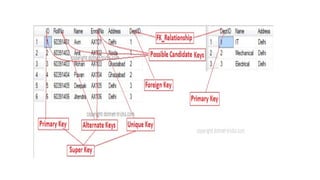
The document explains the concept of keys in database management systems (DBMS) and their role in retrieving records and establishing relationships among tables. It describes various types of SQL keys, including super key, candidate key, primary key, alternate key, composite key, unique key, and foreign key, along with their characteristics and examples. Each key type serves a unique purpose in identifying records uniquely or facilitating relationships across different tables.