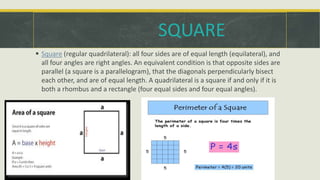
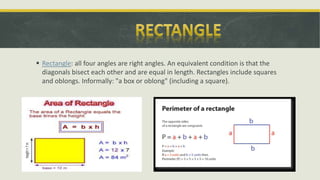
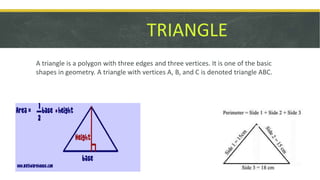
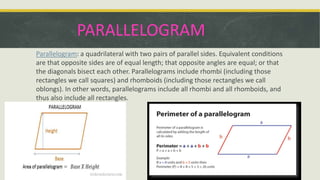
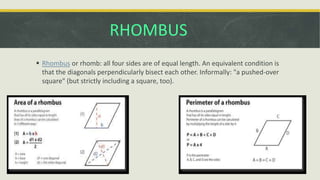
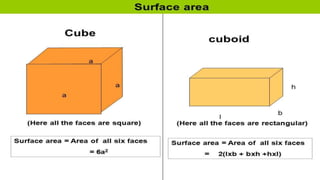
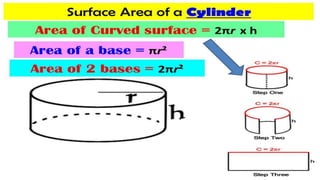
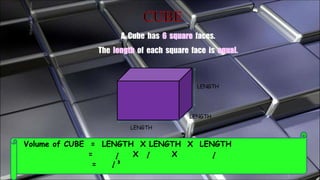
The document covers geometric concepts including areas, surface areas, and volumes of quadrilaterals, polygons, and solids. It defines various shapes such as squares, rectangles, triangles, parallelograms, trapezoids, and rhombuses, detailing their properties and relationships. Additionally, it provides formulas for calculating volumes of cubes and cuboids.