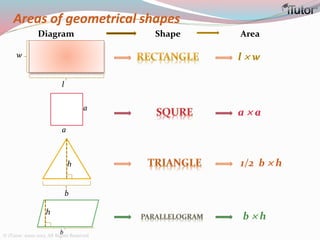
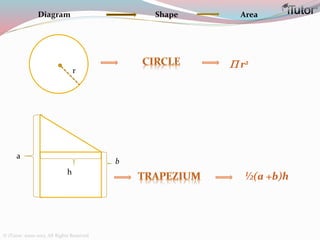
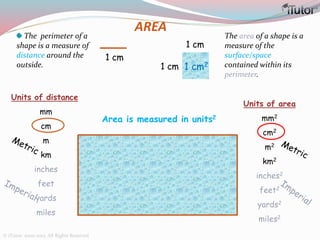
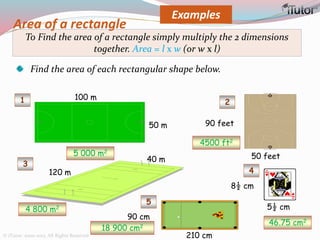
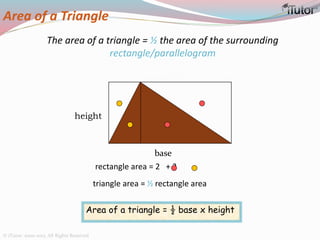
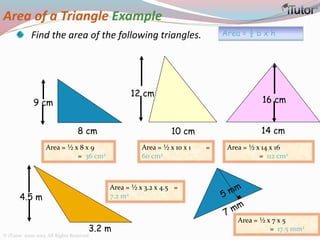
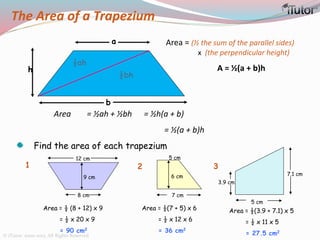
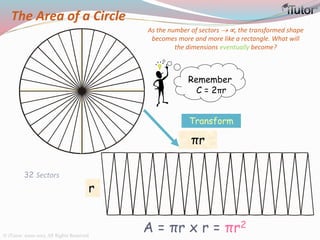
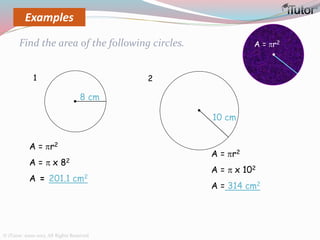
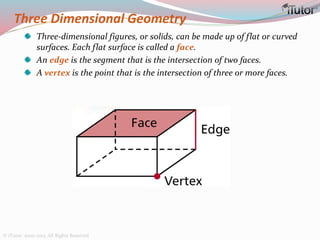
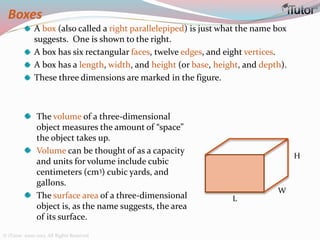
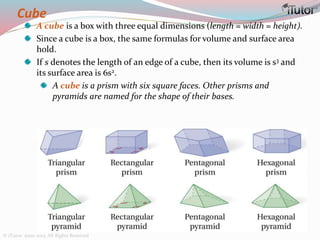
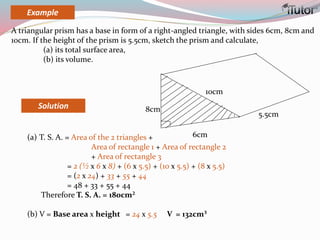
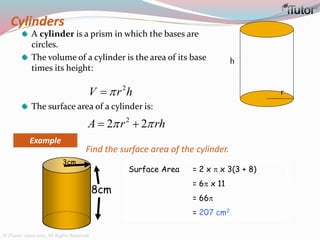
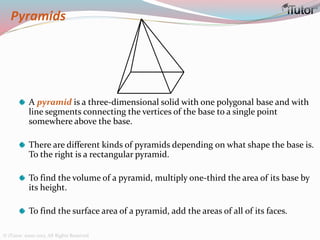
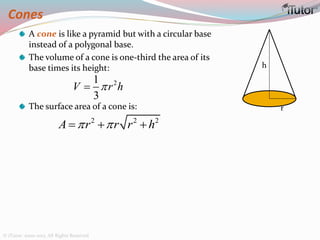
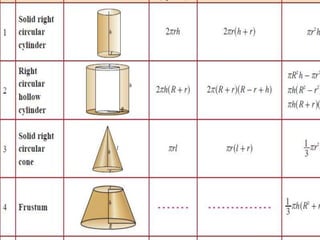
This document is a comprehensive guide to geometry, focusing on the calculations of perimeters, areas, and volumes of various shapes, both two-dimensional and three-dimensional. It explains key concepts such as planes, surfaces, and different geometric shapes, providing formulas and examples for calculating areas and volumes of rectangles, triangles, trapeziums, boxes, prisms, cylinders, pyramids, and cones. The document emphasizes the importance of understanding both surface area and volume in the context of solid geometry.