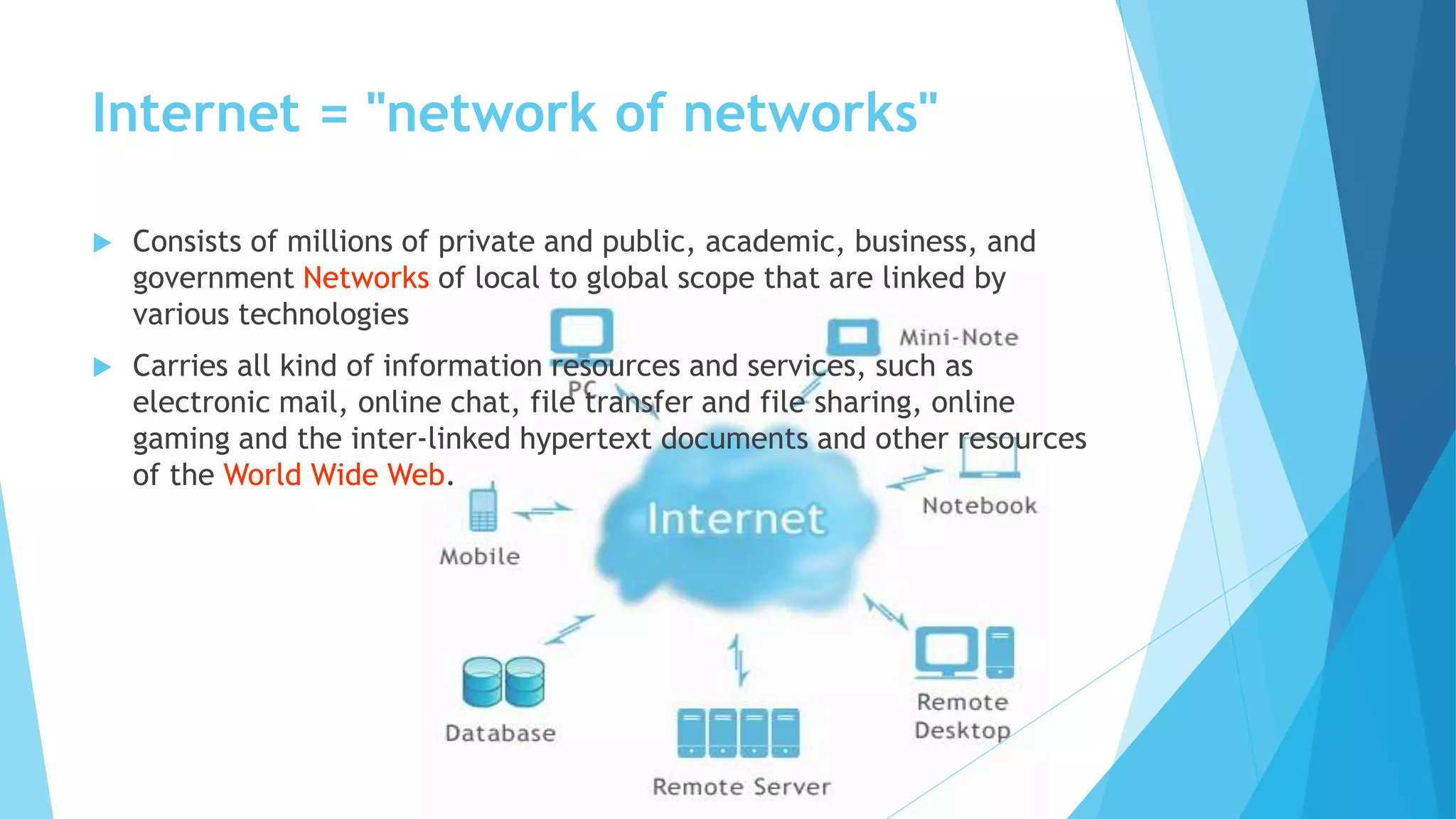
The document provides a comprehensive overview of cyber security and privacy, covering topics such as hacking methods, information gathering techniques, and types of malware. It includes sections on prevention strategies for email hacking, social engineering, and internet banking threats. The concluding emphasis is on the need for awareness, vigilance, and protective measures against various cyber threats.







![Prevention –Email Hacking
Use osk instead of our physical keyboard.
Create a dedicated free mail address to use in the Risky sites.
Never use your Personal Email password while registering in known/unknown
web portals.
Never Reply to spams.
Use Bcc: and remove addresses when forwarding mails.
Use “[at]” instead of @. eg: myemail[at]gmail.com.
Don’t make mailto: links when building websites.
Don’t create an Easy to guess email address and password.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cybersecurityandprivacy-150402130057-conversion-gate01/75/Cyber-security-and-privacy-10-2048.jpg)




