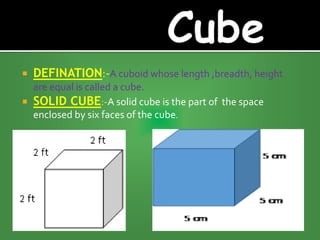
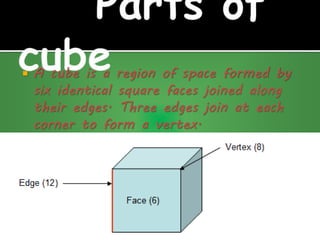
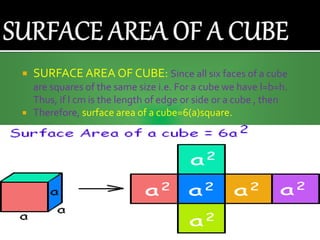
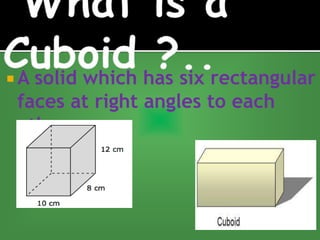
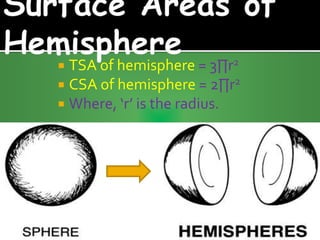
This document defines and provides formulas for calculating surface areas and volumes of various 3D shapes including cubes, cuboids, cylinders, cones, spheres, and hemispheres. It states that the total surface area of a cube is 6 times the area of one face, and the volume is the cube of the edge length. The total surface area of a cuboid is 2 times the sum of the area of the base and lateral faces, and the volume is length times breadth times height.