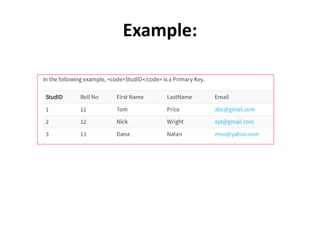
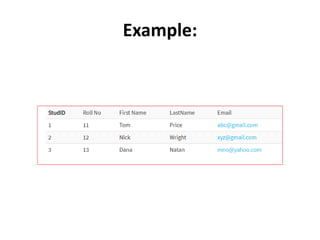
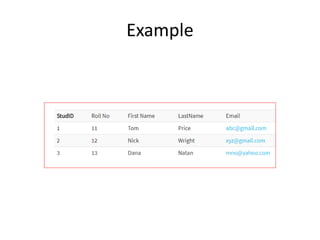
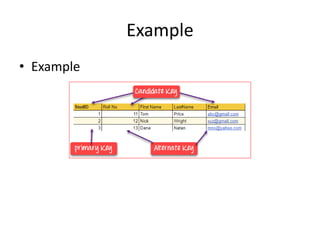
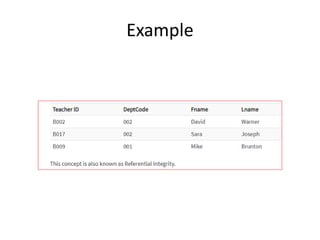
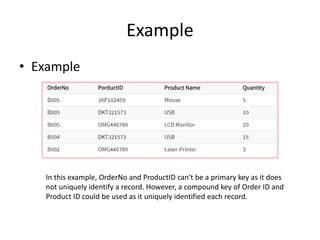
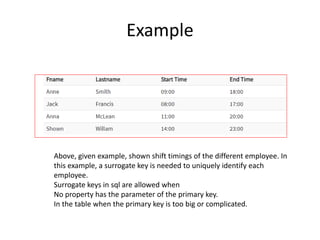
Keys in DBMS help uniquely identify rows in tables. There are several types of keys: super keys identify rows but may have extra attributes; primary keys uniquely identify rows and cannot be duplicate or null; foreign keys create relationships between tables by referencing the primary key of another table. Candidate, alternate, compound, composite, and surrogate keys also uniquely identify rows but have their own distinguishing properties. Primary keys cannot be modified if referenced by foreign keys.