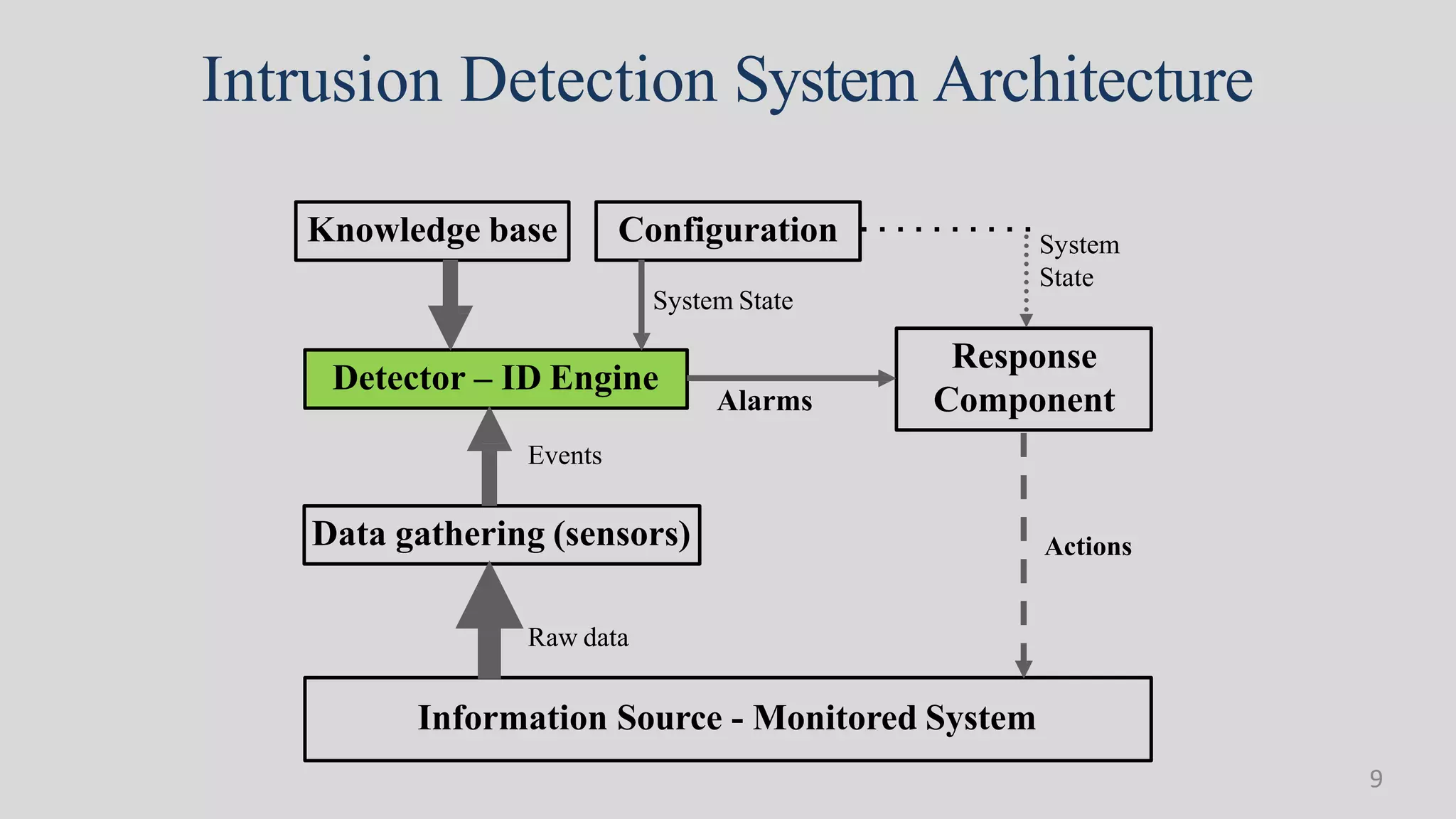
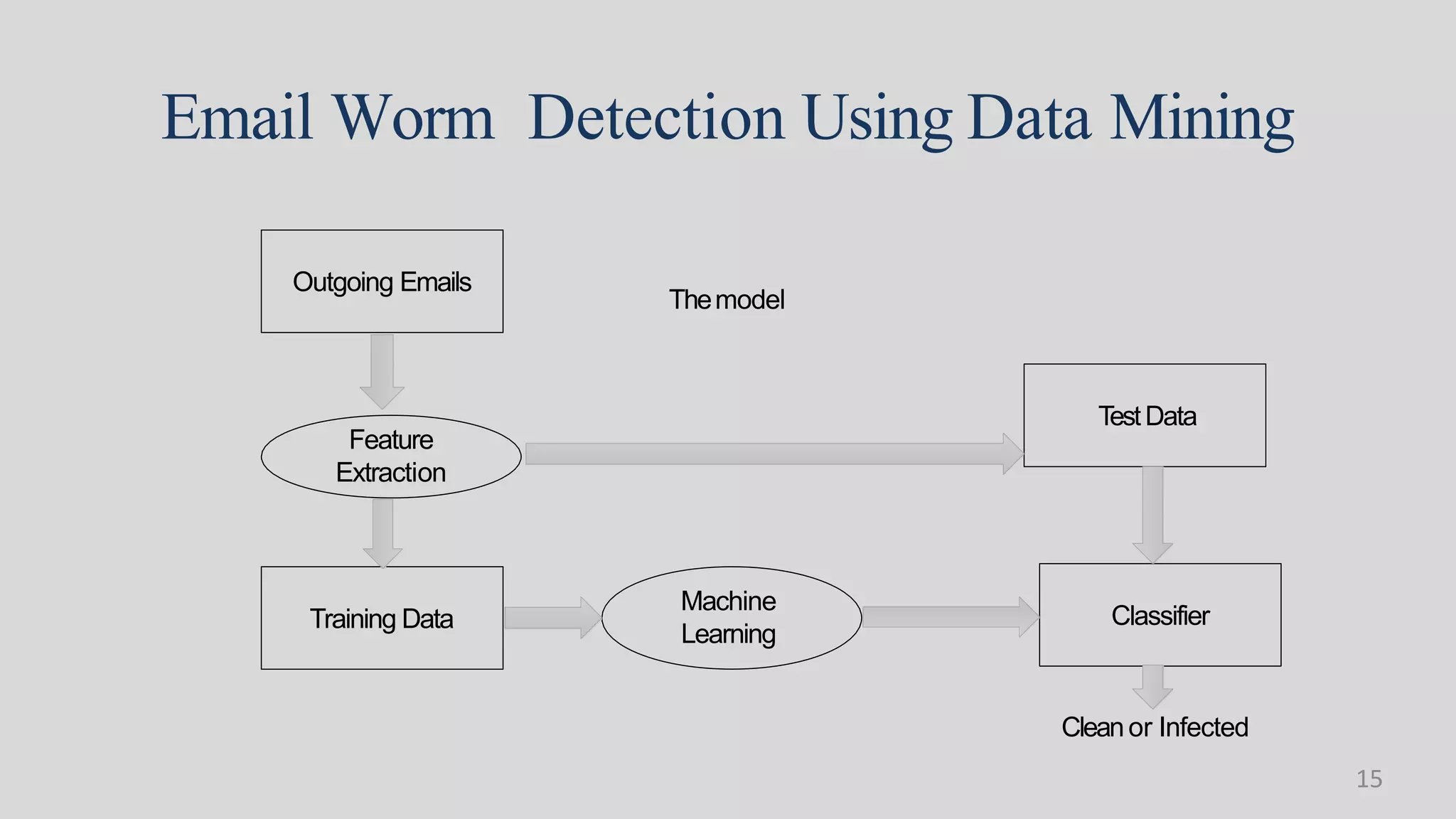
This document discusses the role of data mining in cyber security and intrusion detection. It begins with defining cyber security and cyber crimes. It then discusses how data mining can help with intrusion detection by applying algorithms to network traffic data to identify abnormal activities and security threats. Specifically, it outlines how classification methods like neural networks and clustering can be used to detect malware, build models of normal network behavior, and identify deviations that may indicate security issues. The goal is to use data mining to help detect a wide range of intrusions in a timely manner.