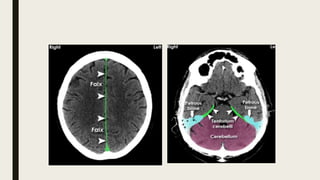
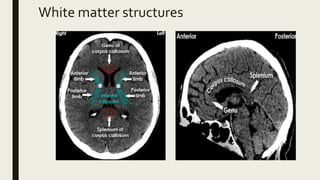
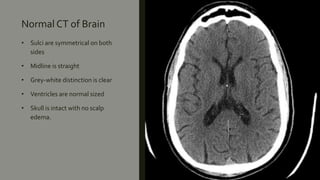
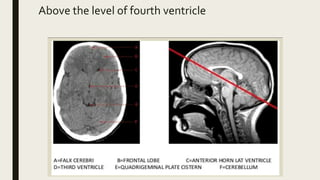
This document discusses the radiological anatomy of the brain as seen on CT scans. It begins by outlining the systematic approach used to interpret CT scans, including assessing symmetry, midline structures, cross-sectional anatomy, and skull and soft tissues. It then describes key anatomical structures visible on CT such as the cranial fossae, meninges, fissures, ventricles, grey and white matter. The document also discusses how CT is used to identify ischemic strokes at different stages, from immediate changes like hyperdense vessels, to acute swelling, subacute resolving swelling, and chronic infarction. It notes CT perfusion can identify the infarct core and penumbra using parameters like CBV, CBF, MTT and