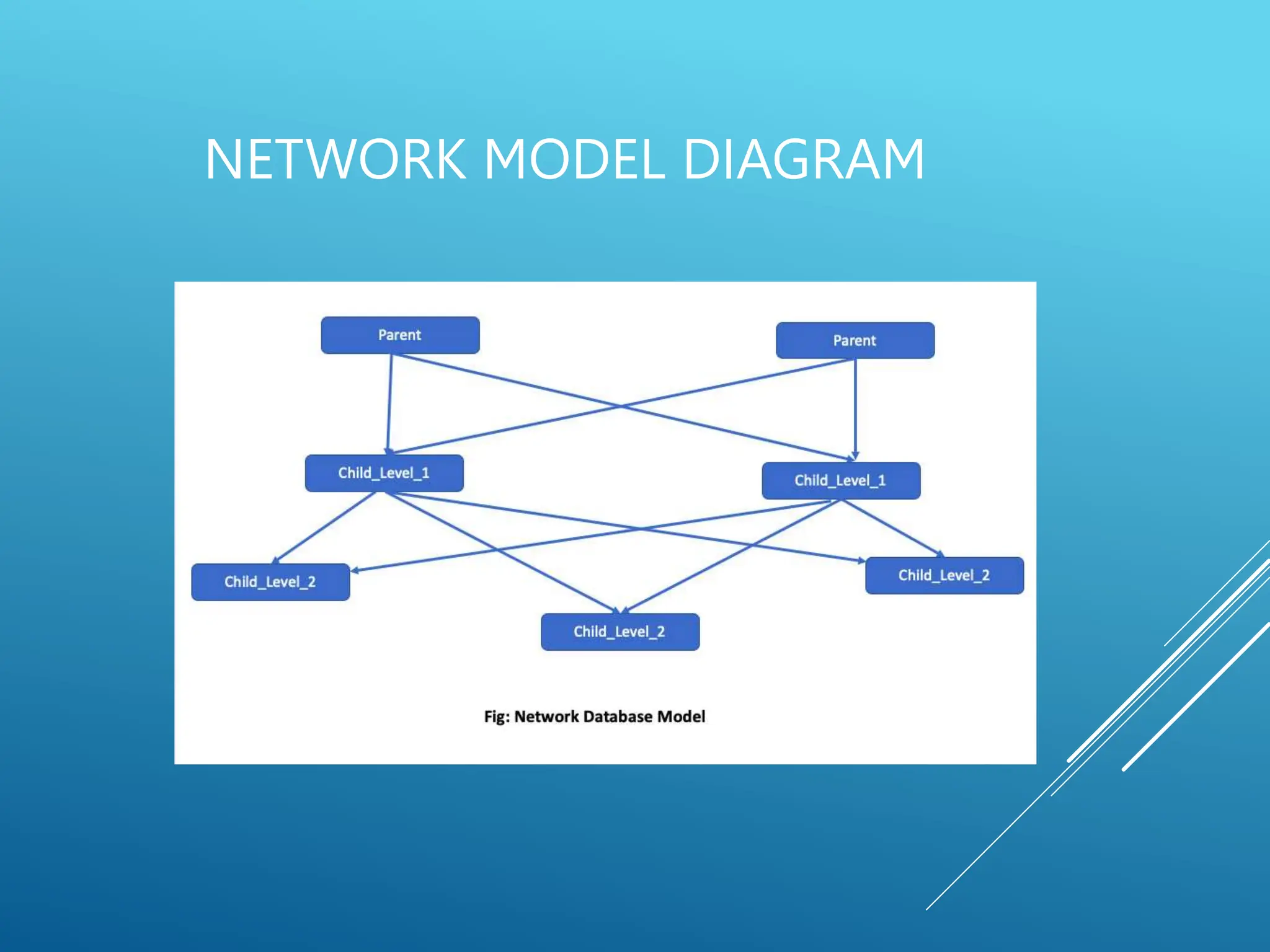
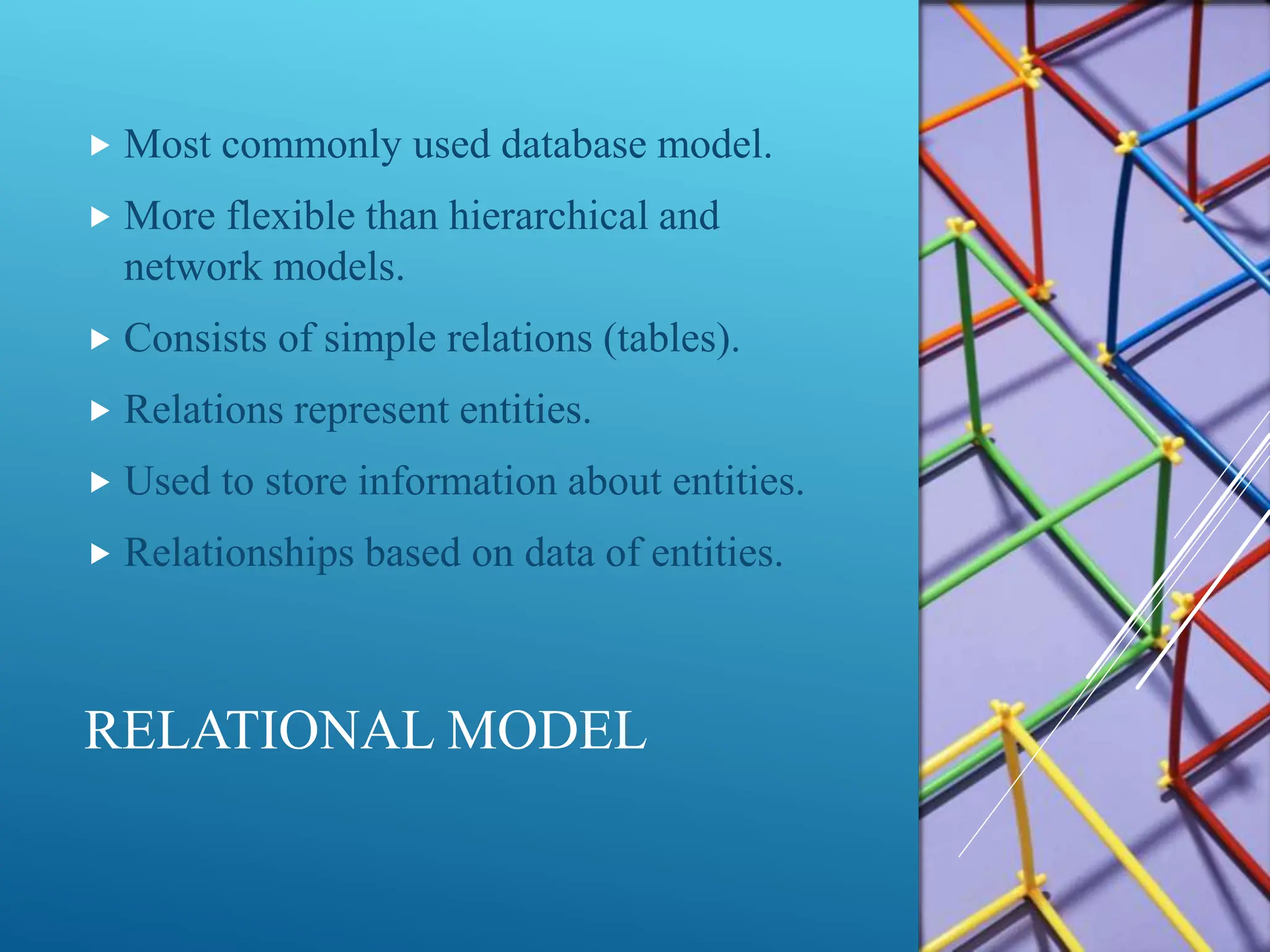
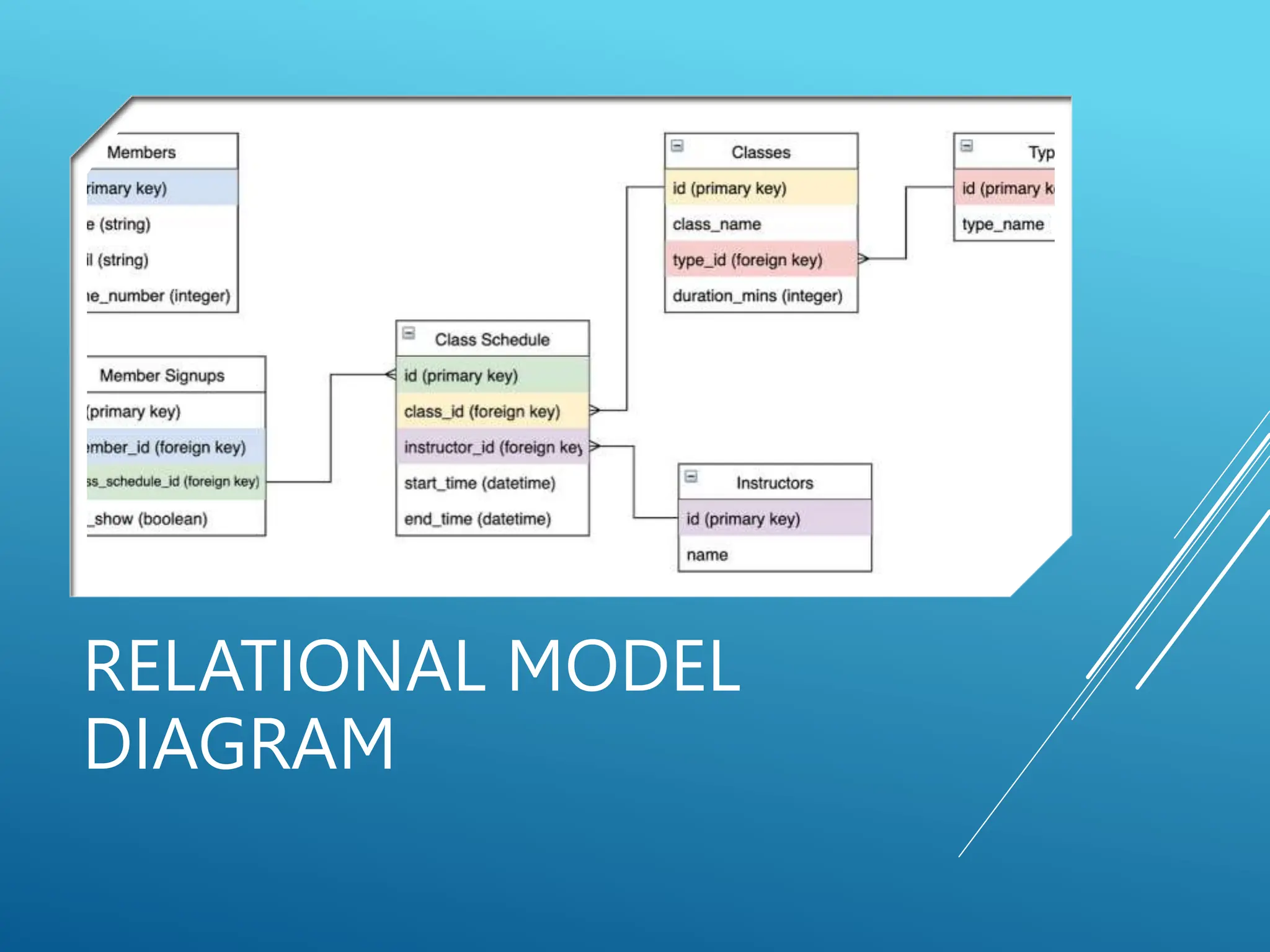
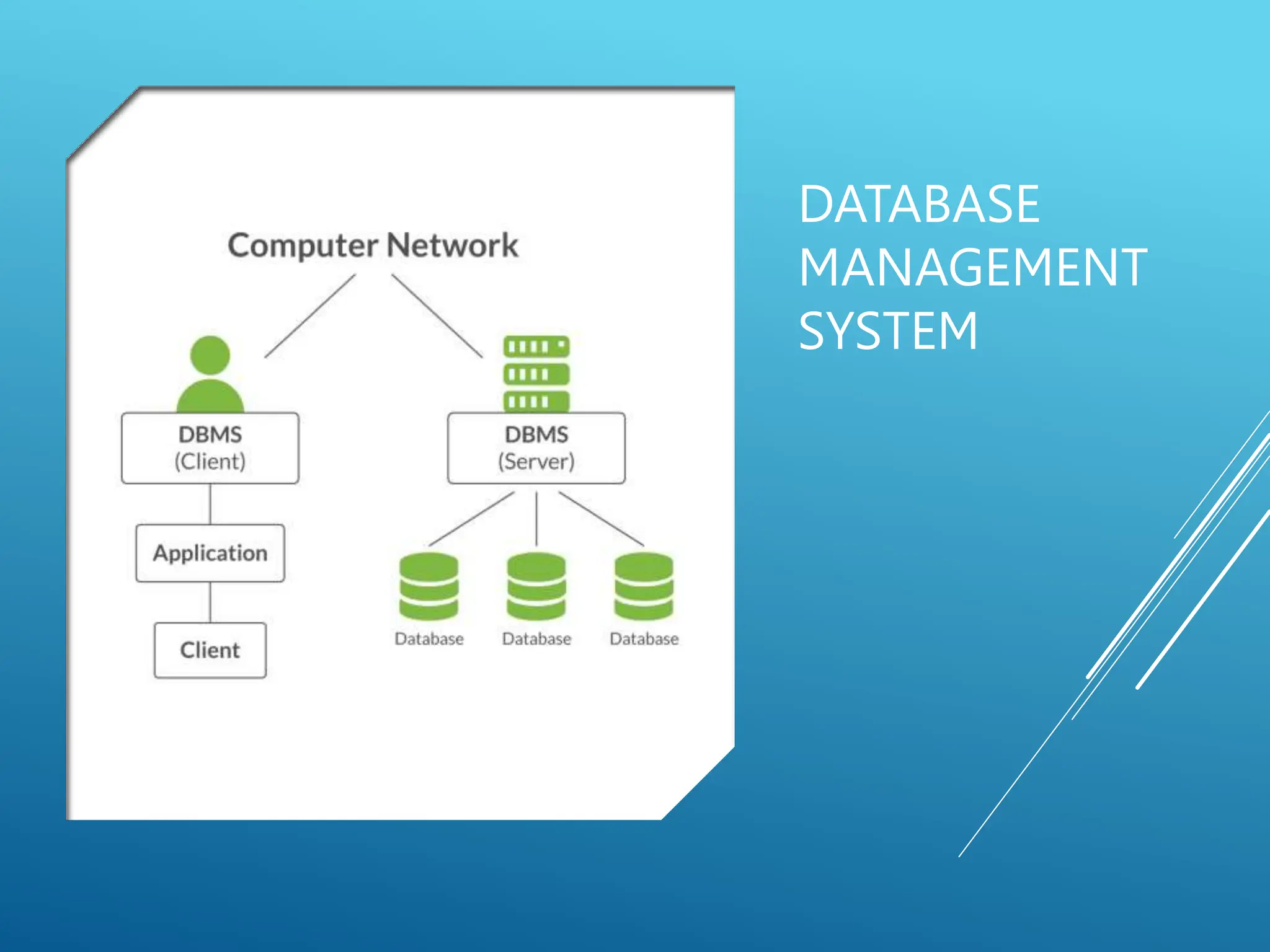
The document discusses database models, defining what they are and outlining different types including hierarchical, network, and relational models. It also explains the concept of a database management system (DBMS), its objectives such as shareability, availability, evolvability, and database integrity. Overall, it emphasizes the importance of efficient data organization and management through various models and objectives.