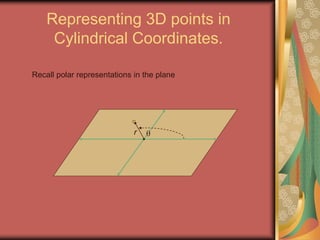
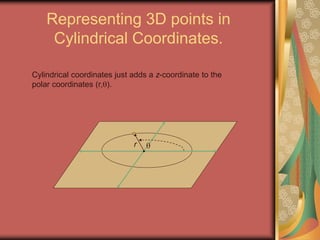
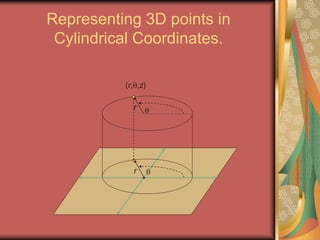
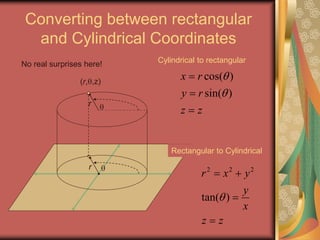
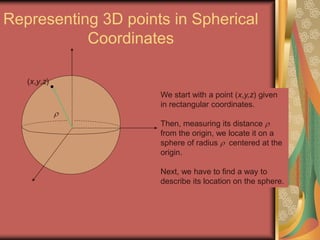
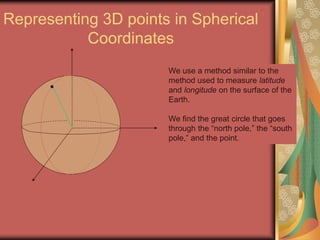
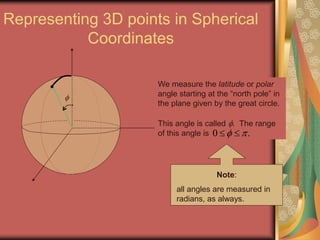
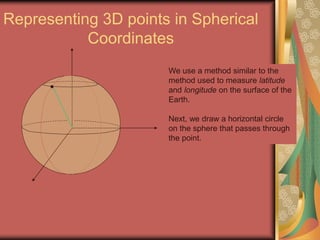
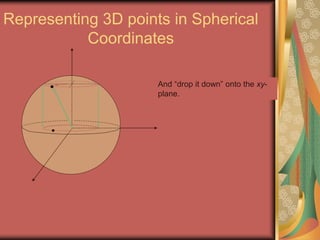
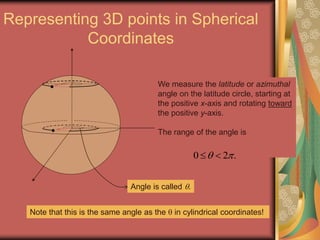
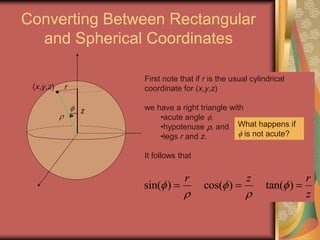
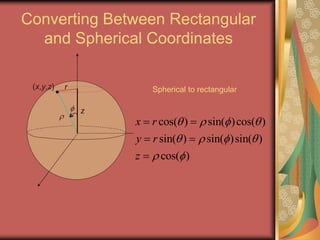
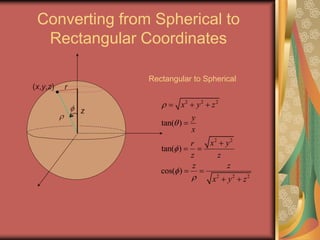
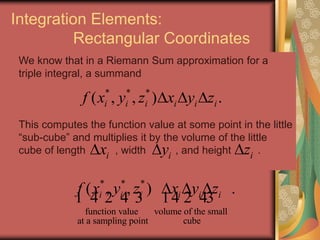
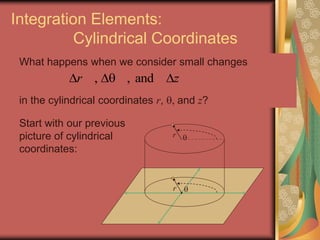
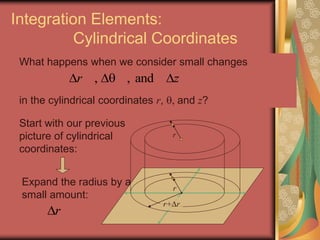
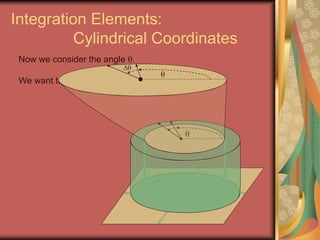
The document discusses representing points in 3D space using cylindrical and spherical coordinate systems. It explains that cylindrical coordinates extend the 2D polar coordinate system (r,θ) by adding a z-coordinate. Spherical coordinates represent points using three values - the radial distance ρ, the azimuthal angle θ, and the polar angle φ. The document also covers converting between rectangular and cylindrical/spherical coordinates, and discusses how the elements of integration change based on the coordinate system used.