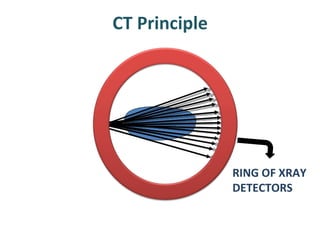
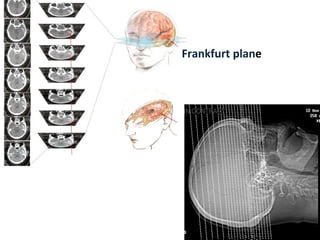
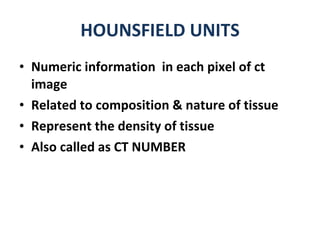
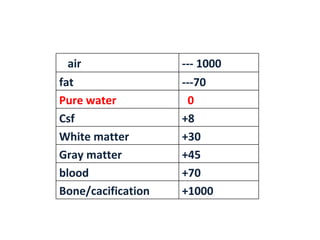
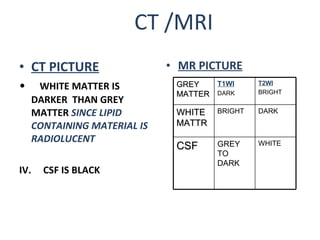
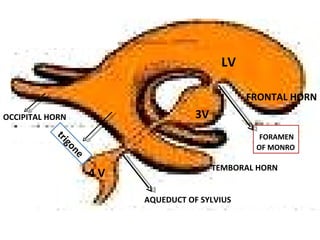
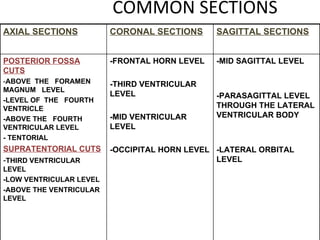
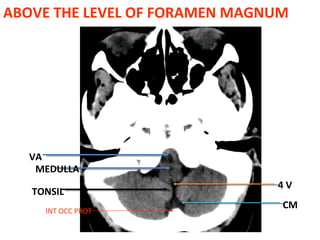
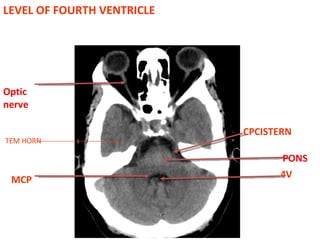
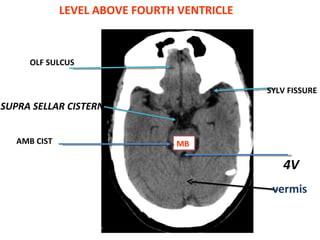
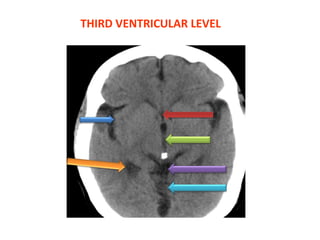
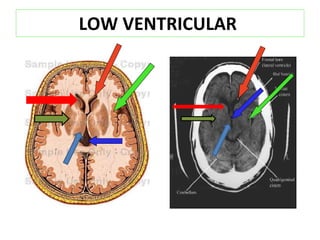
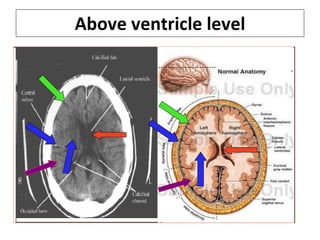
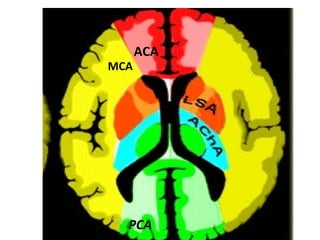
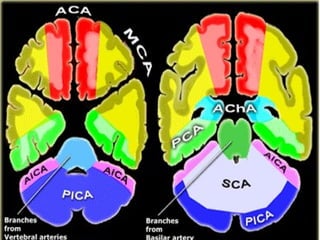
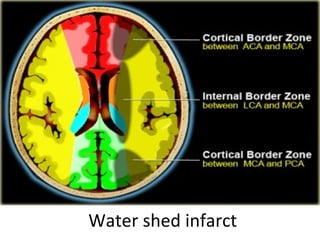
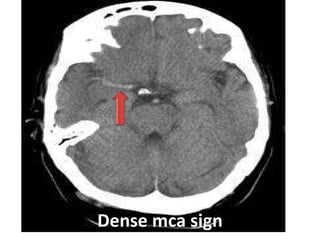
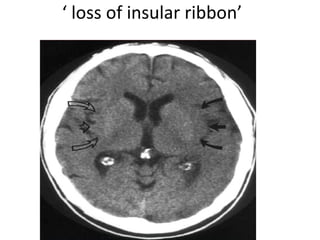
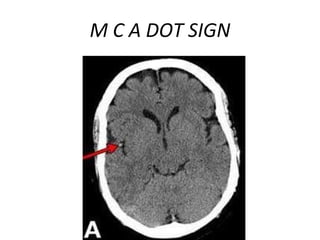
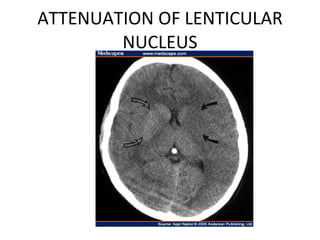
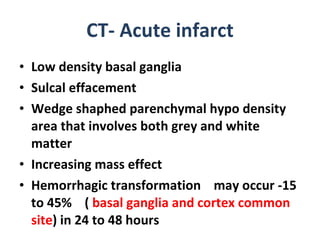
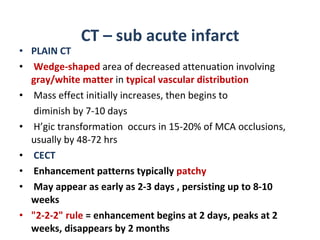
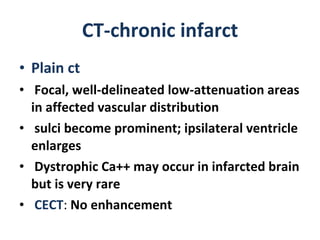
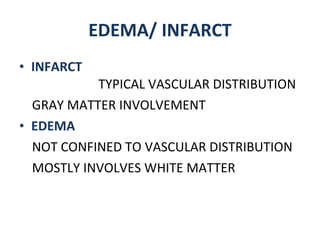
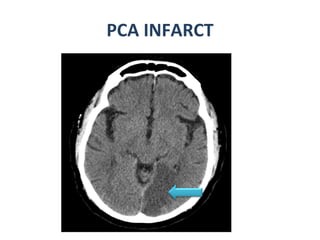
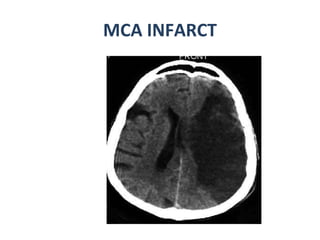
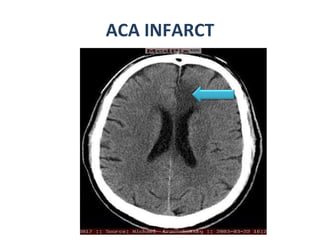
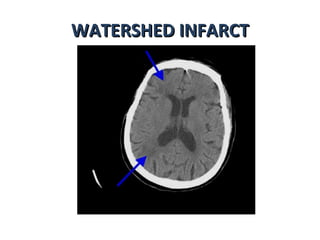
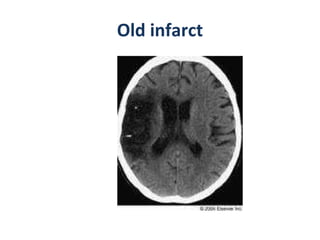
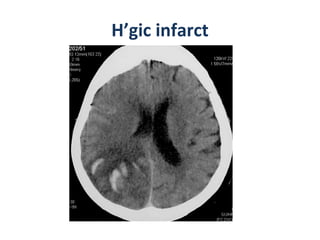
CT scanning provides images of brain tissue based on density differences detected by x-rays. The images produced use Hounsfield units to represent densities on a scale where air is -1000 and bone is +1000. On CT, white matter appears darker than gray matter and CSF appears black. Common sequences seen on CT include axial, coronal, and sagittal cuts at various anatomical levels. CT is used to identify acute ischemic strokes within 12 hours by detecting hyperdense arteries, and in subsequent days can identify low density infarcts and hemorrhagic transformations. Chronic infarcts appear as well-defined low attenuation areas.