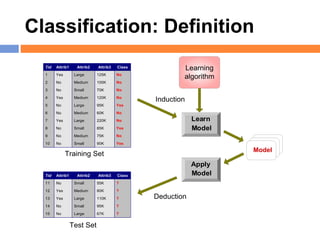
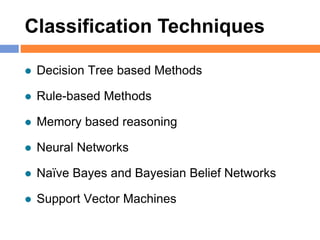
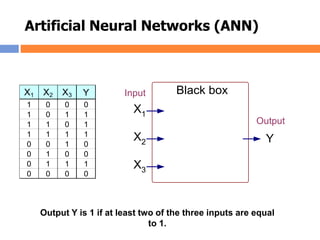
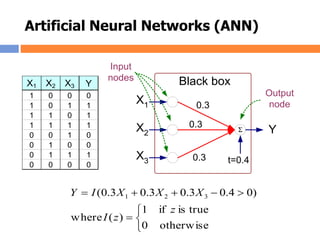
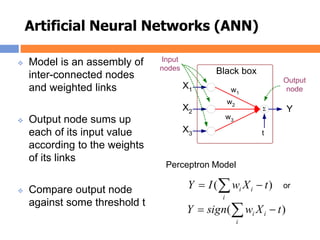
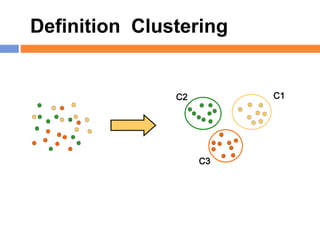
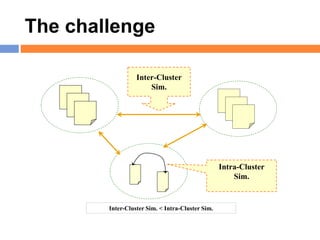
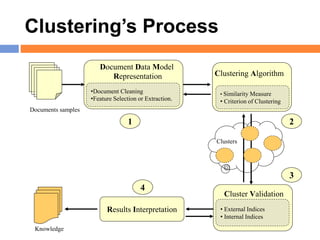
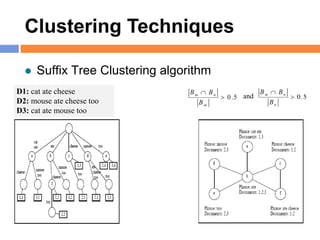
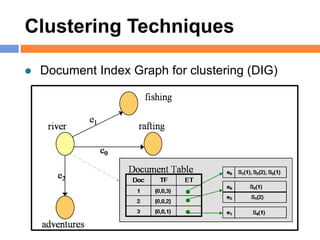
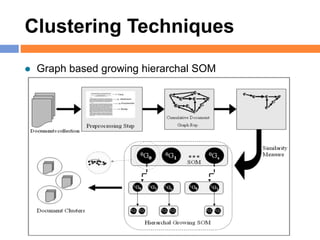
The document outlines methods and techniques for document clustering and classification, detailing classification definitions, learning algorithms, and various clustering approaches. It describes the goals of classifying records based on attributes, as well as the challenge of organizing diverse document collections into meaningful clusters. Key techniques for both classification and clustering, including decision trees, neural networks, and hierarchical clustering, are also discussed.