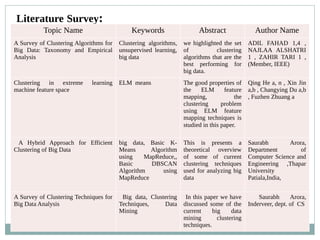
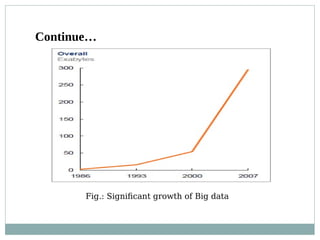
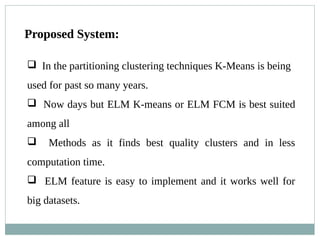
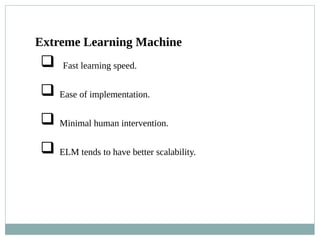
The document presents a survey of clustering techniques for big data analysis, detailing challenges in analyzing large datasets and the necessity for efficient clustering methods. It proposes the Extreme Learning Machine (ELM) K-means algorithm as a solution, highlighting its advantages such as fast learning speed and minimal human intervention. The study concludes that while current techniques are useful, new methodologies are still needed for real-time data analysis.







![ELM k-Means algorithm
Input: k : the number of clusters,
L : the number of the hidden-layer nodes,
D : a data set containing m objects.
Output : A set of k clusters.
Method :
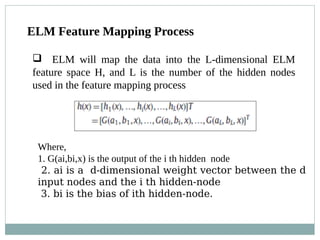
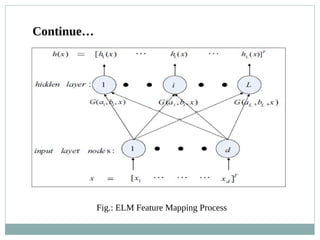
1: Mapping the original data object sin D into the ELM feature
space H using h(x)=[H1(x),….,hi(x),…hl(x)]T ;
2: Arbitrarily choose k objects from H as the initial cluster centres;
3: repeat
4: (Re) assign each object to the cluster to which the object is the most
similar , based on the mean value of the object sin the cluster;
5: Update the cluster means , i.e. , calculate the mean value of the
objects for each cluster;
6: until no change in the cluster centres or reached the maximal
iteration number limit.
7: return A set of k clusters.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/currentclusteringtechniques-150324005523-conversion-gate01/85/Current-clustering-techniques-19-320.jpg)