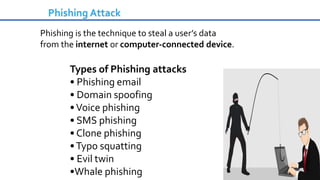
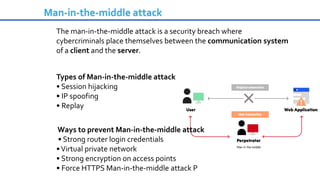
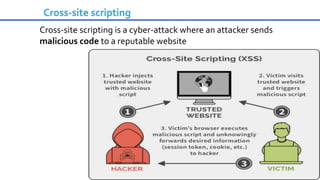
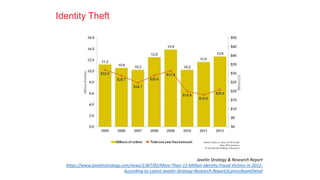
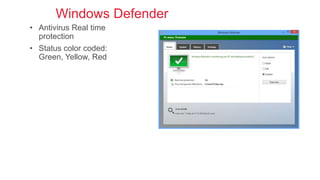
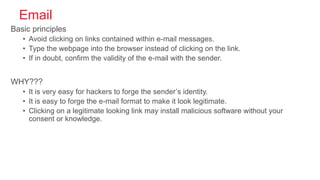
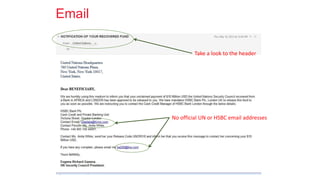
Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting internet-connected systems from cyber attacks, grounded in the principles of confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Various cyber threats, including phishing, malware, and advanced persistent threats, pose risks to data and systems, with techniques to mitigate these threats outlined. The document further emphasizes the importance of user awareness and proactive measures to ensure online privacy and security.