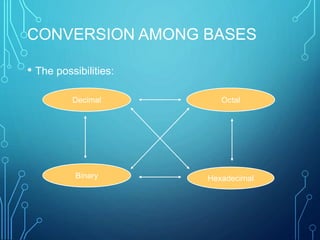
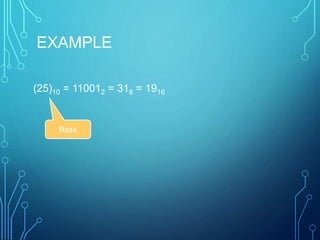
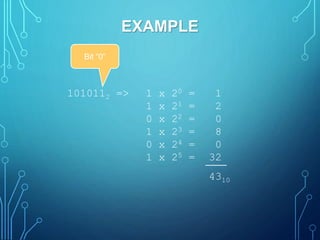
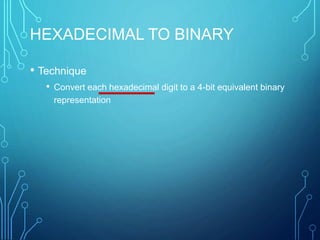
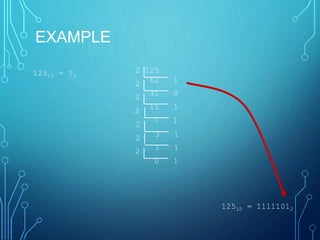
This document introduces group members Md. Ilias Bappi and Md.Kawsar Hamid and presents information on number systems and conversions. It discusses the decimal number system and defines ones' complement and twos' complement in binary. It provides examples of converting between binary, decimal, octal, and hexadecimal systems using appropriate techniques like multiplying bit positions by powers of the base. Conversions include binary to decimal, octal to decimal, hexadecimal to decimal, decimal to binary, octal to binary, hexadecimal to binary, decimal to octal, octal to hexadecimal, and binary to decimal representations of fractions.