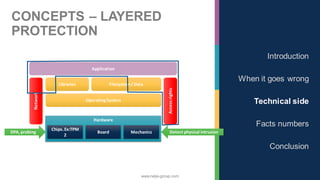
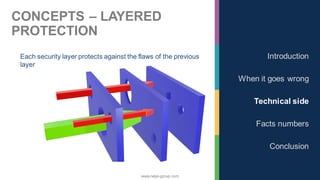
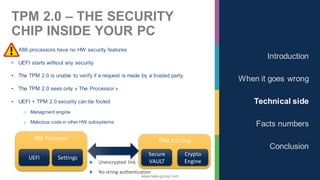
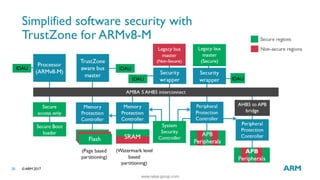
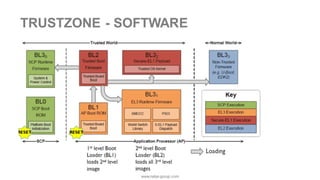
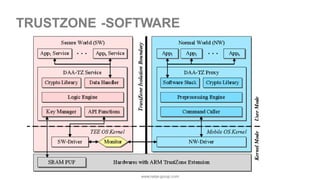
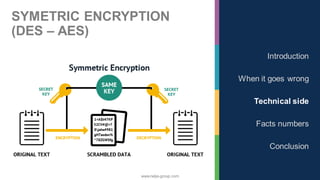
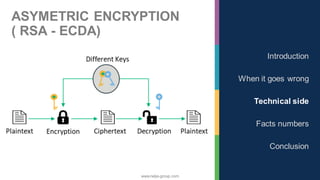
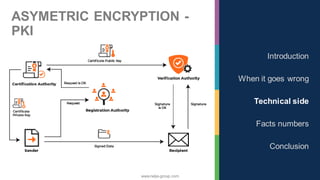
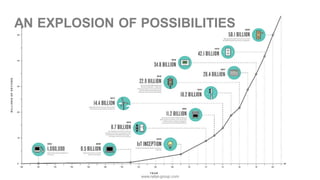
The document discusses the significance of cybersecurity in protecting computer systems and data from various threats, including malicious attacks and data breaches. It outlines different types of cybersecurity threats, such as social engineering and ransomware, and emphasizes the importance of safety and reliability in technology, particularly in the context of IoT devices. The conclusion highlights the growing financial and social risks associated with cybersecurity incidents and the need for proactive measures during the design phase of technology.