Embed presentation
Downloaded 1,102 times






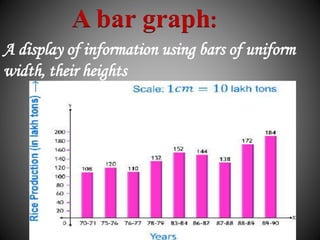
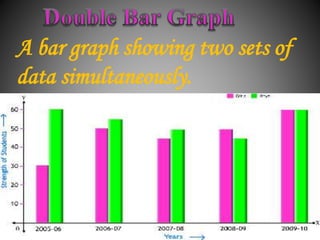
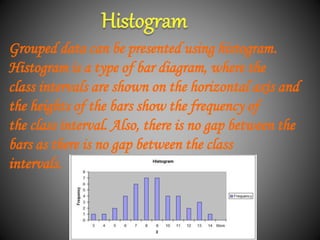
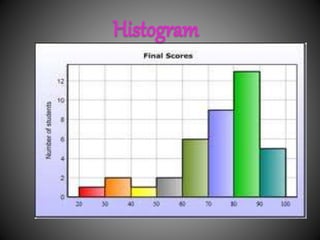
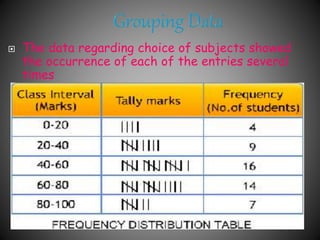
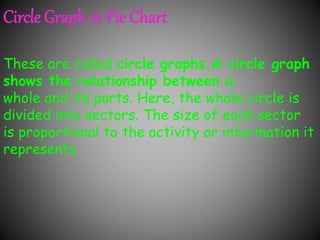
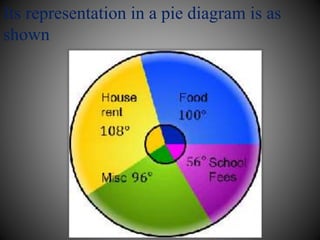
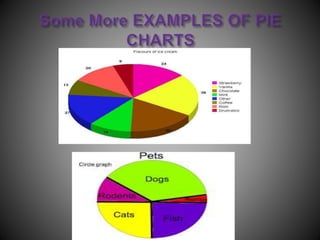


There are several commonly used diagrams to represent numerical data, including pictographs, bar graphs, double bar graphs, and pie charts. Pictographs use symbols or pictures to represent data, with each symbol representing a certain value. Bar graphs display data using uniformly wide bars of varying heights. Double bar graphs show two sets of data simultaneously. Pie charts, also called circle graphs, show the relationship between a whole and its parts by dividing a circle into sectors proportional to the parts.














