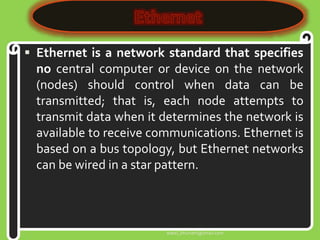
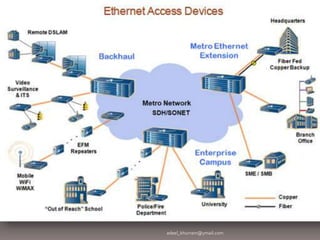
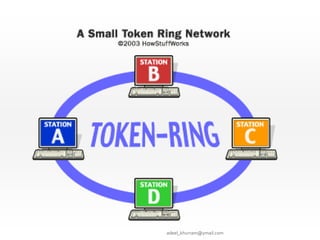
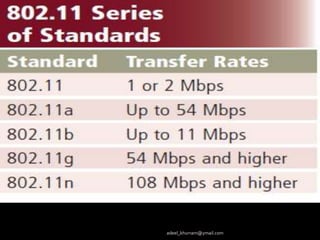
This document discusses several network communication standards and protocols. It explains that organizations like ANSI and IEEE establish network standards that specify how devices connect to networks and communicate. It describes several widely used standards including Ethernet, which defines cable-based networking, as well as wireless standards like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, RFID, WiMAX, and TCP/IP, which is the standard protocol that ensures data is routed and delivered correctly over the Internet.