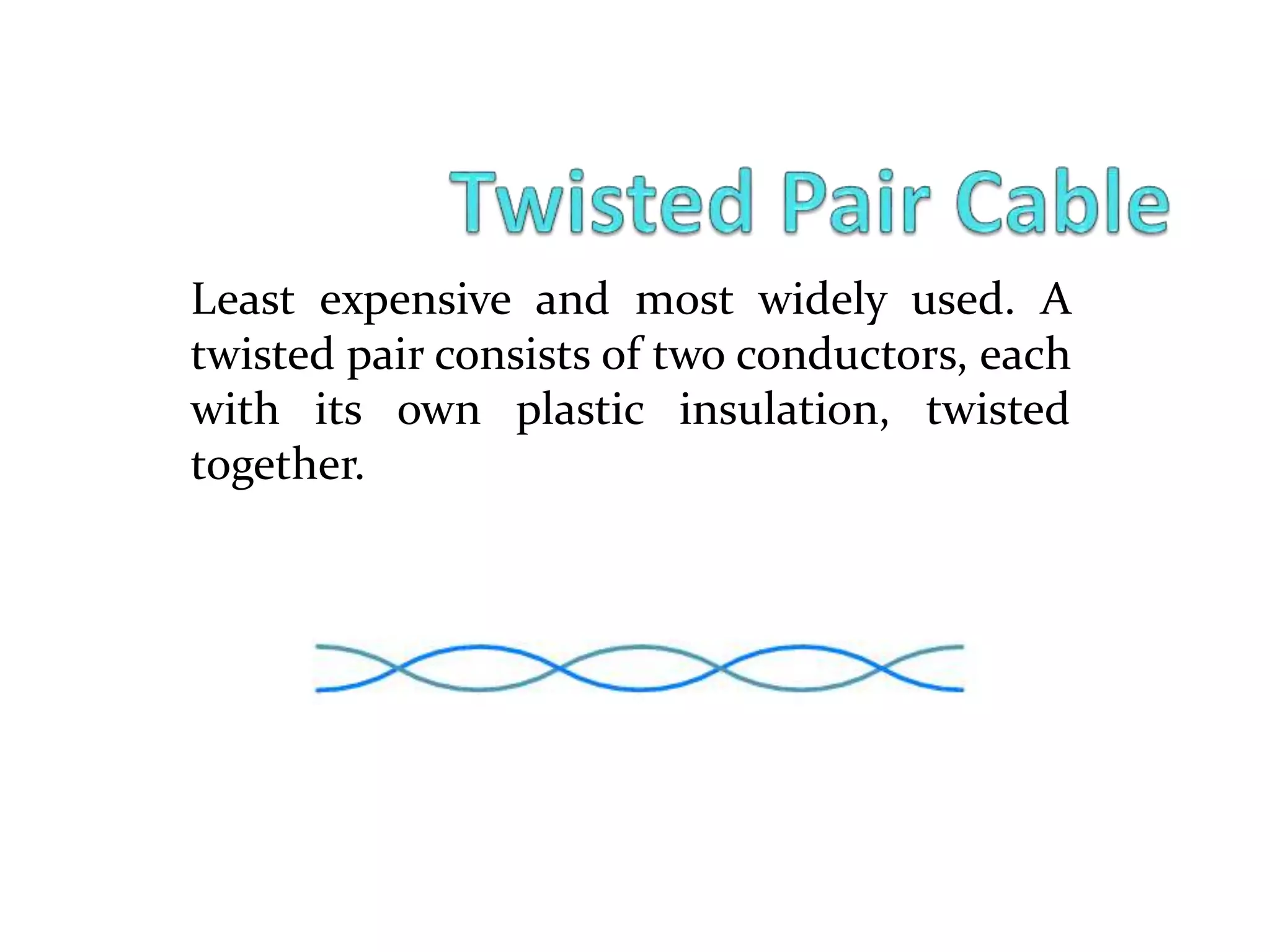
Data communication involves the exchange of data between devices via a transmission medium. It has five key components: a message, sender, receiver, medium, and protocol. There are three main modes of data communication: simplex, half duplex, and full duplex. Guided media like twisted pair cables, coaxial cables, and fiber optic cables provide a physical channel for transmission, while unguided media like radio waves, microwaves, and infrared transmit electromagnetic waves without a physical medium.