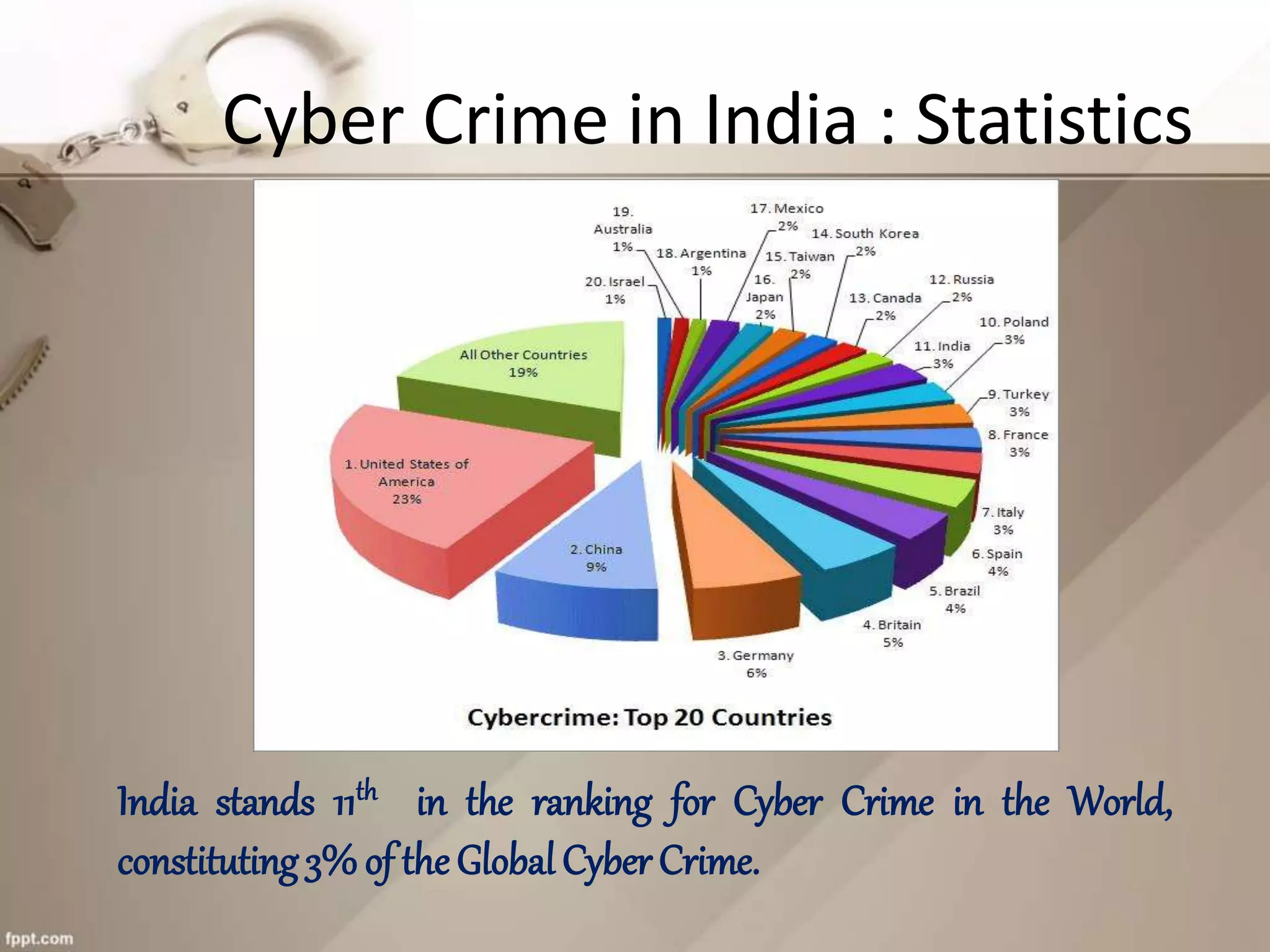
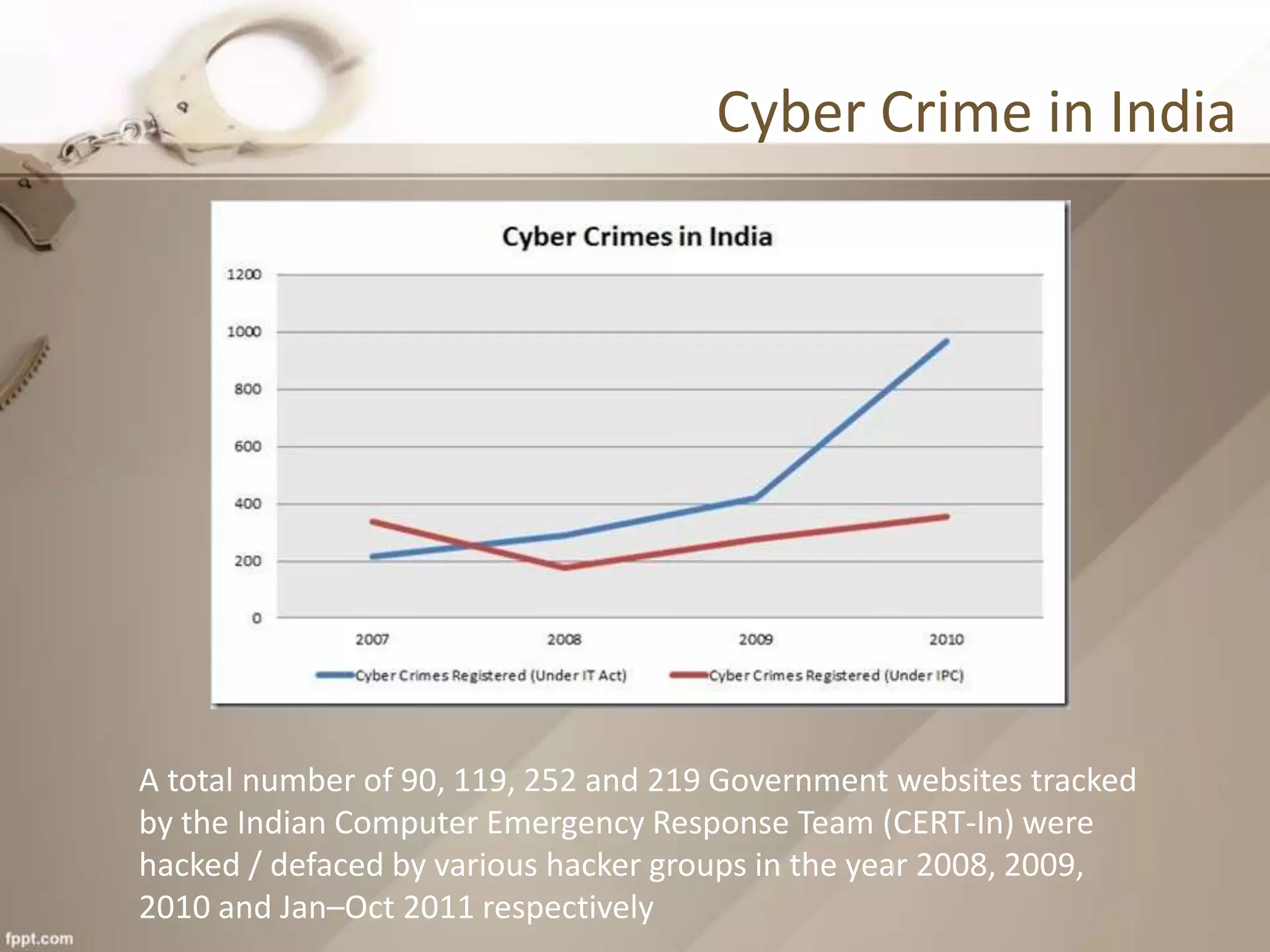
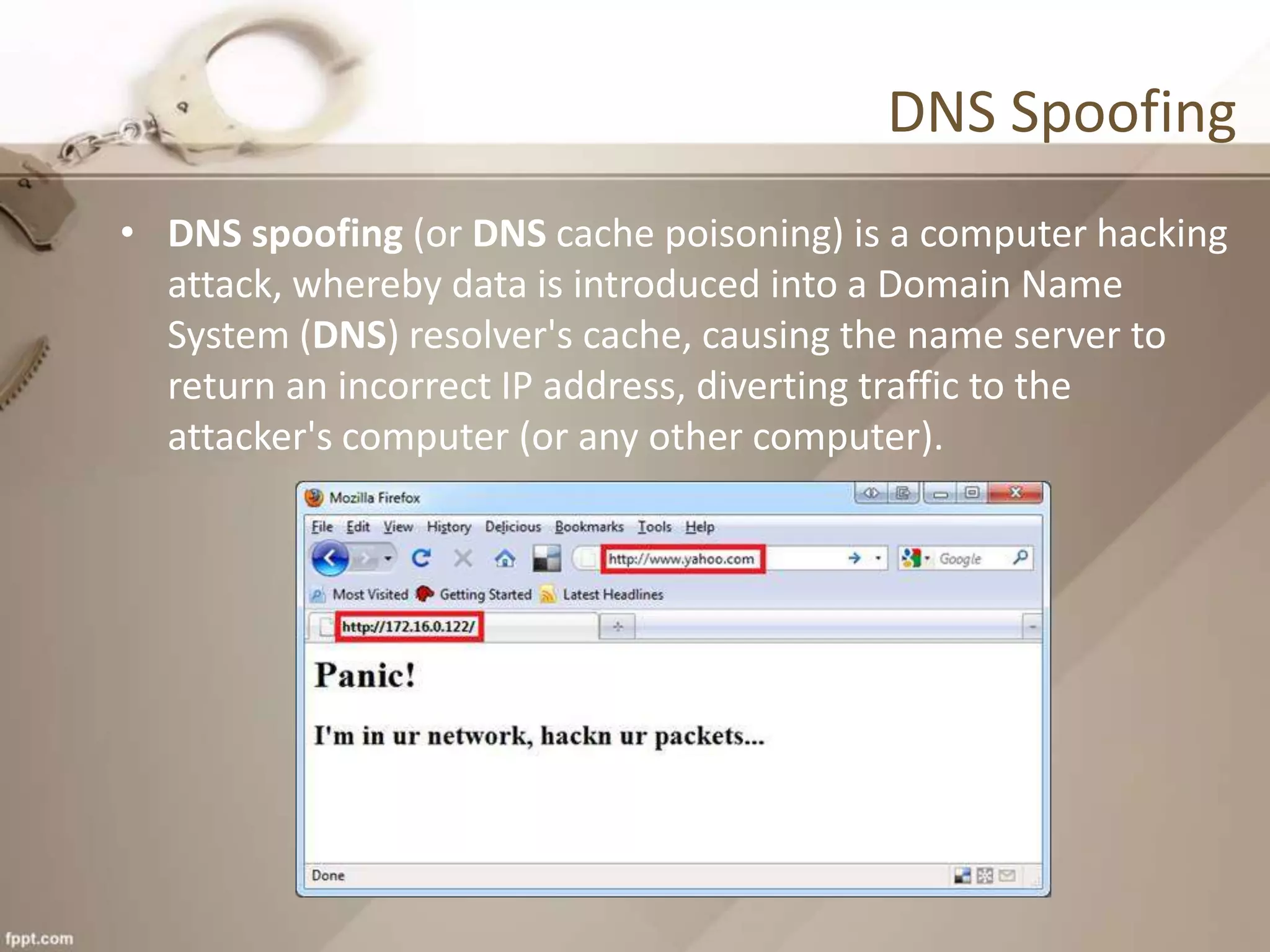
The document provides an overview of cyber crime, detailing its definition, common forms, and specific instances in India, including statistics and types of attacks. It highlights major cyber laws in India aimed at combatting these crimes and offers guidance on how individuals can protect themselves online. The content also discusses various cyber attack methods and the implications of cyber crime on national security and the economy.