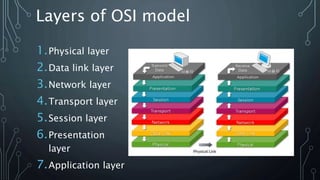
The document presents a detailed overview of the OSI model, which serves as a framework for understanding networking technologies and their interrelationships. It outlines the seven layers of the OSI model, detailing their functions, devices involved, and associated protocols. The document also discusses the merits and demerits of the OSI model as a reference tool in networking.