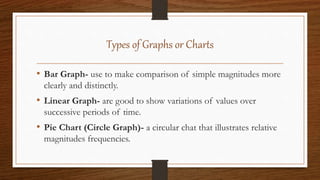
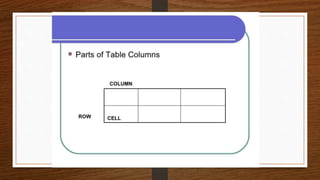
This document discusses different methods for presenting data, including textual, tabular, and graphical presentation. Tabular presentation organizes data into rows and columns in a table. Textual presentation uses statements and numbers to describe data. Graphical presentation shows variations and relationships of data using visual formats like bar graphs, line graphs, and pie charts. Each method has advantages - tables provide concise information while graphs attract attention and enable quick comprehension of quantitative data relationships.