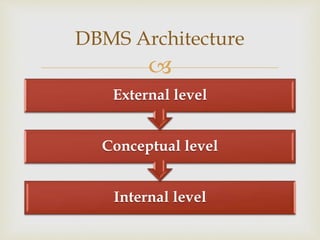
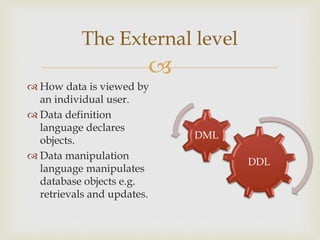
A database is an organized collection of data that models aspects of reality. Database management systems (DBMS) allow users and applications to define, create, query, update, and administer databases. Well-known DBMS include MySQL, PostgreSQL, Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle, SAP, and IBM DB2. A DBMS includes components for data definition (DDL), data manipulation (DML), optimization and execution, data security and integrity, data recovery and concurrency, and a data dictionary. The DBMS architecture has three levels - an external level for users, a conceptual level representing the database contents, and an internal level for low-level storage.