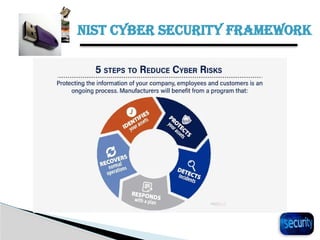
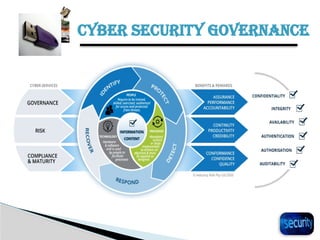
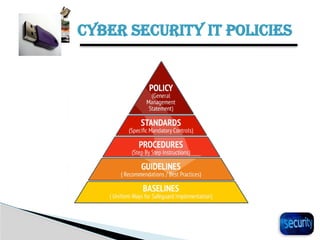
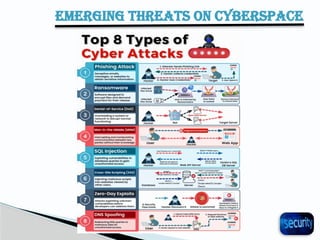
The document discusses the importance of cyber security in banking, emphasizing the protection of sensitive customer data, maintaining trust, and compliance with regulations. It outlines various cyber threats banks face, such as hacking and phishing, while providing best practices for enhancing cyber security, including using antivirus software and backing up important files. Additionally, it highlights the necessity of cybersecurity governance and policies to manage risks and establish a secure operational framework.