This document presents a model for a local area network (LAN) based application for inter-office communication. The authors designed a messenger software to be installed on an organization's LAN to allow staff to communicate and share information efficiently. The software was developed using Java and analyzed using various UML diagrams. It uses a client-server model with the control part installed on the server and messenger part on clients. The software allows users to send short messages, memos, letters and access an electronic bulletin board. It was tested on a campus LAN network and achieved the objectives of enabling free communication between staff during office hours through a centralized and secure system.



![A Model of Local Area Network Based Application…
www.theijes.com The IJES Page 39
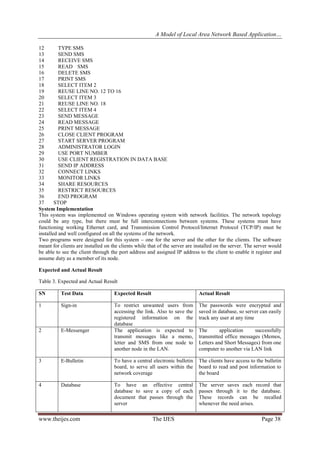
However, the system was designed and tested on dual core and Pentium system in a fully functioning LAN
environment.
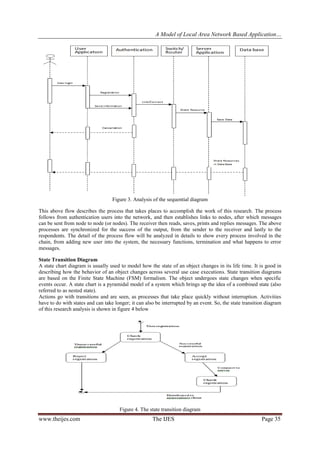
Discussion of Results
This system was installed in a campus LAN with a cable network, and it worked efficiently except, of course, on
some systems with bad LAN cable. However, the transmission was a bit slow, despite that the LAN speed was
86kbs. For the server to manage the database, there was the need to ensure that every transmission passes
through network server instead of moving straight to the receiver system. This was what slowed down the
information transmission speed. Nevertheless, the main objectives of the system were achieved.
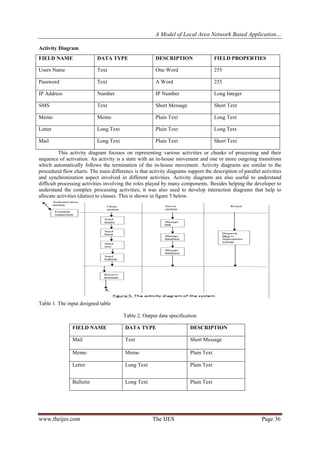
Conclusion
The system was analyzed in a LAN environment, and the connection was properly systemized in a linked chain.
Both the client application and server application were carefully installed and linked through the IP addresses,
though the program recognized clients through the port numbers, for sending and receiving of signals from both
ends to various units.
Recommendation
The recommendation is for any researcher that is interested in this work to study further on how to integrate
multimedia into this communication system. Also, he should work towards increasing the speed and extend this
program to work on Wide Area Network (WAN).
REFERENCES
[1]. Ajah, I. A.and Igboji, K. O. (2011).Internet Fundamentals and File Management, Willyrose& Appleseed Coy,Abakaliki Nigeria.
[2]. AmrYoussef, M. (2012).Data Communication and Computer Networks, Concordia University, Montreal.
[3]. Beaker, R. (1993). Reading in Groupware and Computer Supported Cooperative Work, Sam Meter, C.A.
[4]. Cohen J. (1988). Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Science, Lawrence Erlbaum, HillDale, NJ. United State.
[5]. Deepti, M.and Alok, M. (2012).“Effective Communication, Collaboration, and Coordination in eXtreme Programming: Human-
Centric Perspective in a Small Organization” Department of Computer Engineering, Atilim University, Ankara, Turkey.
[6]. Ditte, M. F. and Rasmussen, J.(2011), What a Waste:How Your Computer Causes Health Problem in Ghana.
[7]. Ekemezie, W. N. andNgene, N.J. (2004).Computer and Information Technology, Sam press Ltd Enugu, Nigeria.
[8]. Ellis, M. (1991), Computer and Information Processing, Irwin inc, USA.
[9]. Encarta, (2009), Microsoft Encarta Dictionary, Microsoft Inc. USA.
[10]. Hutchinson, S. E. and Sawyer, S. C. (2000). Using Information Technology, 3rd Edition, Irwin, McGraw-Hill Boston, USA.
[11]. Mardav, W. (2006).Computer Networks are Essential for Day-to-day Communication, Universityof Tennessee.
[12]. Mbam, B. C. E. (2009).Internet Made Easy, Academic Treasure International,Abakaliki, Nigeria.
[13]. Mowbray, T. J., &Zahavi, R. (1995). The essential CORBA: systems integration using distributed objects (pp. I-XVI). New
York: Wiley.
[14]. Okechukwu, Oliver O. (2009).Introduction to System Analysis and Design,Madonna University Press Ltd, Uwani Enugu,
Nigeria.
[15]. Orfali, R.,Harkey,D. and Edwards, J. (1994).Essential Client/Server Survival Guide,John Wiley &Sons, United Kingdom.
[16]. Palo, A. (2003).A New Traffic Control Algorithm for Packet Switching Networks,Lixia Zhang XEROX Palo Alto Research
Center, Coyote Hill Road, Canada.
[17]. Pidd M. (1998). Computer Simulation in Management Science, John Wilet& Sons. Chichester England.
[18]. Rajib, M. (2010).Fundamentals of Software Engineering, PHI Learning private Limited, New Delhi, India.
[19]. Robinson S. (1994). Successful Simulation: A Practical Approach to Simulation Projects, McGraw-Hills Maiden, England.
[20]. Stephen M. (2008).CCNA Self-Study: Introduction to Cisco Networking Technologies, Cisco Press CA, USA.
[21]. William, B. K. (1999). The Essential Client/Server Survival Guide, John Willey and Sons Inc.Chichester, England.
[22]. Wiley,C. (2009).Periodicals InterScience, Inc. Published online, (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/hfm.20164.Zhili,
S. (2005).Satellite Networking Principles and Protocols, John Wiley & Sons Ltd, University of Surrey, England.URL:
http://www.uic.edu/depts/accc/lan/lanintro.html UIC Academic Computing & Communication Centre; the University of Illinois
Chicago, USA.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/d0451032039-150624035518-lva1-app6892/85/A-Model-of-Local-Area-Network-Based-Application-for-Inter-office-Communication-8-320.jpg)