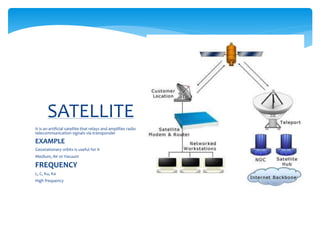
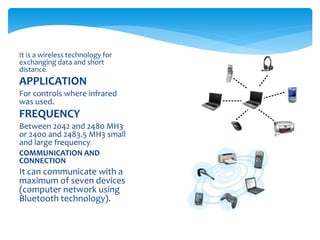
Data communication involves transmitting data from one location to another using transmission media. It requires a message, sender, receiver, medium/communication channel, and encoder/decoder. Communication media refers to the means of delivering and receiving data, including wired media like coaxial cable, twisted pair cable, and fiber optic cable, and wireless media like microwaves, satellite, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth. Wired communication uses physical connections like cables while wireless uses technologies like radio frequencies.