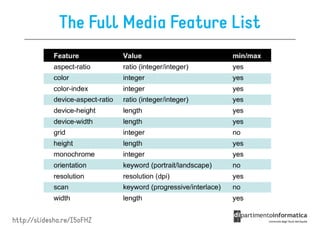
This document provides an overview of CSS3 features including basics, selectors, the box model, positioning, fonts, visual effects, and media queries. Some key points covered include:
- CSS3 is the presentation companion of HTML5 and allows for simpler, more performant, and accessible web design.
- New CSS3 features are supported by most modern browsers and provide benefits like fewer images, less code, and better search engine optimization.
- CSS3 introduces properties for backgrounds, borders, text effects, transitions, transforms, animations and flexible box layout.
- Media queries allow styling to adapt based on conditions like device width, orientation and resolution.





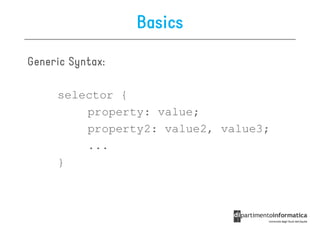









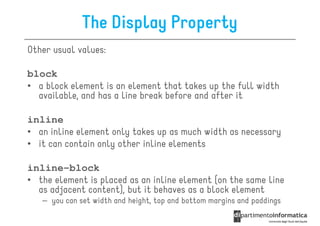
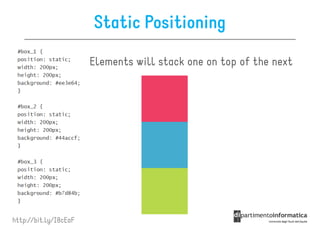
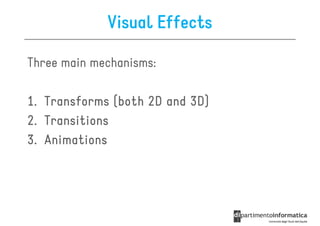
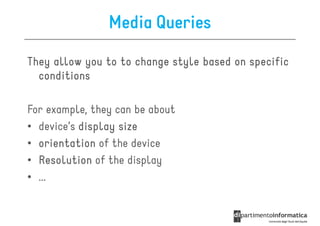
![Other Selectors from CSS1 & CSS2
• div p all <p> elements inside a <div>
• div>p all <p> elements where the parent is a <div>
• div+p all <p> elements that are placed immediately
after <div>
• [target] all elements with a target attribute
• [target=_blank] all elements with target=
"_blank“
• p:first-child
p:first- every <p> element that is the first
child of its parent](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture11-120430105757-phpapp02/85/CSS3-Refresher-20-320.jpg)
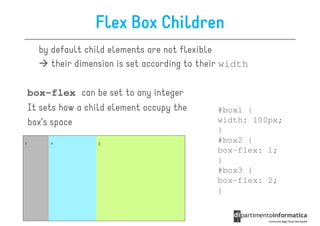
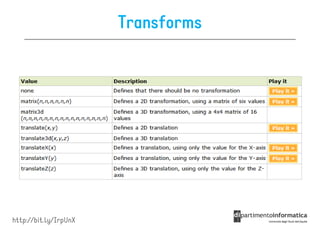
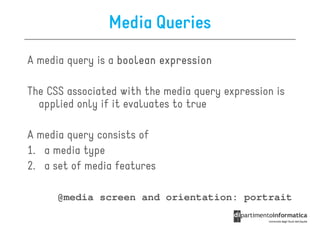
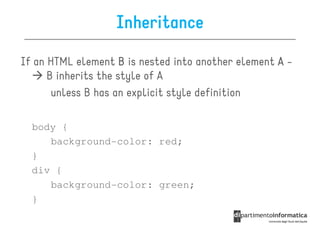
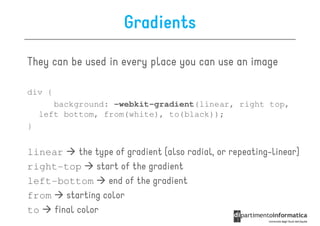
![Some selectors introduced in CSS3
• a[src^="https"]
a[src^="https"]
src every <a> element whose src
attribute value begins with "https”
a[src$=".pdf
src$=".pdf"]
• a[src$=".pdf"] every <a> element whose src attribute
value ends with ".pdf”
a[src
src*=“mobile"]
• a[src*=“mobile"] every <a> element whose src
attribute value contains the substring “mobile“
p:nth-
• p:nth-child(2) every <p> element that is the second
child of its parent
p:nth-last-
• p:nth-last-child(2) every <p> element that is the
second child of its parent, counting from the last child
• :not(p) every element that is not a <p> element](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture11-120430105757-phpapp02/85/CSS3-Refresher-21-320.jpg)