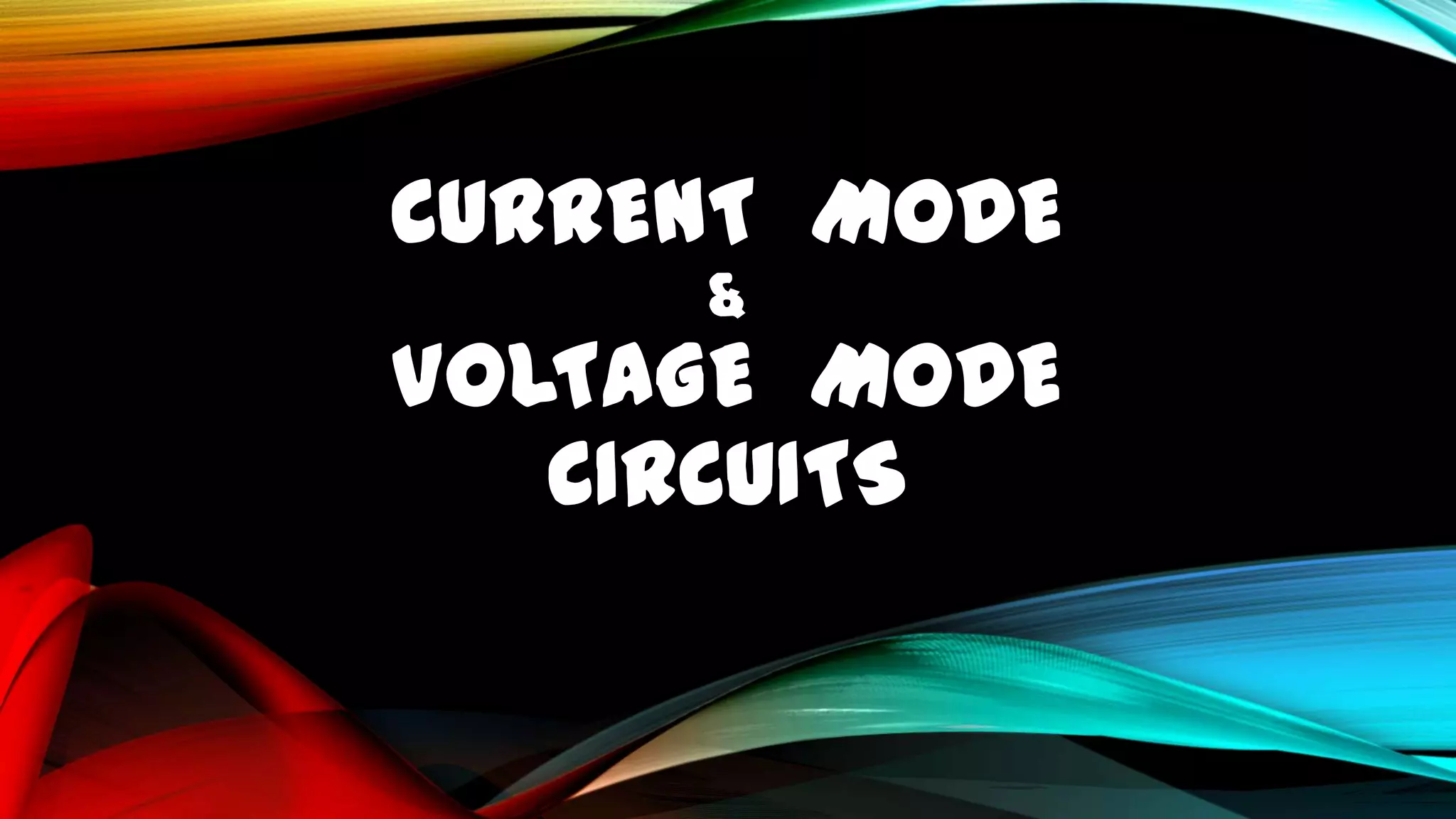
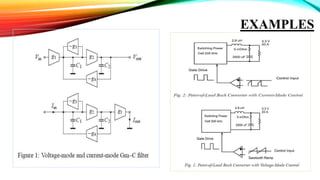
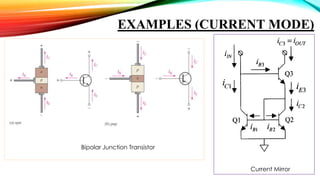
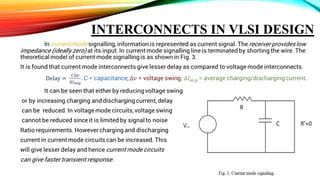
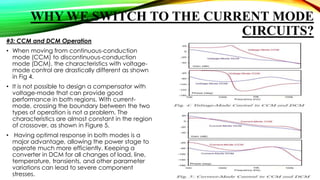
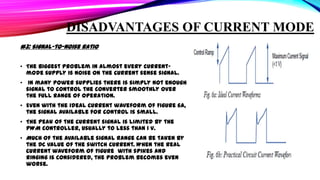
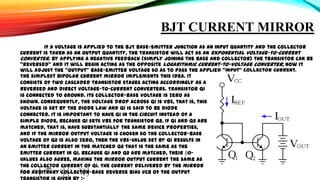
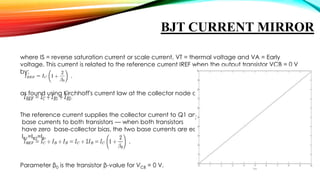
This document discusses current mode and voltage mode circuits. It begins by defining voltage mode and current mode circuits, noting that the definitions are not entirely precise as every circuit has both voltages and currents. It then provides examples of current mode circuits including the bipolar junction transistor and current mirror. It discusses how current mode and voltage mode signaling works for interconnects in integrated circuits. It notes several advantages of current mode circuits including lower power consumption and higher speed. It also discusses differences between the two modes and reasons for switching to current mode circuits such as easier compensation and better operation in continuous and discontinuous conduction modes. Potential disadvantages of current mode are also outlined like current sensing challenges and subharmonic oscillations.