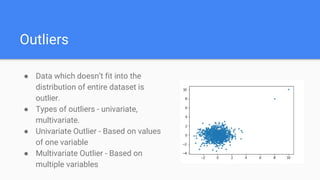
This document discusses data preprocessing techniques for machine learning. It covers common preprocessing steps like normalization, encoding categorical features, and handling outliers. Normalization techniques like StandardScaler, MinMaxScaler and RobustScaler are described. Label encoding and one-hot encoding are covered for processing categorical variables. The document also discusses polynomial features, custom transformations, and preprocessing text and image data. The goal of preprocessing is to prepare data so it can be better consumed by machine learning algorithms.





![MinMaxScaler
● One of the most popular scaling method
● Works on data which is not normally
distributed
● Brings the data in range of [0,1] or [-1,1]
● Skewness maintained but data bought to
same scale
● The two normal distributions are kept
separate by the outliers that are inside the
0-1 range.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datapreprocessing-180913171228/85/Data-Preprocessing-7-320.jpg)





![Polynomial Features
● Sometimes we need to add complexity to the model
● Convert data to higher degrees.
● Hyper-parameter it takes is degree
[ X, Y ] [ 1, X, Y, XY, X^2, Y^2 ]
Polynomial Transformer (2)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datapreprocessing-180913171228/85/Data-Preprocessing-16-320.jpg)
![Custom Transformer
● Sometimes, in-built transformers are not sufficient for data cleaning or
preprocessing.
● Custom Transformers allow Python functions to be used for transforming
data
[ X, Y ] [ log(X), log(Y) ]
Custom Transformer (log)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datapreprocessing-180913171228/85/Data-Preprocessing-17-320.jpg)