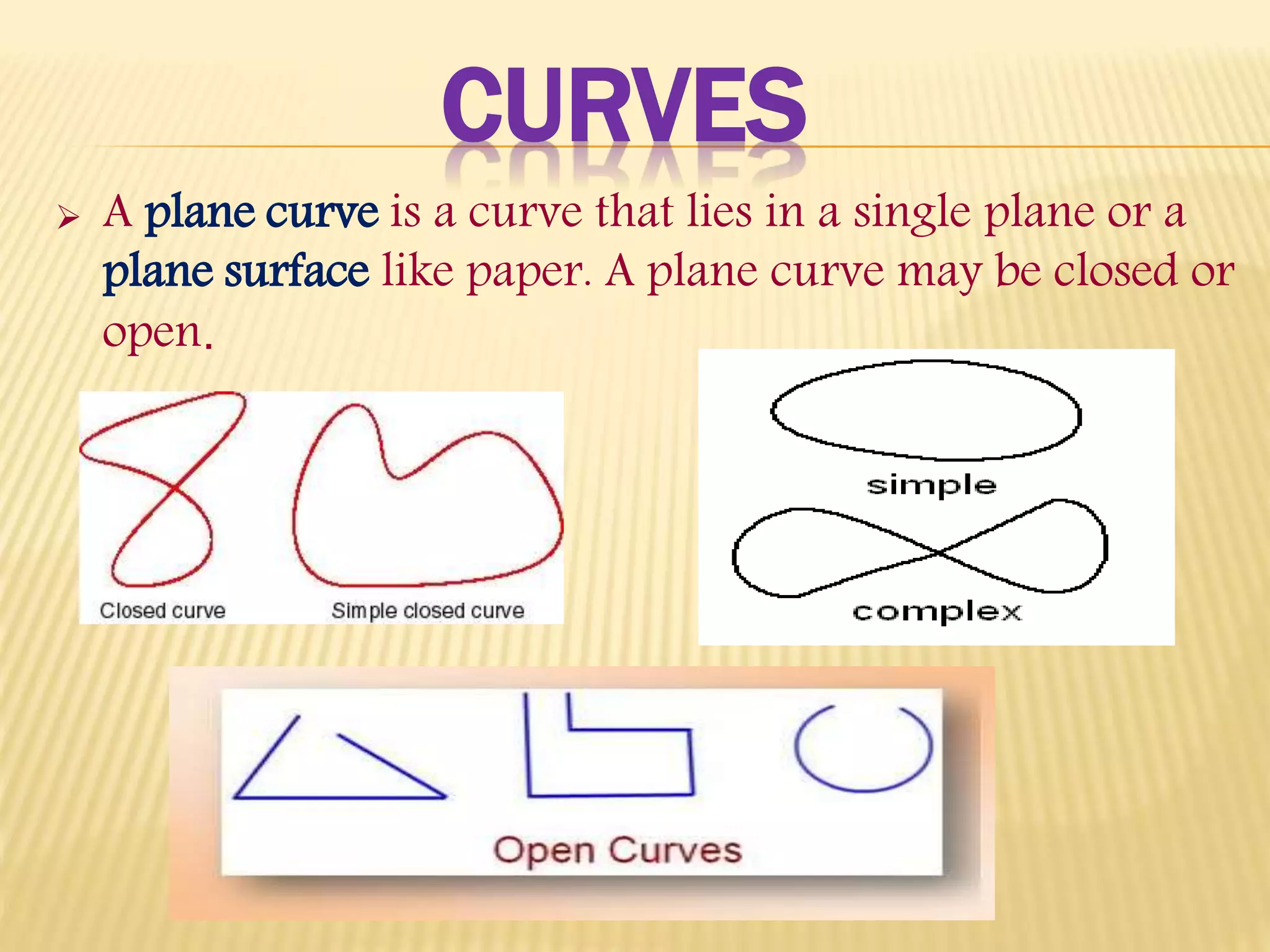
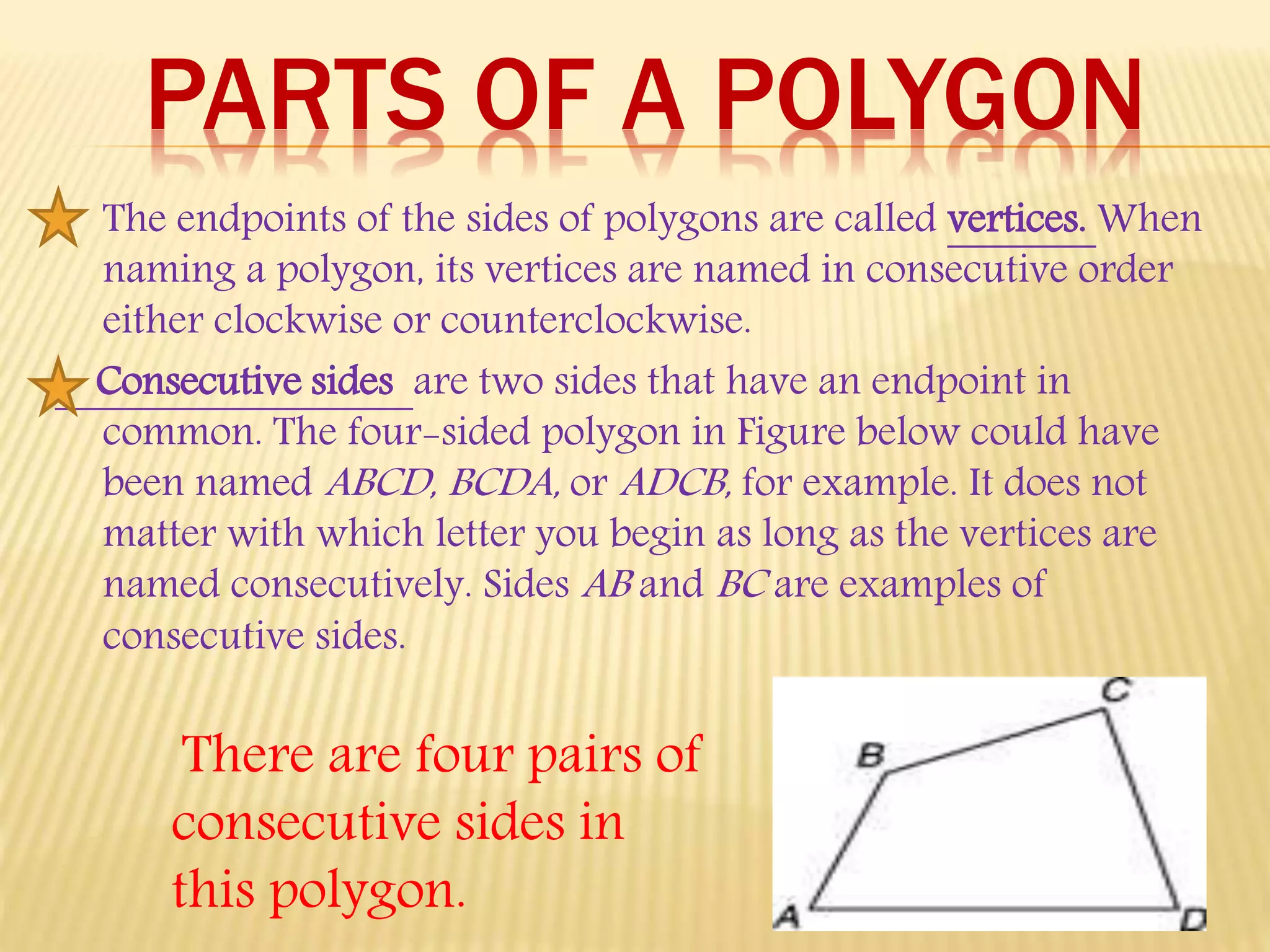
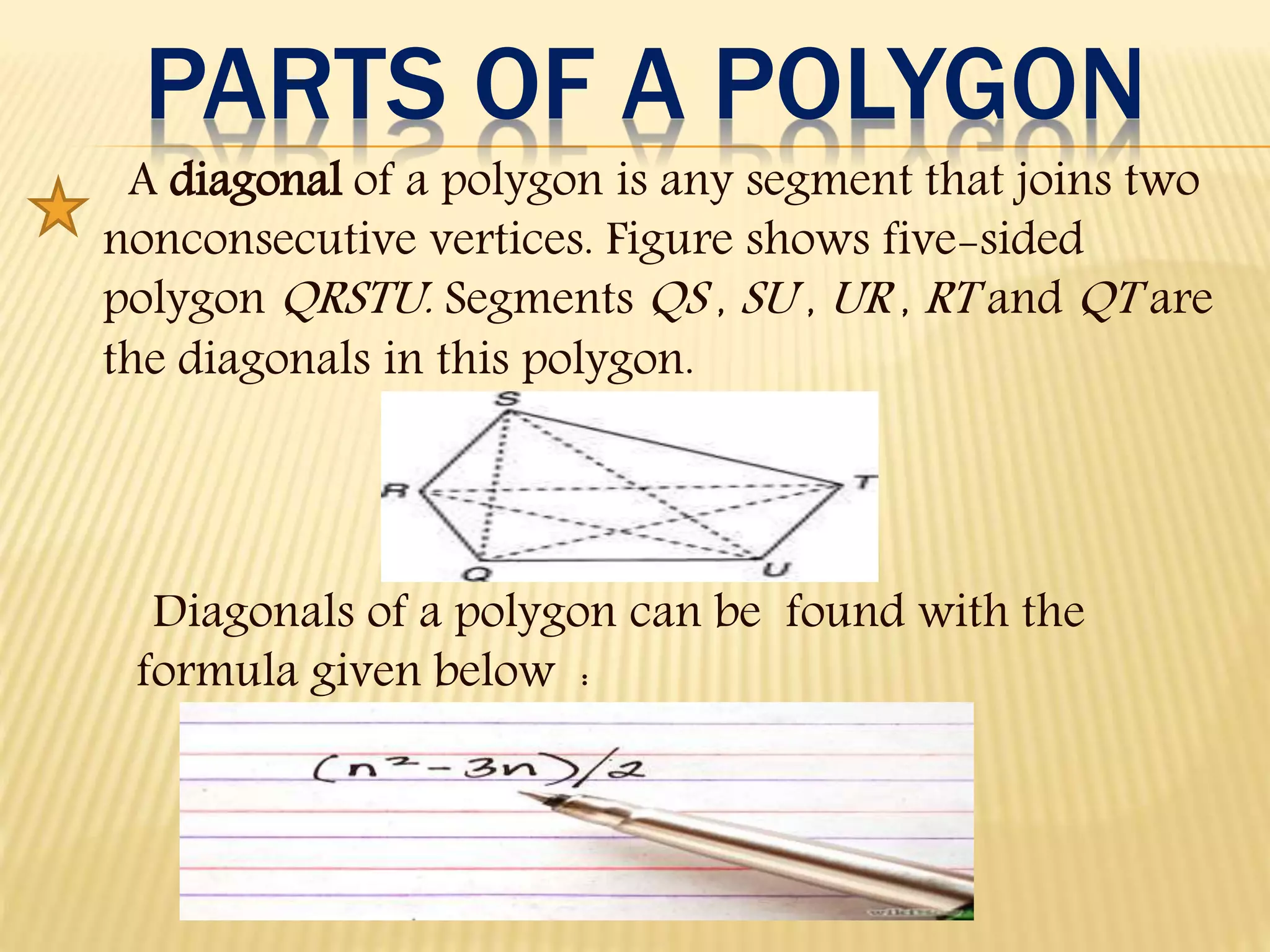
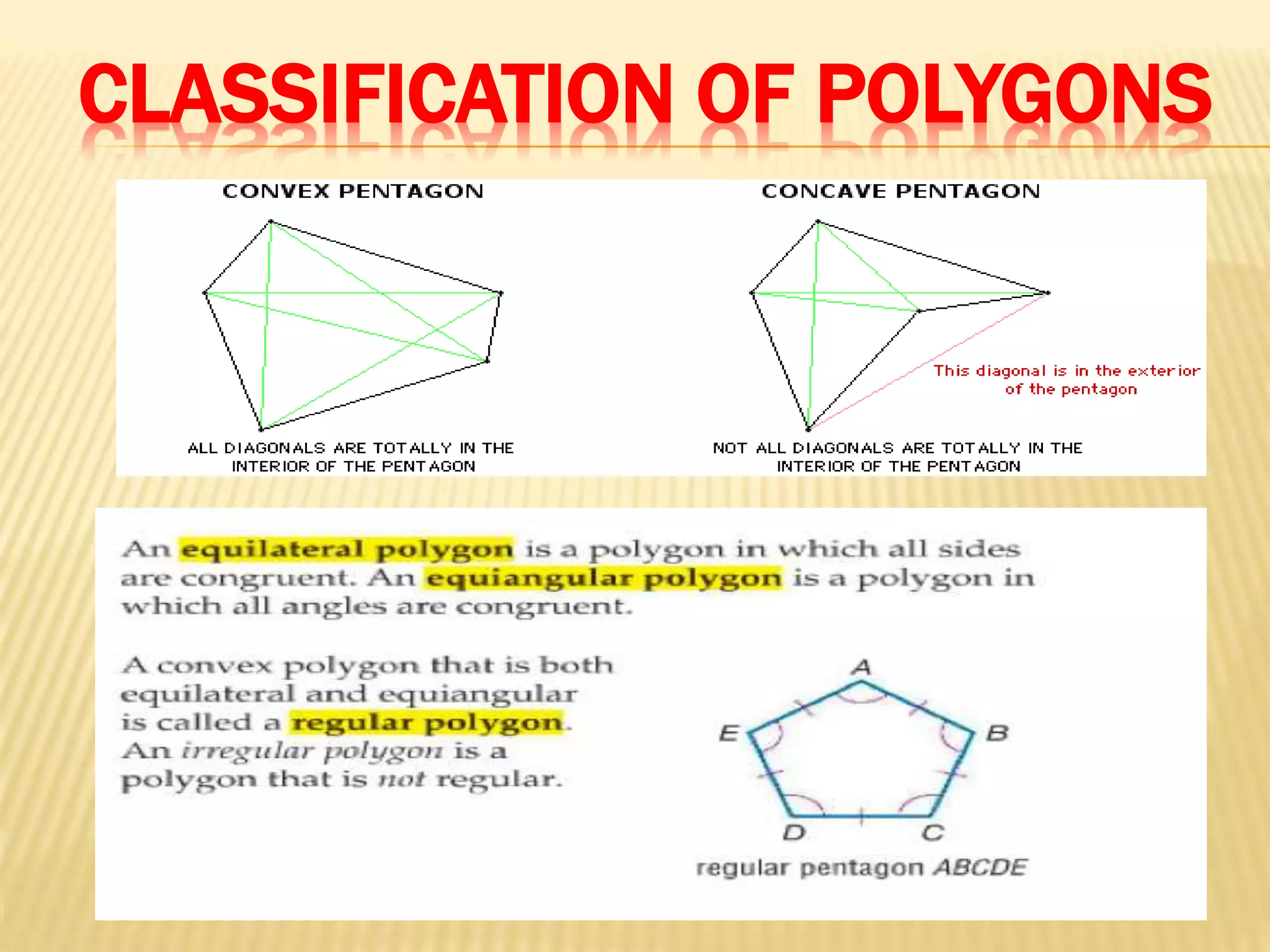
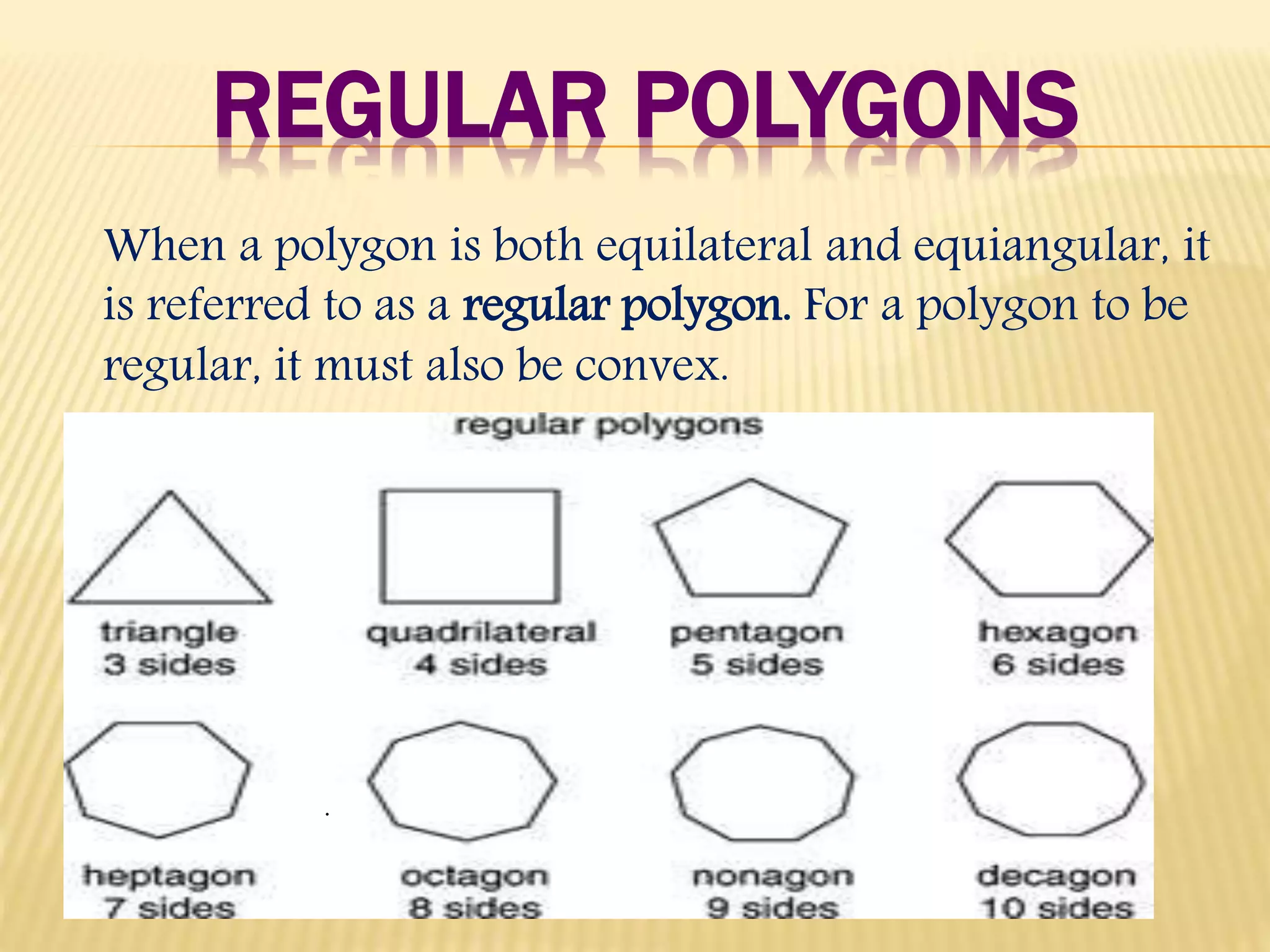
1. The document defines and classifies different types of polygons, with a focus on quadrilaterals.
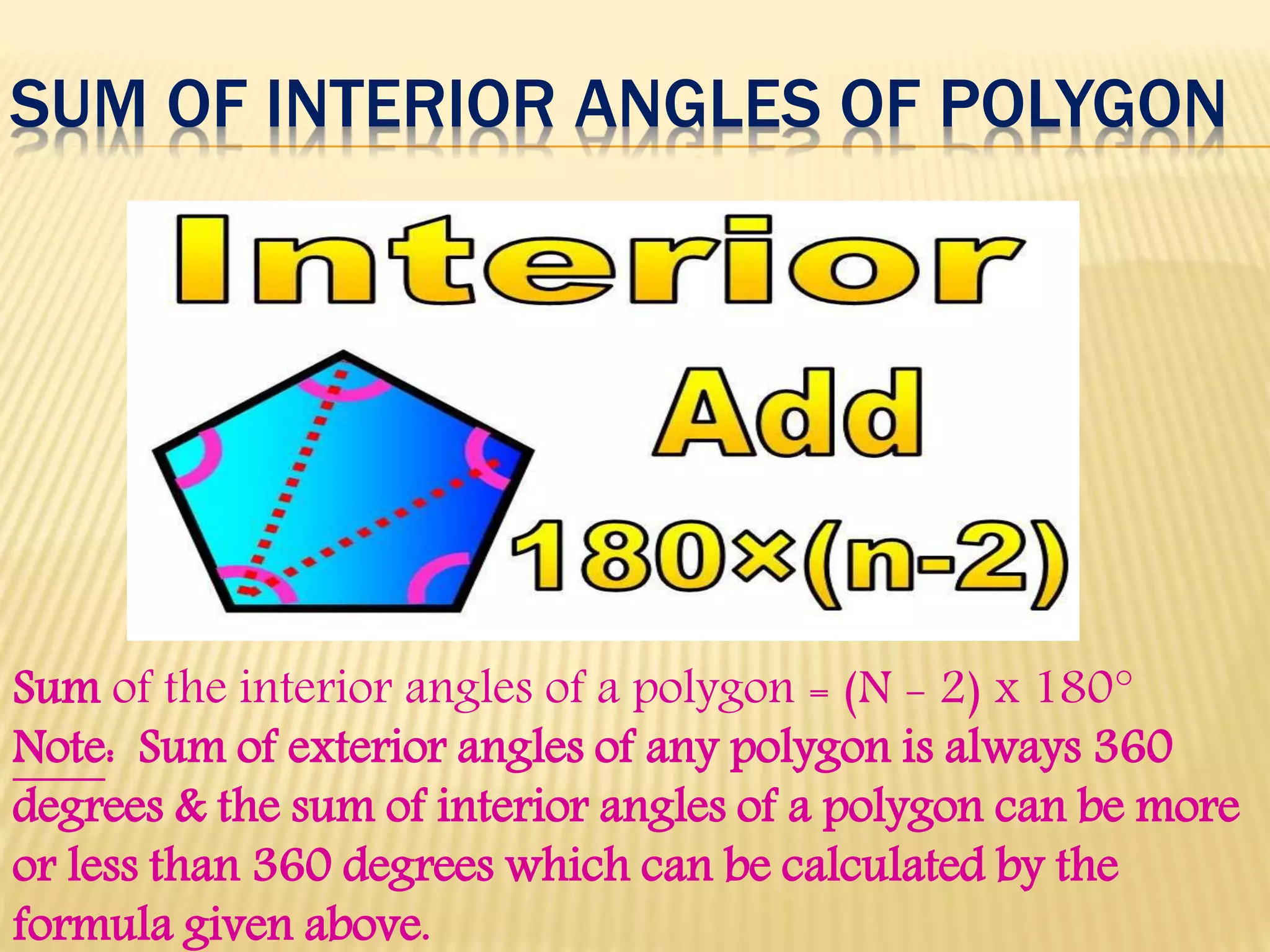
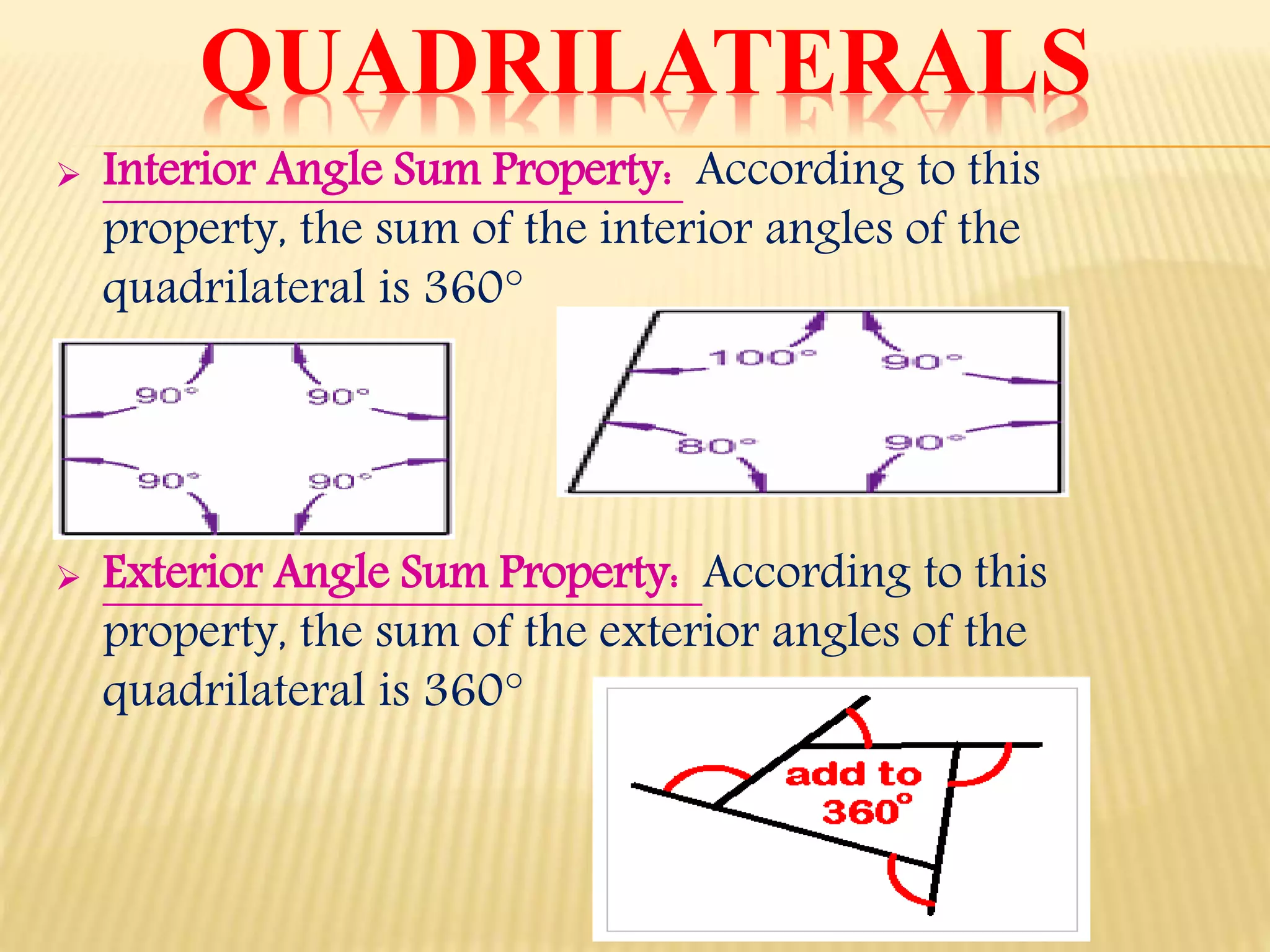
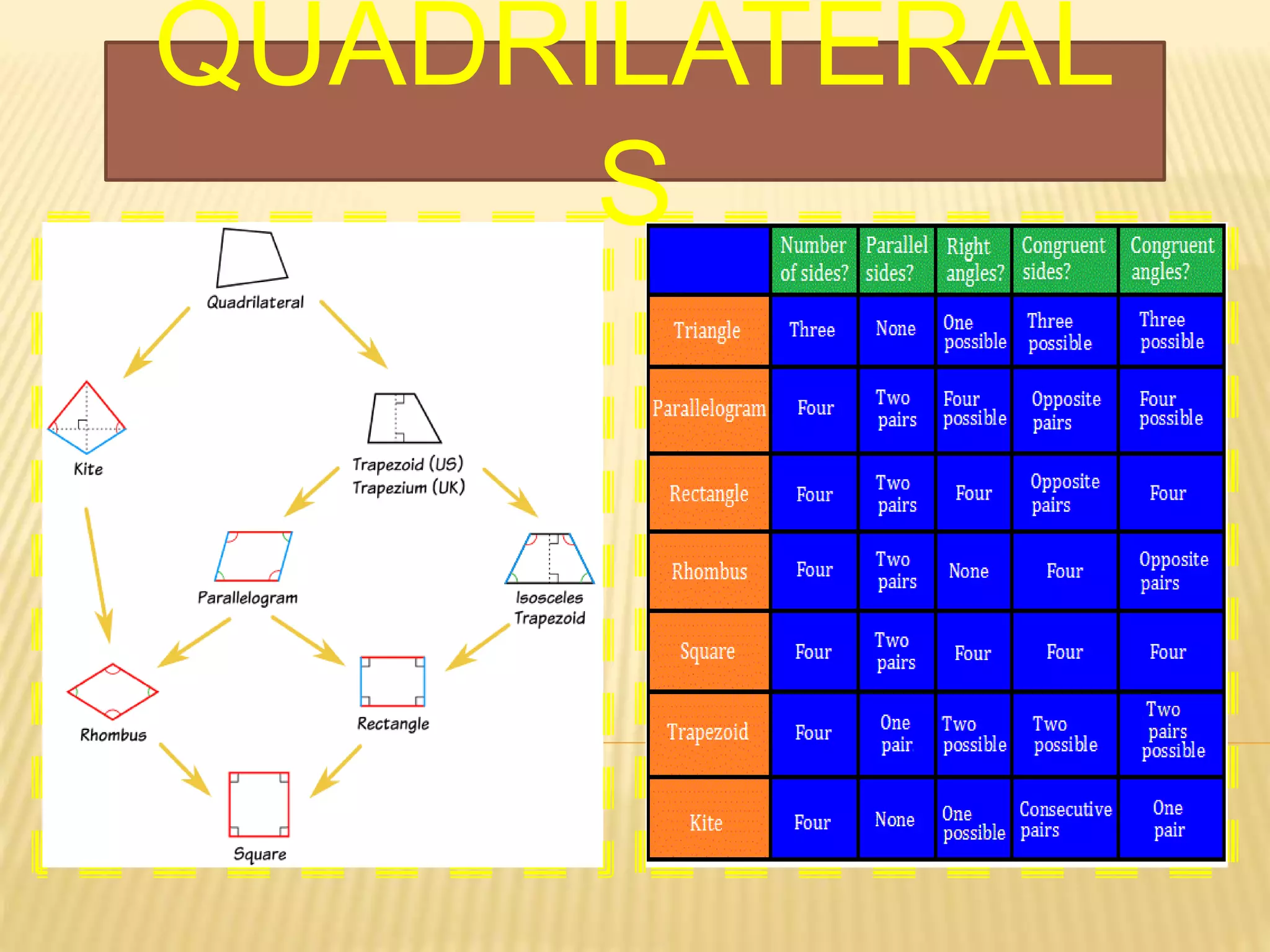
2. It describes properties of quadrilaterals including having four sides, four angles, one pair of diagonals, and the interior angle sum being 360 degrees.
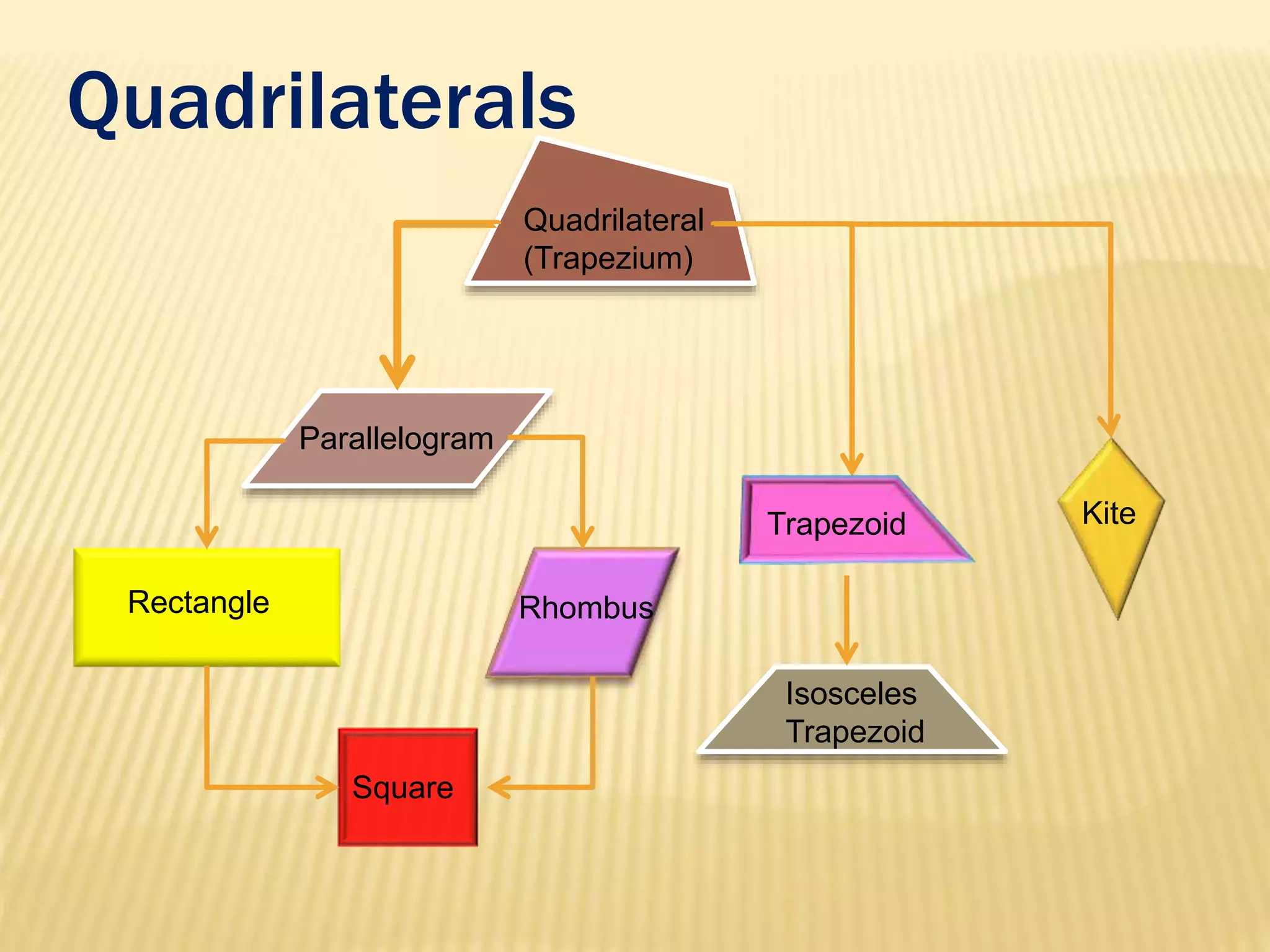
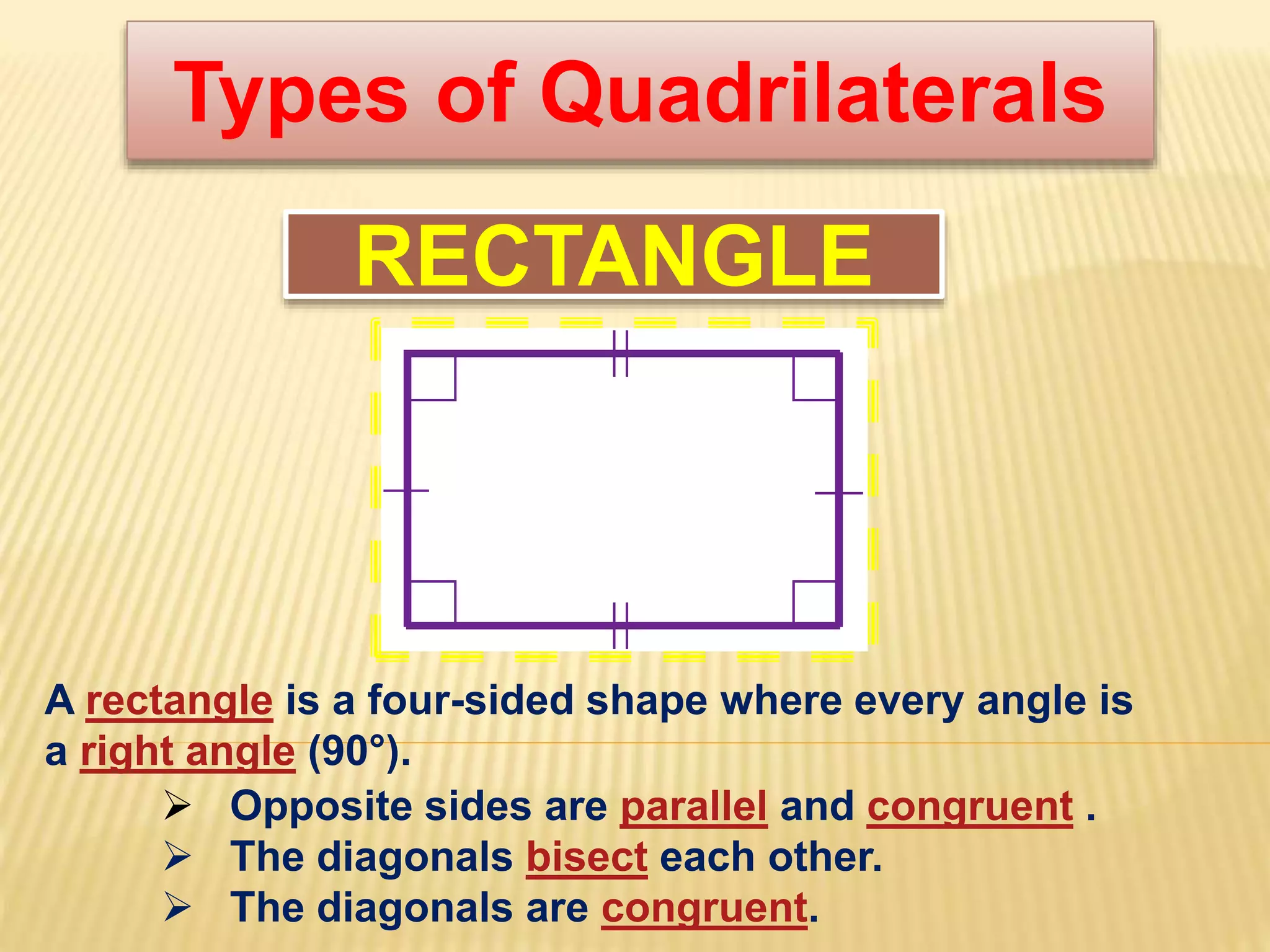
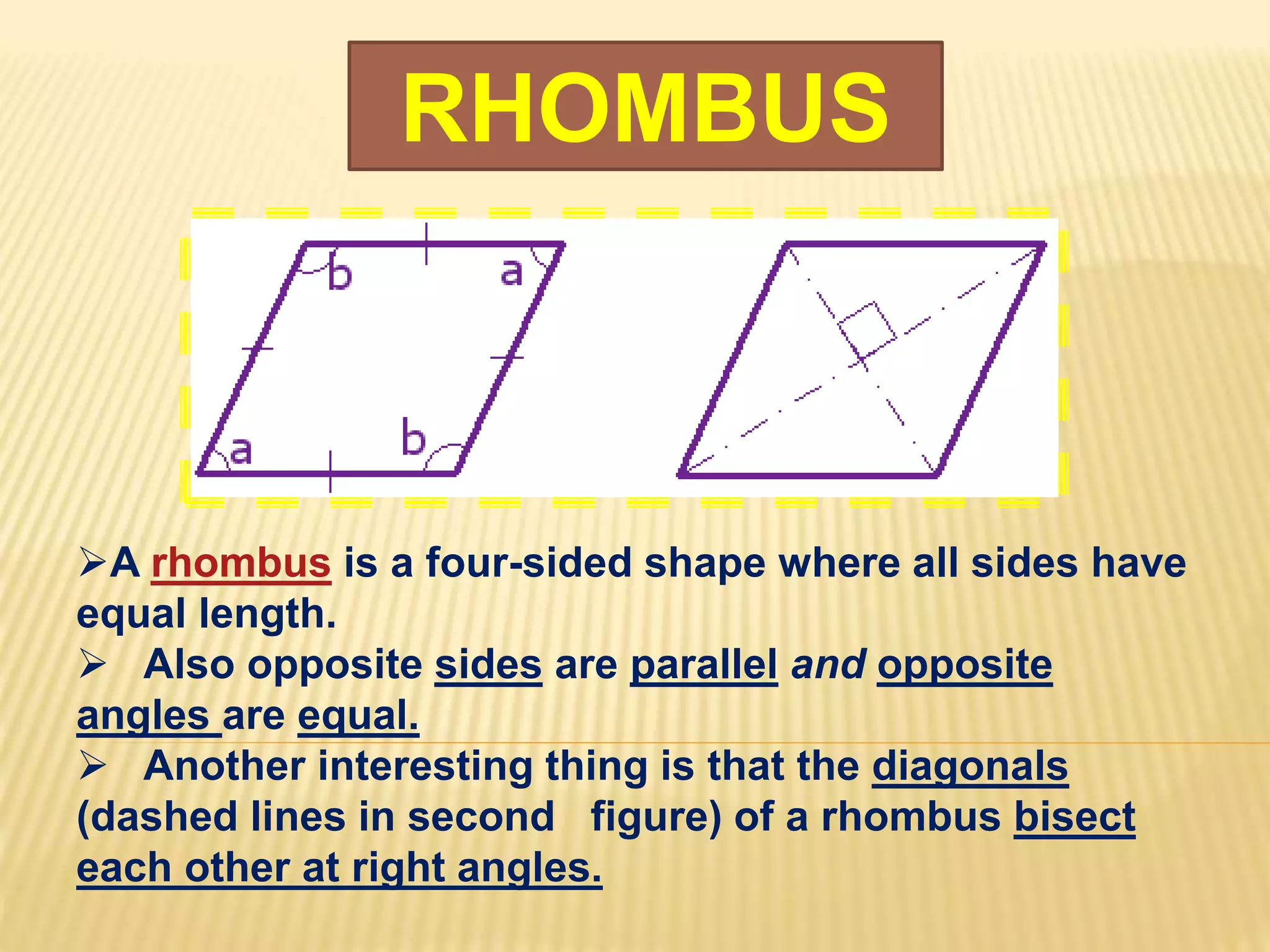
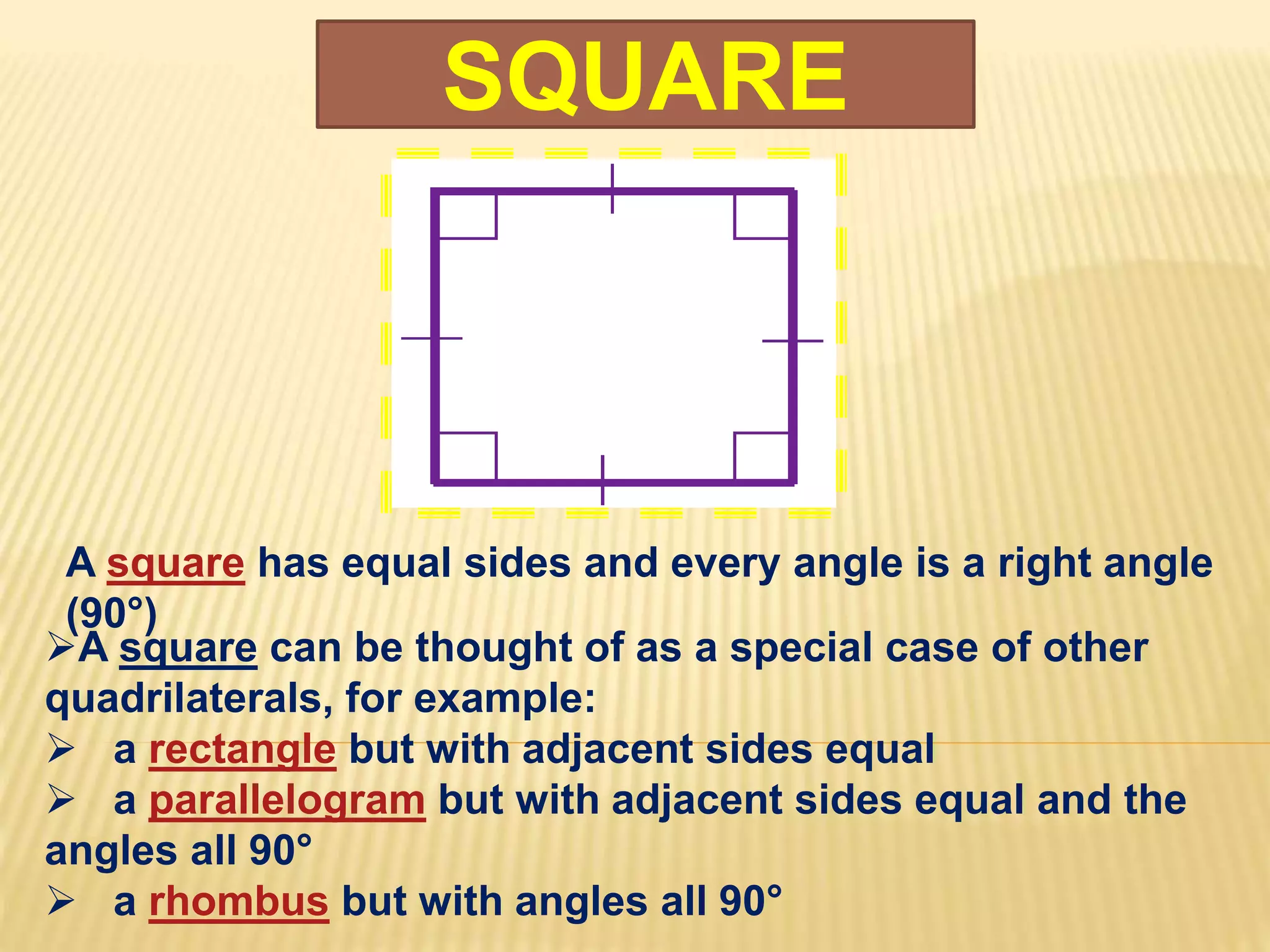
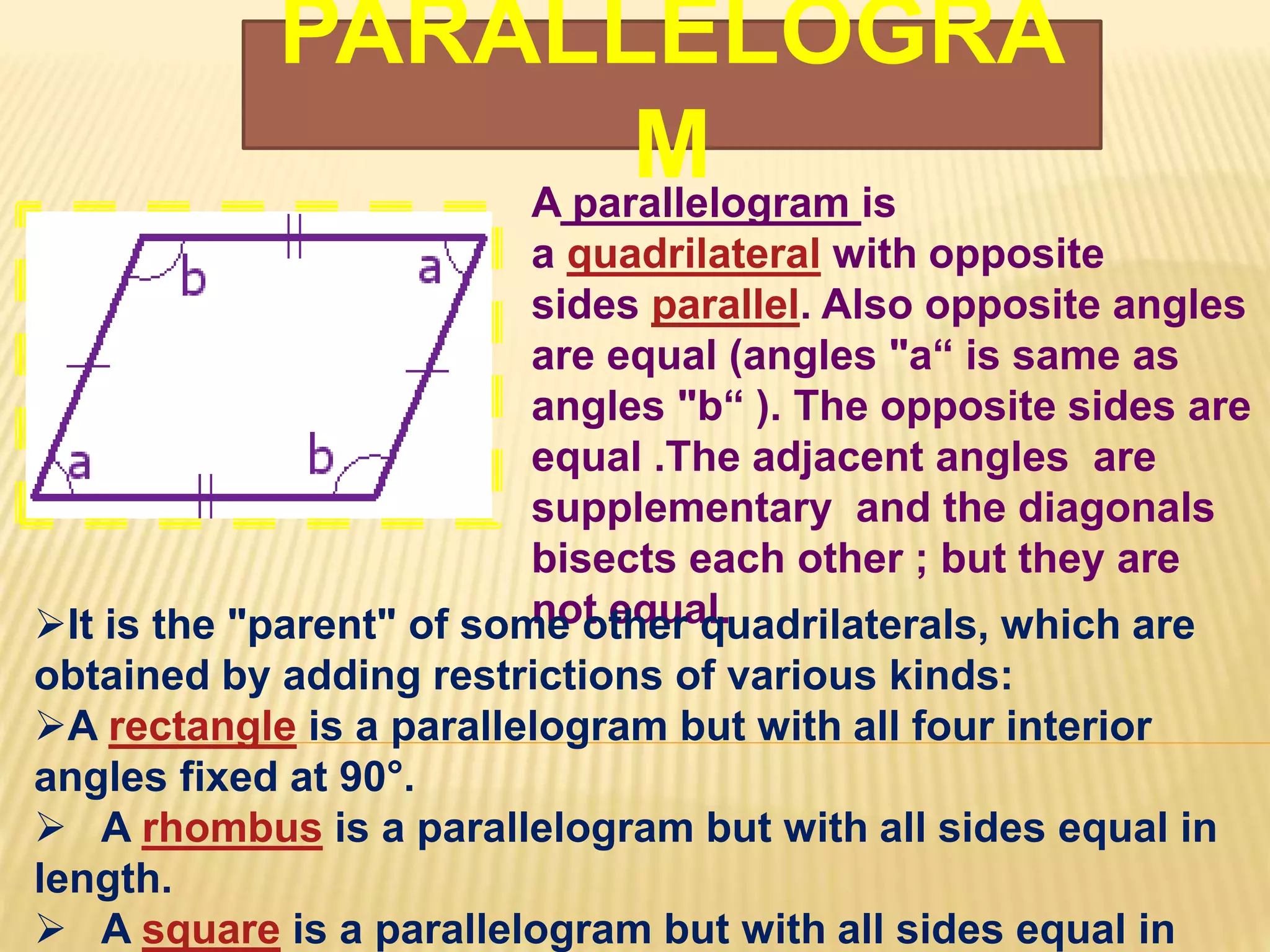
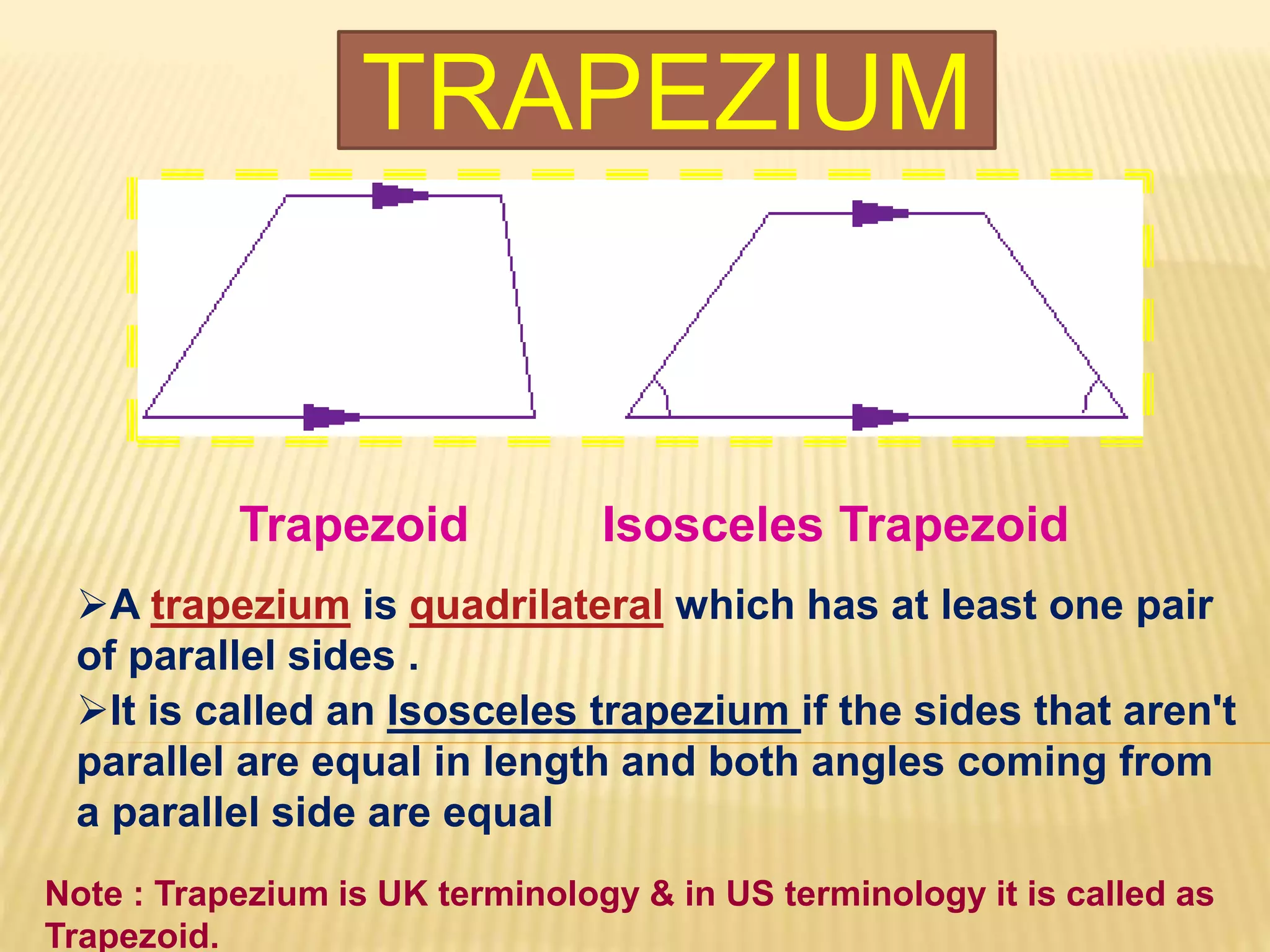
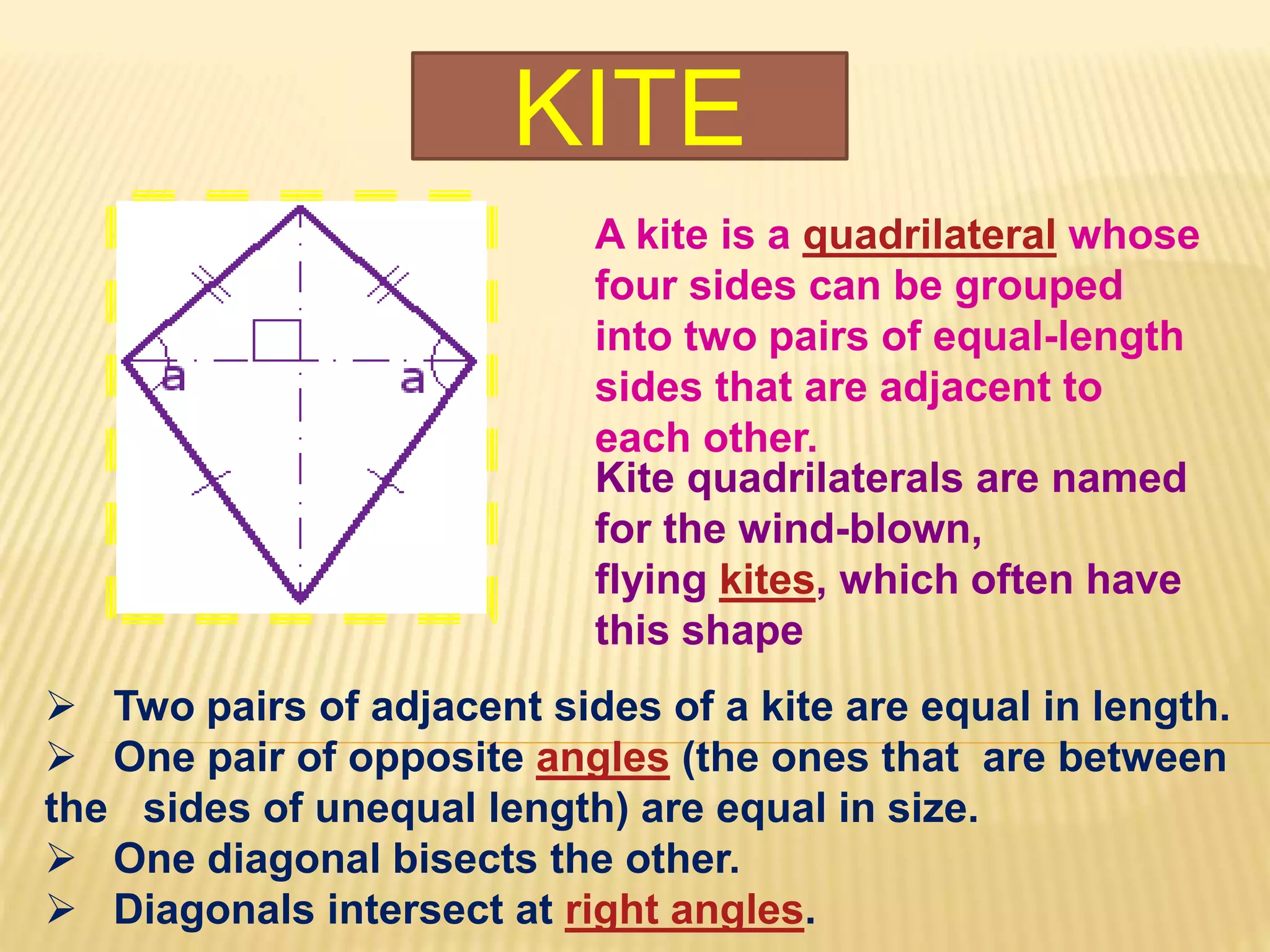
3. Several specific types of quadrilaterals are defined, including rectangles, rhombus, squares, parallelograms, trapezoids, kites, and trapeziums. Their defining properties are provided.