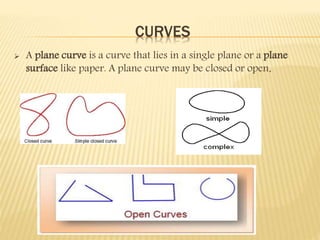
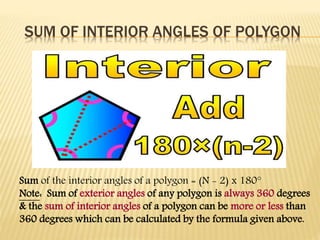
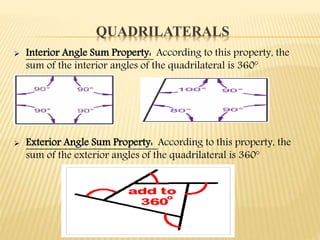
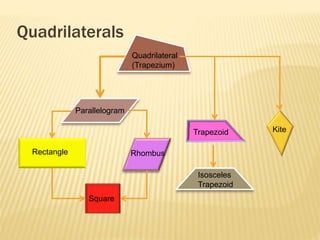
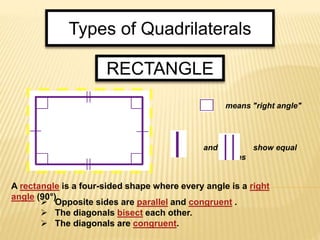
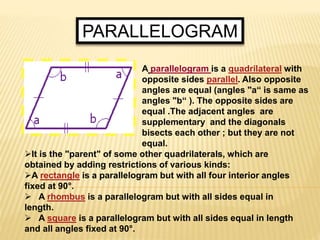
This document defines and classifies polygons and quadrilaterals. It begins by defining curves and polygons, with polygons being plane figures bounded by three or more straight sides that meet at vertices. It then discusses the parts of polygons including vertices, sides, consecutive sides, and diagonals. Polygons are classified as convex or concave. Specific types of polygons are defined based on their number of sides. The document also discusses regular polygons, interior angles, and formulas for calculating polygon properties. Finally, it defines and provides properties of different types of quadrilaterals including rectangles, rhombi, squares, parallelograms, trapezoids, kites, and trapezoids.