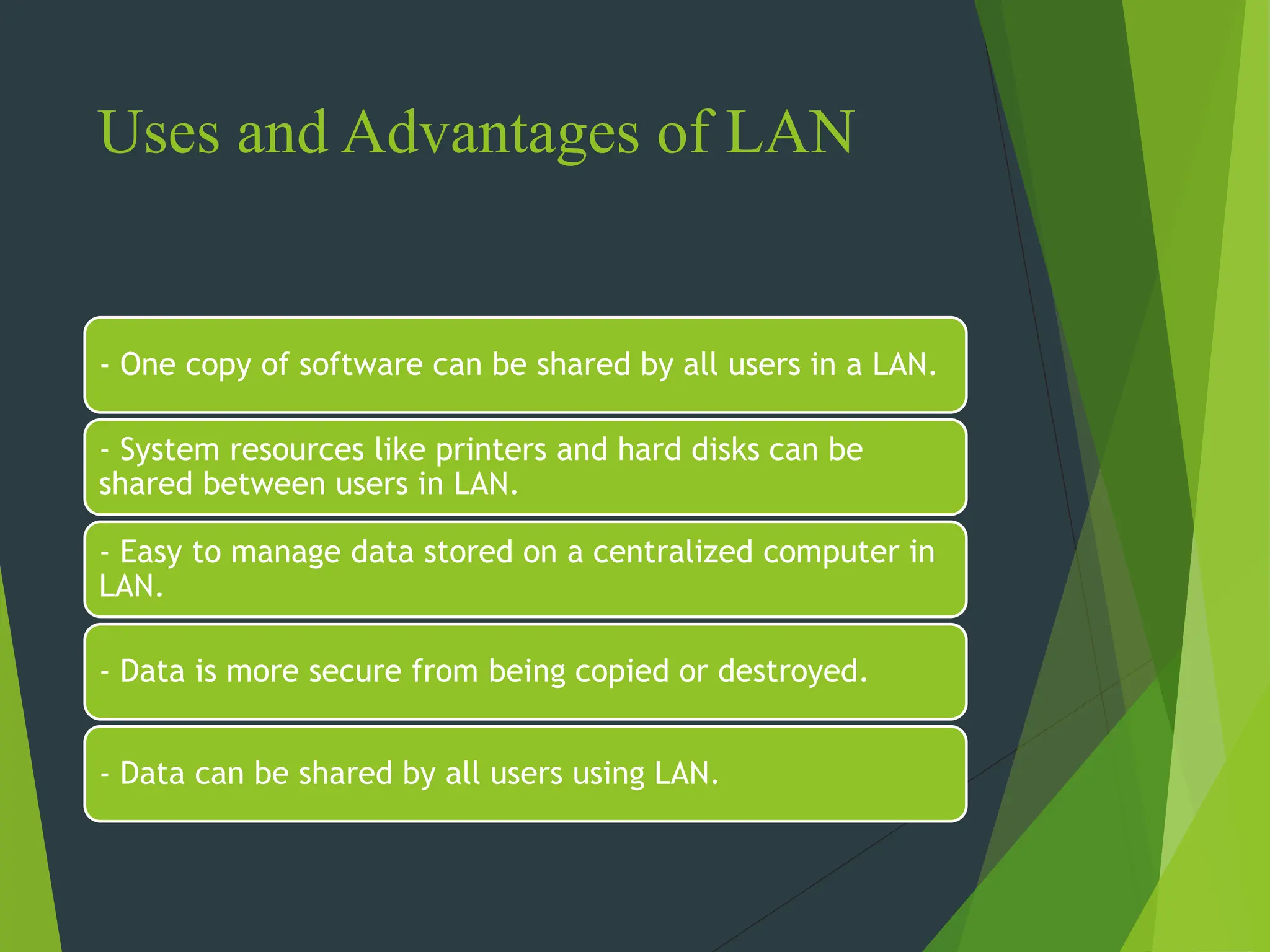
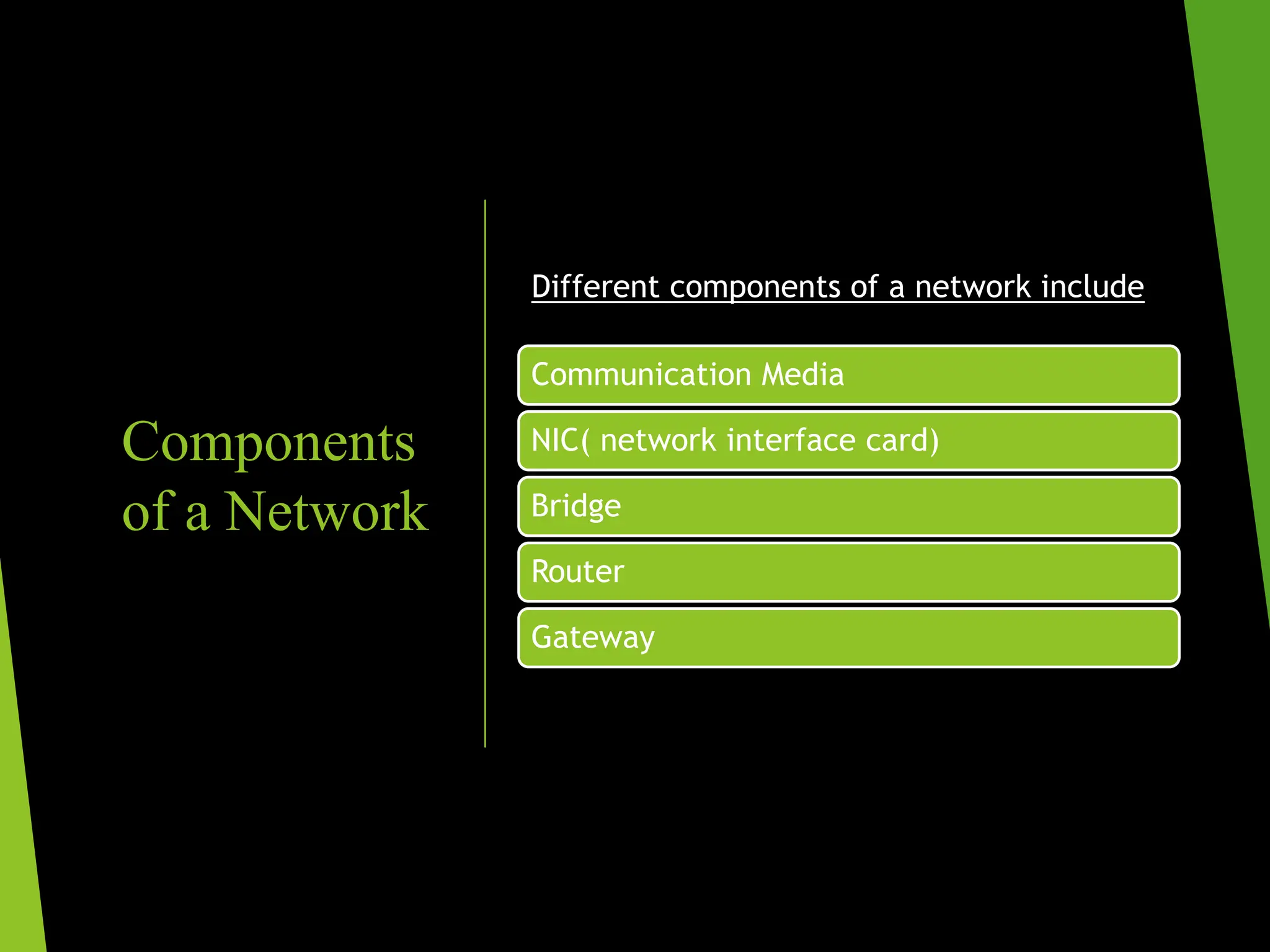
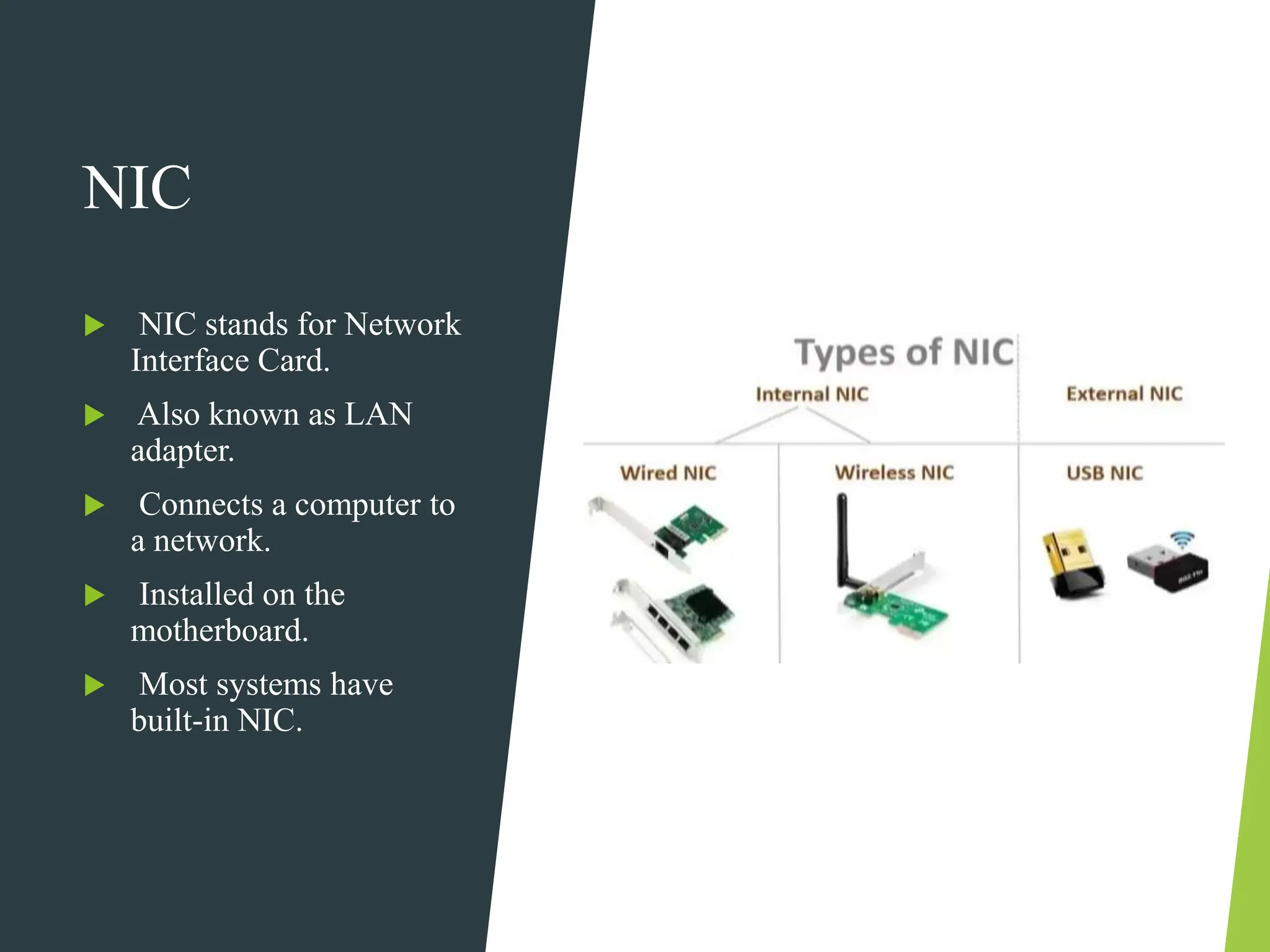
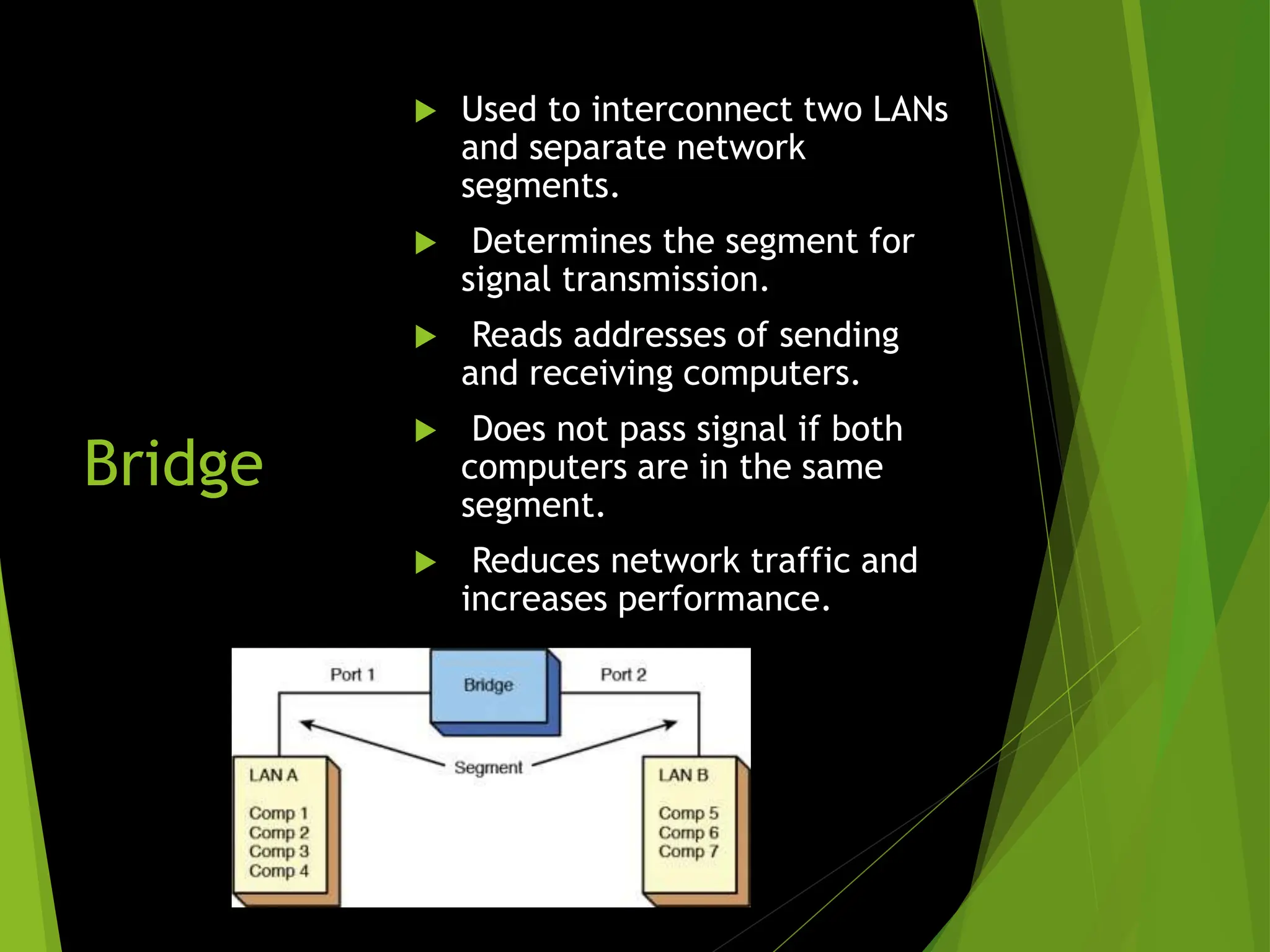
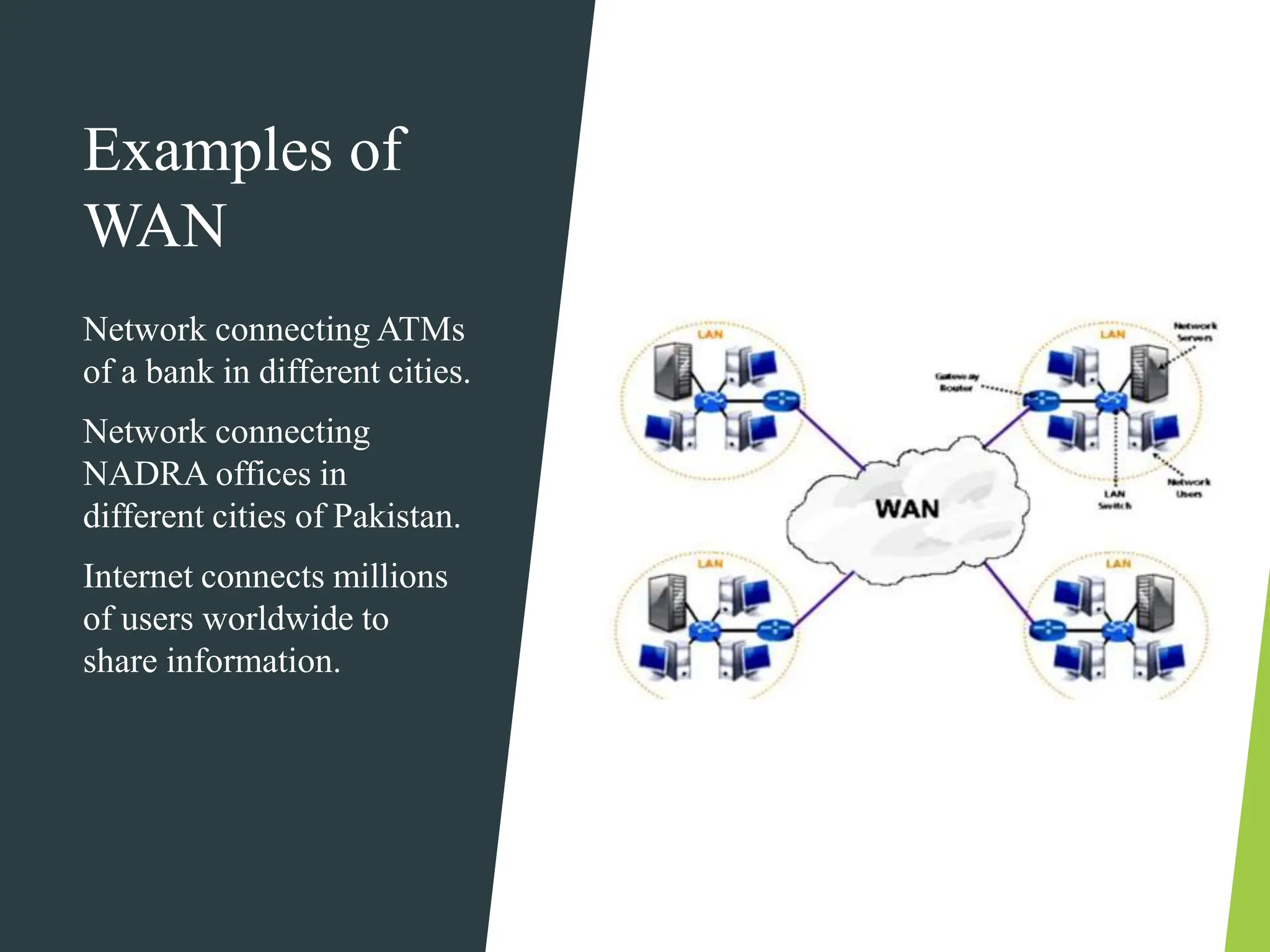
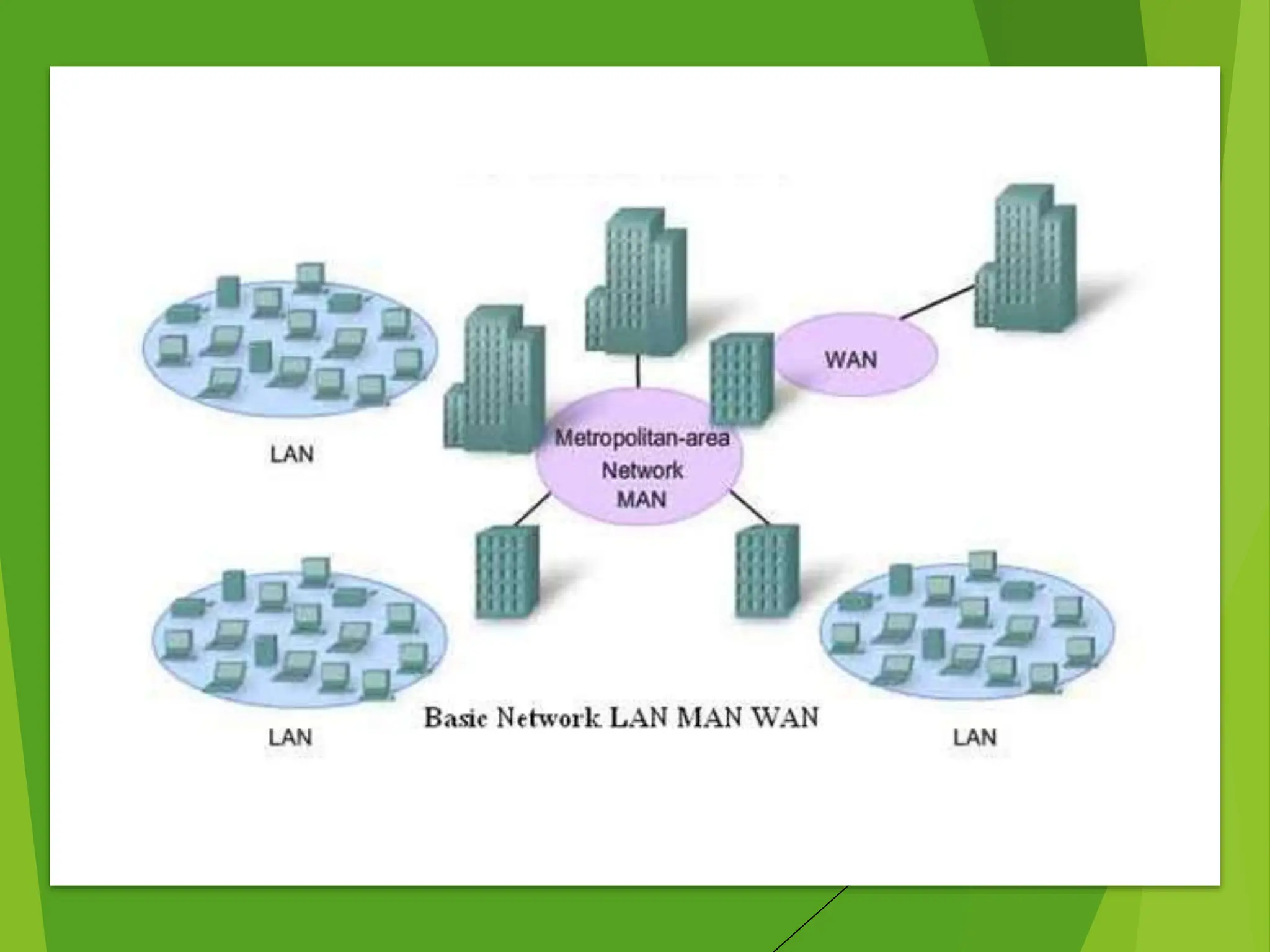
The document discusses the three main types of computer networks: LAN (Local Area Network), WAN (Wide Area Network), and MAN (Metropolitan Area Network), explaining their coverage, uses, and components. LANs are commonly used for small areas, allowing resource sharing within an office; WANs cover large distances, interconnecting multiple LANs, while MANs serve city-sized areas connecting various LANs. Key components of networks include the NIC (Network Interface Card), bridges, routers, and gateways, each serving specific functions in data transmission and network management.