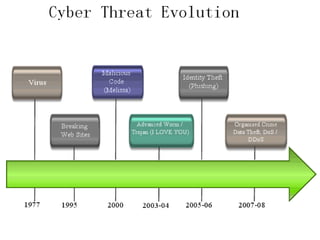
The document discusses cyber crime, its types, and the importance of cyber security in protecting personal information and computers from attacks. It highlights various cyber threats such as hacking, malware, and phishing, alongside practical suggestions for enhancing cyber safety, including software updates, anti-virus programs, and secure password practices. It emphasizes continuous vigilance in maintaining computer security as threats evolve.