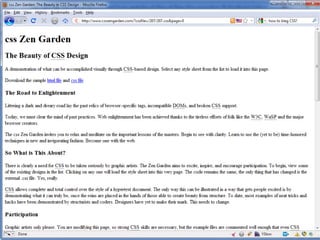
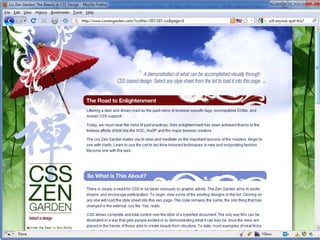
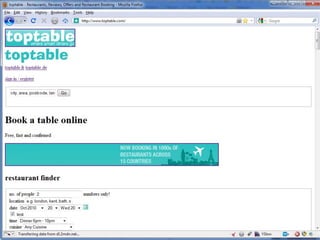
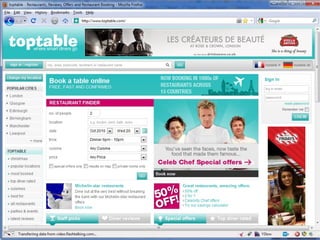
The document provides an overview of CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) including the basics of syntax, selectors, properties and values. It discusses concepts like the cascade, inheritance and specificity which determine how CSS rules are applied. It also covers common problems and challenges with CSS implementation as well as future developments with CSS3.



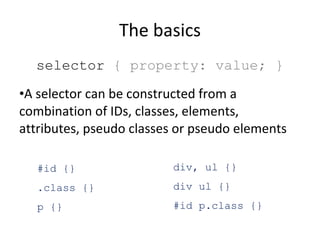
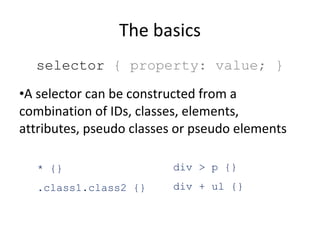
![The basics selector { property: value; } A selector can be constructed from a combination of IDs, classes, elements, attributes, pseudo classes or pseudo elements a[target=_blank] {} :first-child {} :before {} :after {}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/css-110118092526-phpapp01/85/An-Introduction-to-CSS-12-320.jpg)



![Specificity Properties with the !important declaration Inline styles Elements with styles specifically applied, in the following order ID ( #content-body ) Classes, attributes and pseudo-classes (.container, a[target], p:first-line) Elements and pseudo-elements ( div, :hover ) Inherited styles, with the same order as above](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/css-110118092526-phpapp01/85/An-Introduction-to-CSS-16-320.jpg)










