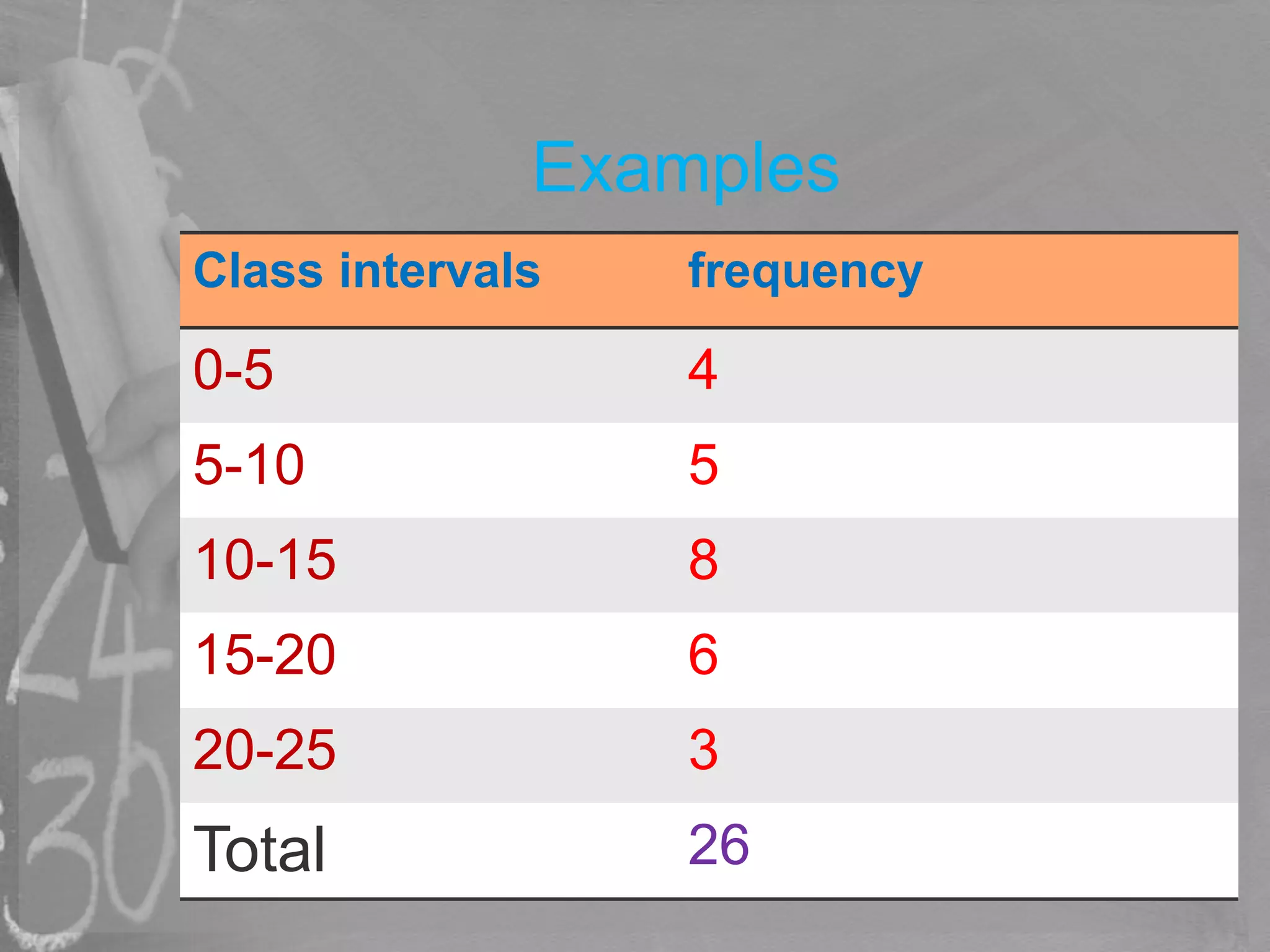
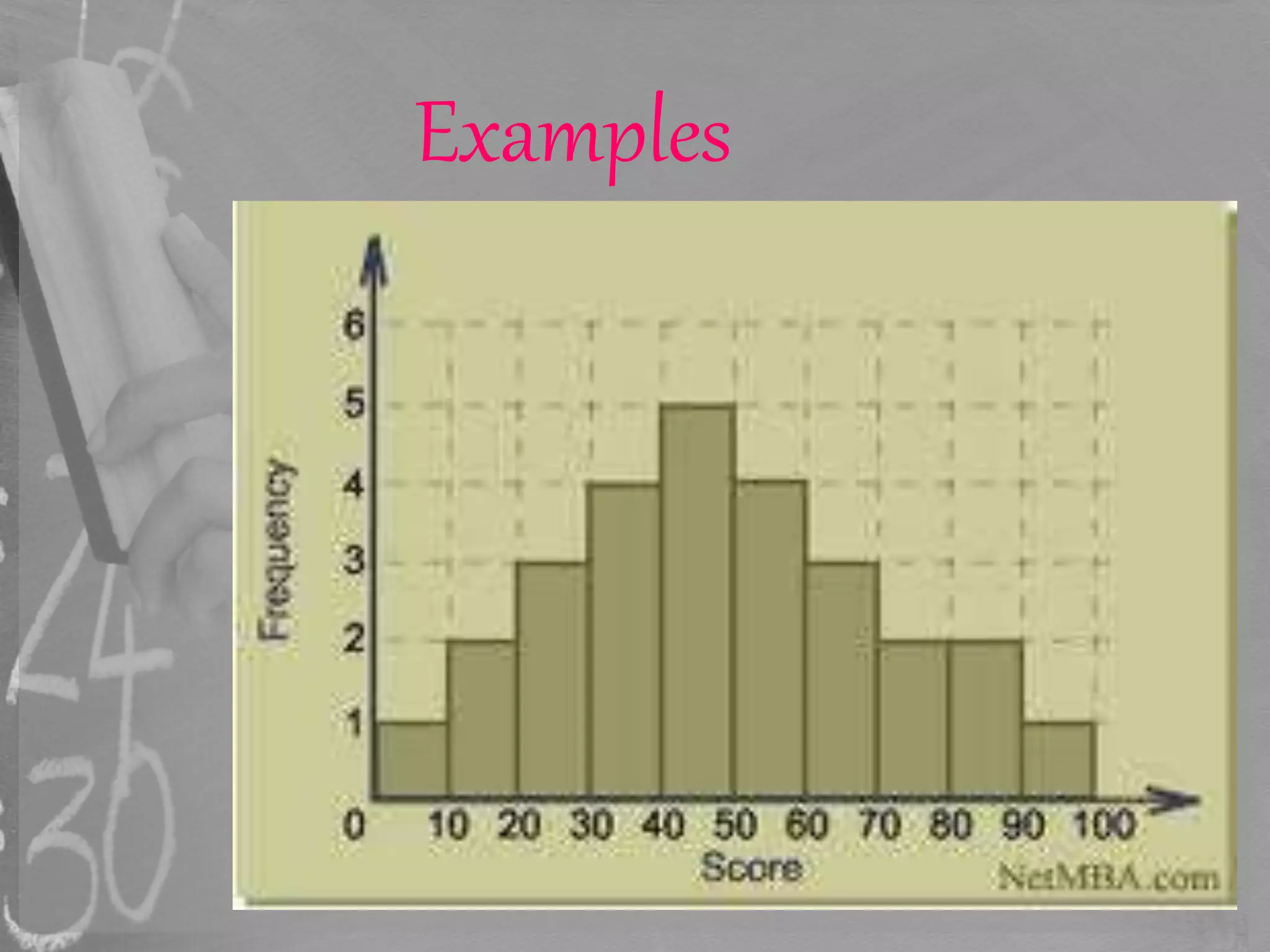
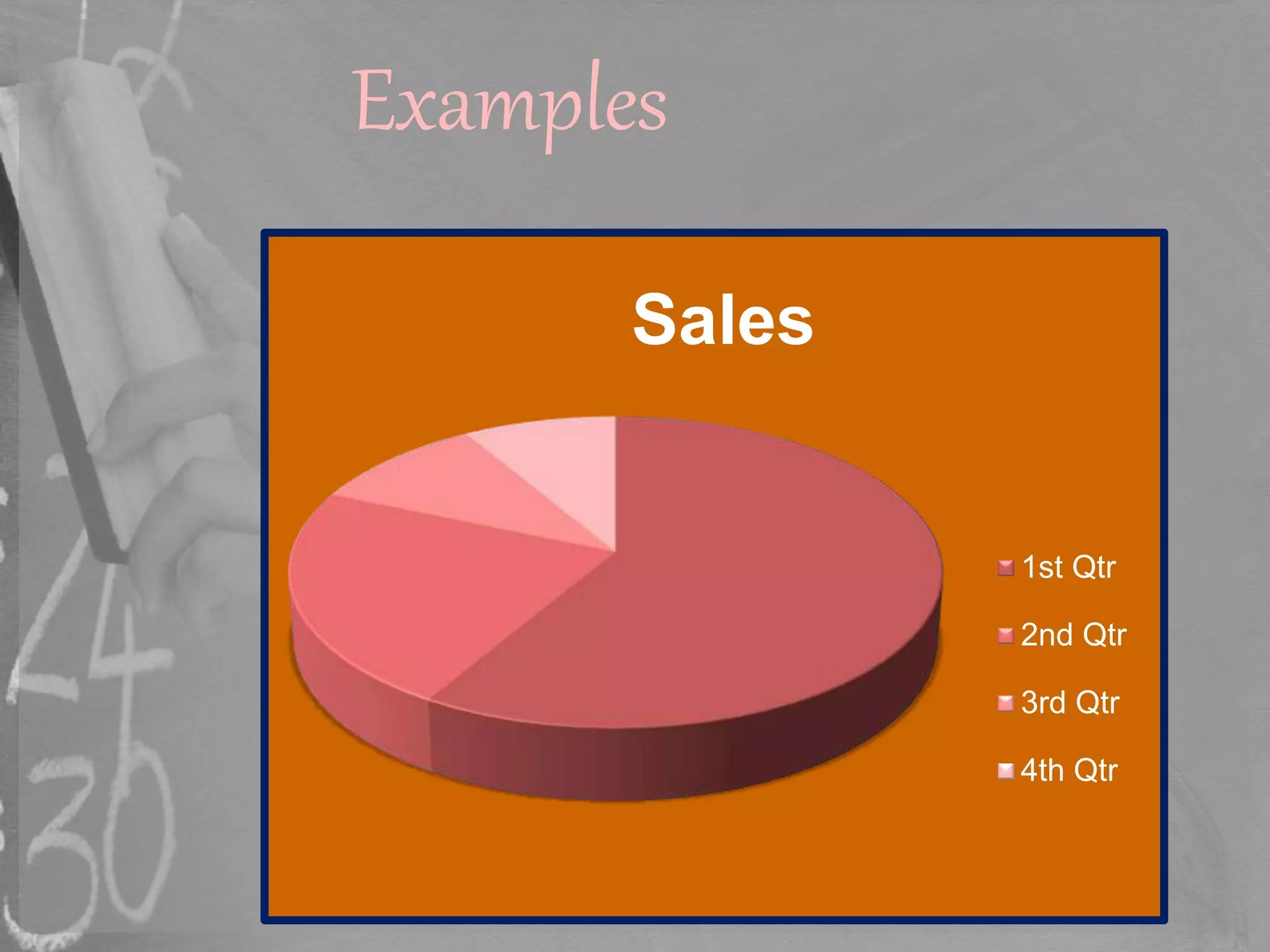
This document discusses different methods of graphically representing data, including bar graphs, double bar graphs, histograms, and pie charts. It provides examples and descriptions of each type of graph. Bar graphs are used to plot discrete data and can be vertical or horizontal. Double bar graphs compare two sets of data with two bars. Histograms show data points within ranges. Pie charts illustrate proportions, with the arc length of each sector proportional to the quantity it represents.