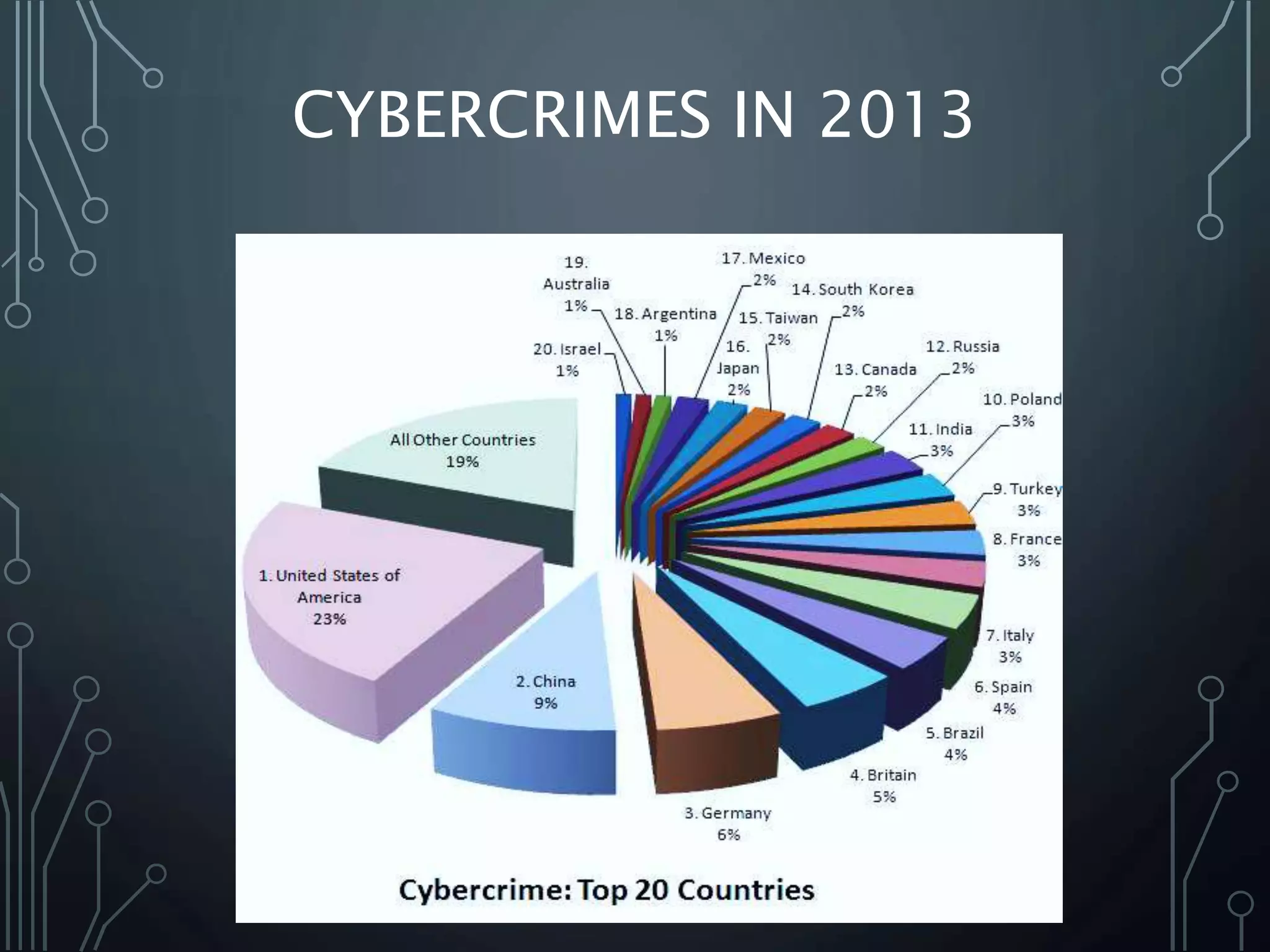
The document discusses the importance of cyber security, defining it as the protection of computer and network systems against theft, damage, and unauthorized access. It outlines various types of cyber crimes, notable historical events related to cyber crime, and presents strategies for personal, organizational, and national cyber security. Key recommendations include using antivirus software, safeguarding sensitive information, and legislating against cyber crime.