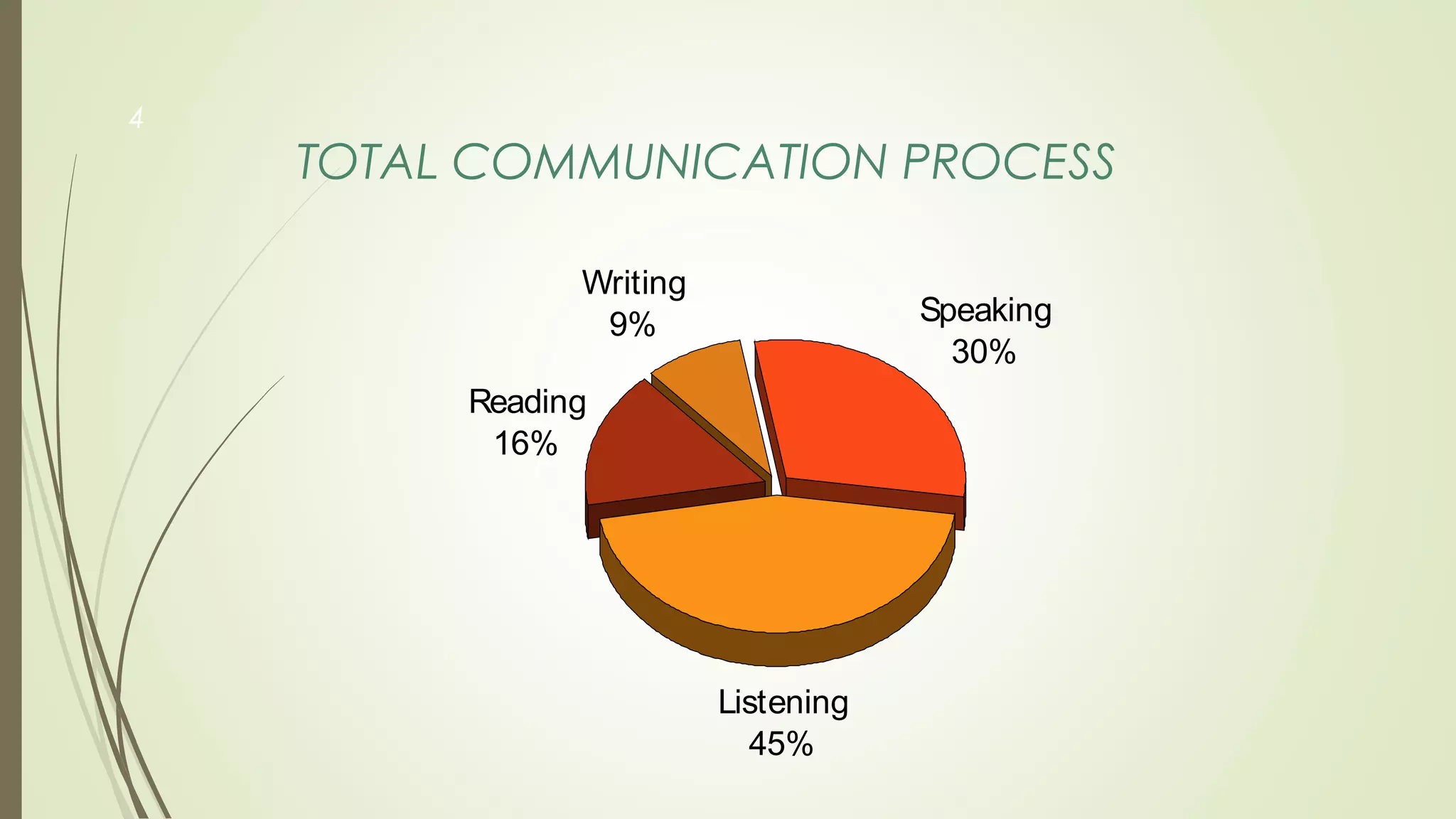
This document provides information about communication skills. It discusses the total communication process, which includes listening (45%), speaking (30%), reading (16%), and writing (9%). It then describes the process of communication, including encoding, decoding, channels, strengths/weaknesses of verbal and written communication, feedback, and barriers to communication such as physical, mechanical, socio-cultural, psychological, and linguistic barriers.