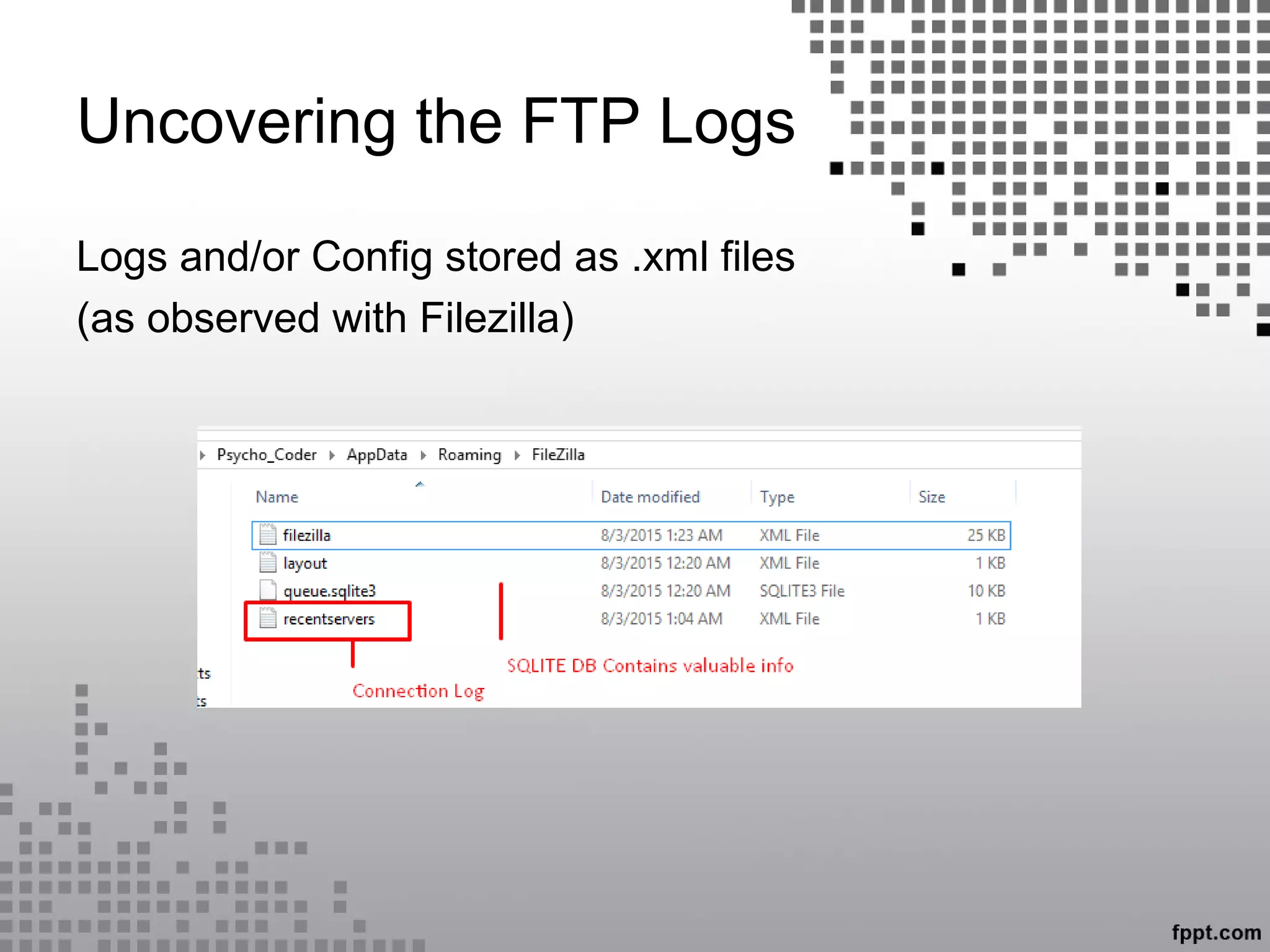
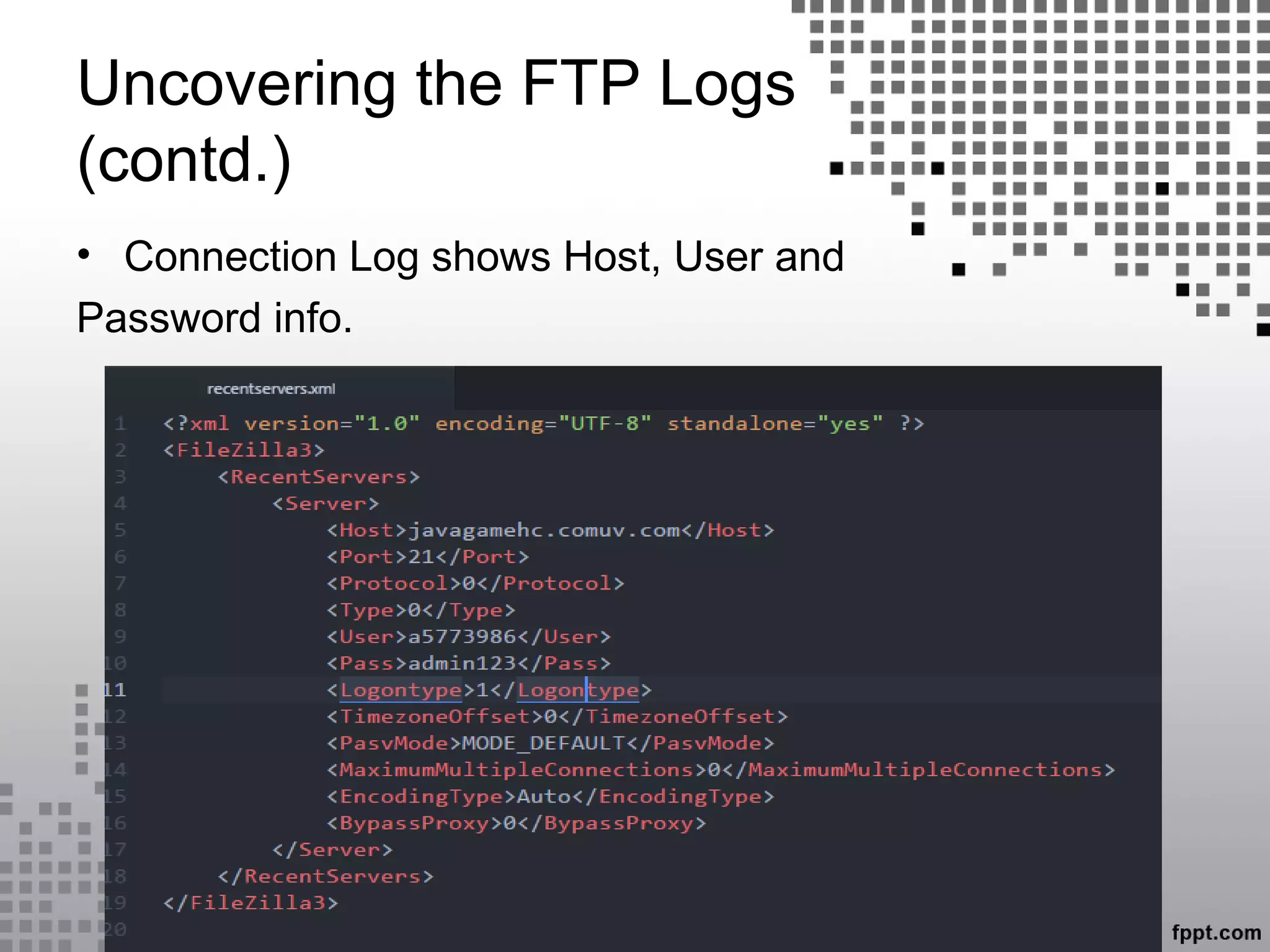
This document discusses server log forensics. It begins by defining logs as files that list actions that have occurred on servers. It then discusses who creates logs, including operating systems, software, and specific locations logs are stored on Windows and Linux systems. Basic terminology is introduced, including definitions of servers, web servers, and FTP. It describes server logs as files automatically created by servers to record activities. It discusses classifying servers and analyzing web server, FTP server, and other logs to uncover forensic evidence about users' activities and attempts like SQL injection.