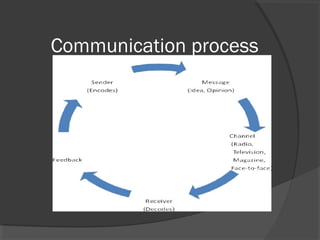
This document defines culture and communication and discusses their relationship to intercultural interactions. It defines culture as the characteristics of a particular group, including language, customs, religion, and arts. Communication is defined as the process of sharing messages, information, and ideas through encoding and decoding signals. Intercultural communication can lead to misunderstandings when people from different cultures do not share the same understanding of gestures, values or language. Key barriers to effective intercultural communication include assumptions of similarity between cultures, differences in language, misinterpreting nonverbal cues, stereotypes, the tendency to evaluate others based on one's own culture, and high anxiety during intercultural interactions.