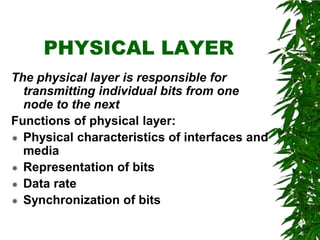
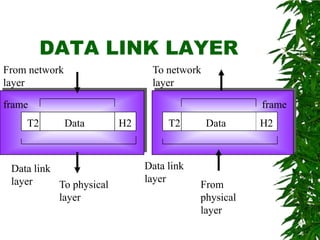
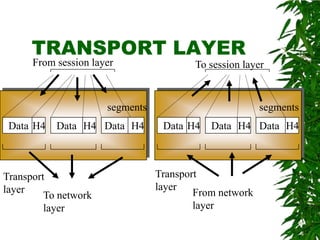
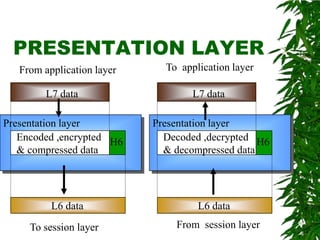
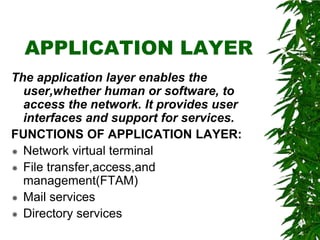
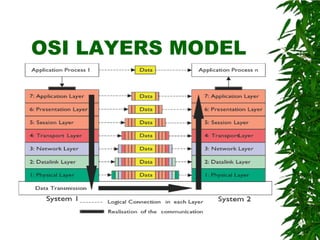
This document provides an overview of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model, which defines seven layers of network communication. It describes each layer's functions and responsibilities, including the physical layer for transmitting bits, the data link layer for framing and addressing, the network layer for routing packets, the transport layer for process-to-process delivery, the session layer for dialog control, the presentation layer for data translation, and the application layer for user interfaces and services. The OSI model was designed by ISO in the late 1970s to provide a standard framework for network protocol implementation across different systems.