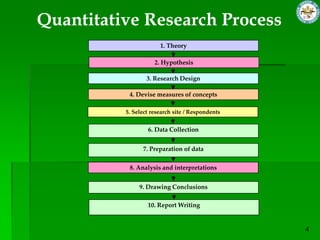
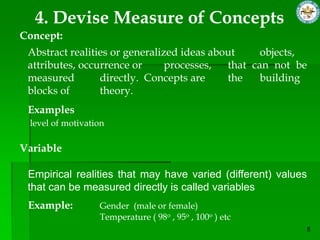
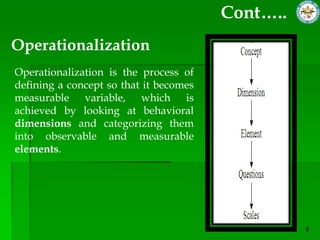
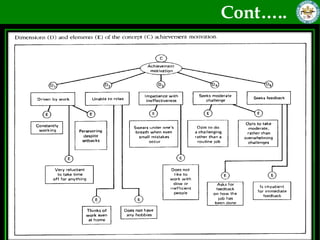
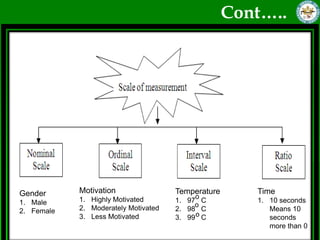
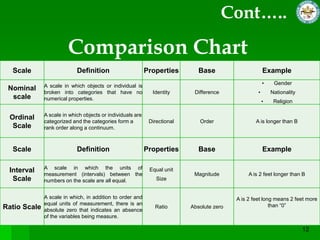
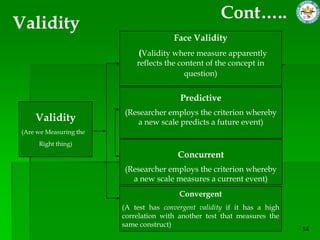
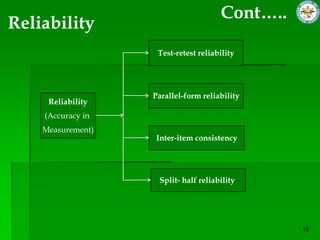
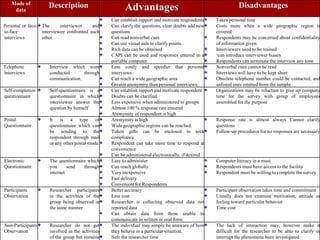
This document discusses quantitative research methods. It defines quantitative research as using numerical data to obtain objective information. The goals of quantitative research are to generalize findings, be objective, and test theories. The quantitative research process involves 10 steps: developing a theory and hypotheses, research design, defining concepts and variables, selecting respondents, data collection, data preparation, analysis, conclusions, and reporting. Several data collection methods are also discussed, including surveys, structured interviews, structured observations, and questionnaires.