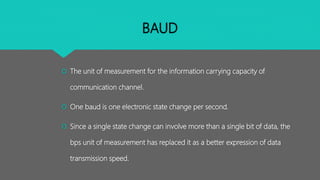
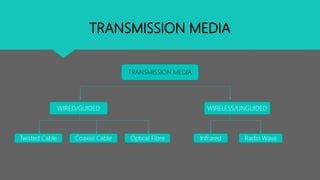
This document discusses key terminology used in data communication. It defines channel, baud, bandwidth, data transfer rate, and transmission media. A channel refers to the physical medium over which data is exchanged, such as cables. Baud measures the information capacity of a channel in state changes per second. Bandwidth refers to a channel's data carrying capacity and is measured in bits per second. Digital bandwidth is measured in bps or Hz, while analog is measured in Hz. Data transfer rate indicates the amount of data transferred per second in units of bps or Bps. Transmission media include wired options like twisted pair cable, coaxial cable, and optical fiber as well as wireless options like infrared and radio waves.