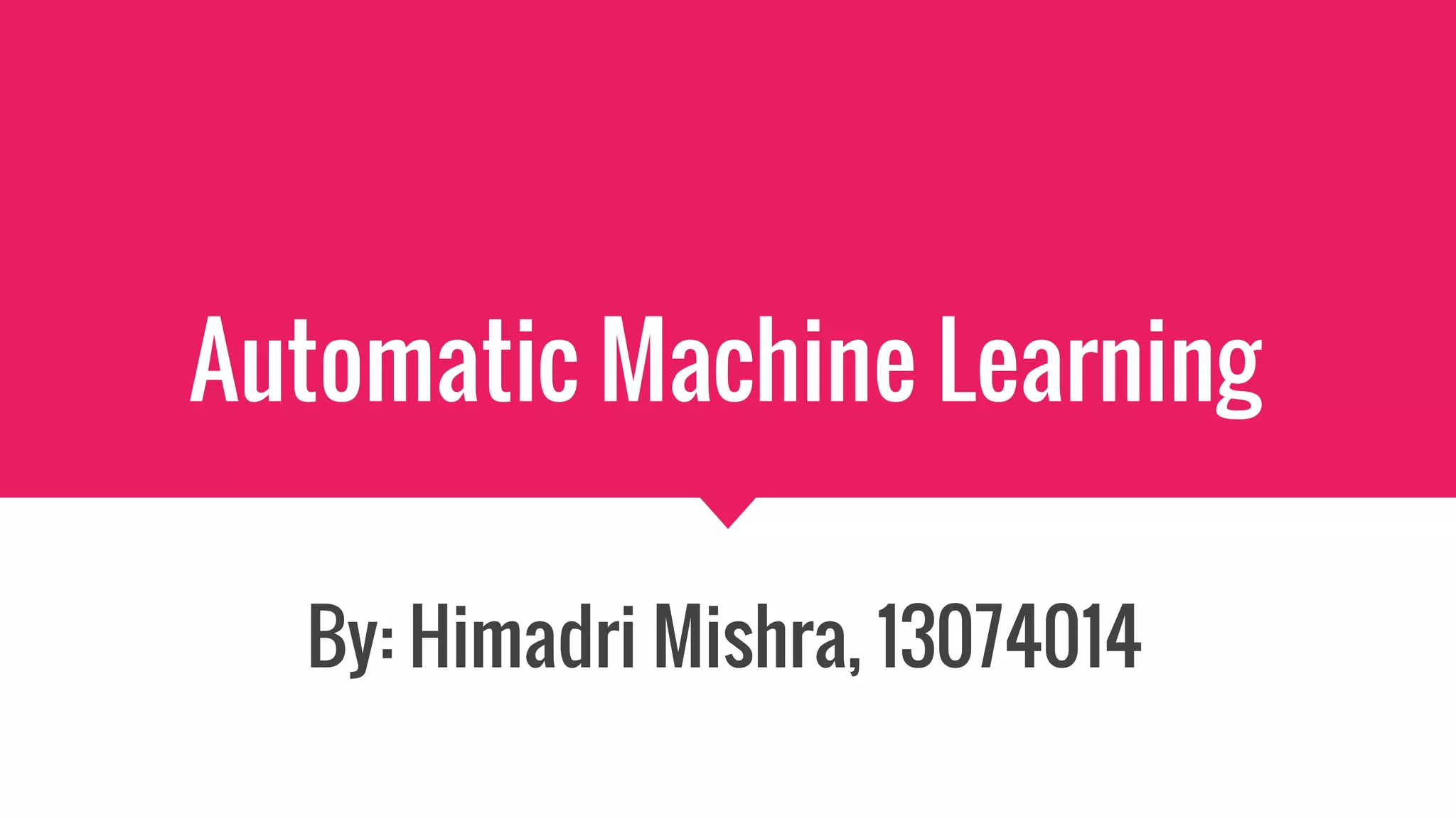
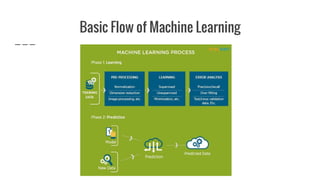
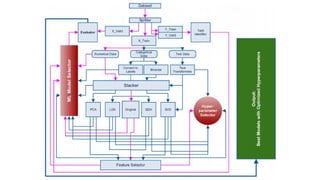
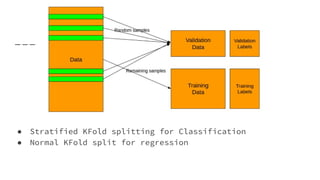
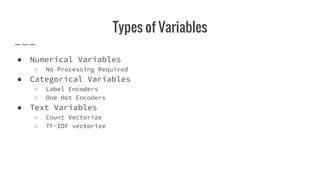
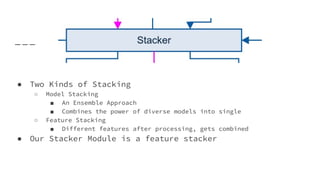
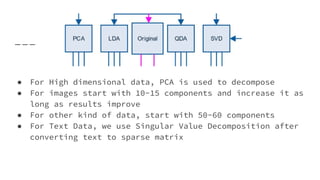
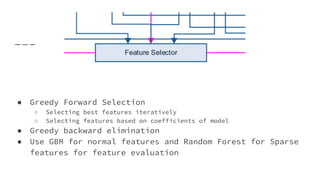
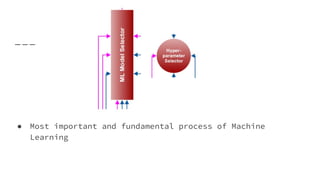
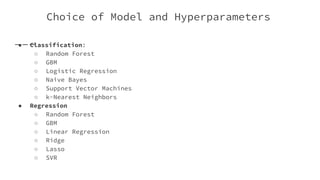
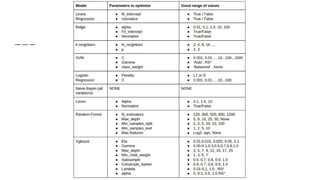
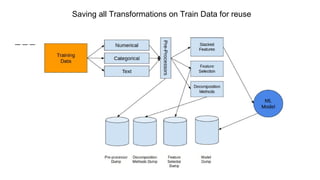
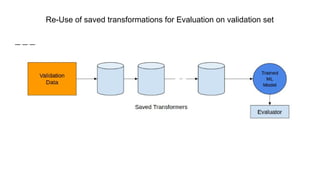
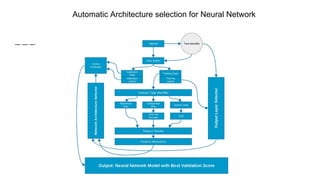
The document provides an overview of Automatic Machine Learning (AutoML), detailing its purpose and methods, including the automation of algorithm selection and hyperparameter tuning to enhance machine learning processes. It highlights various components of the AutoML framework, such as data preprocessing and model selection, and discusses recent advancements like the Auto-Net system that achieved high performance in a competitive setting. Overall, the document emphasizes the growing significance of AutoML in facilitating machine learning for non-experts and its potential to challenge existing methodologies.