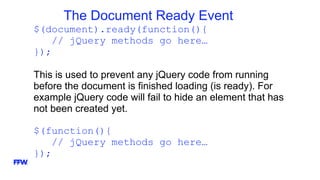
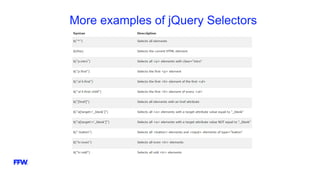
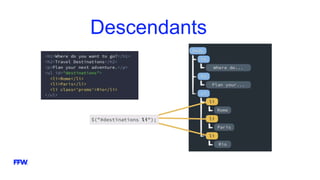
The document provides an overview and introduction to jQuery, including:
1) jQuery is a popular JavaScript library that simplifies client-side scripting of HTML and makes it easier to search, select, and manipulate DOM elements.
2) jQuery syntax uses $ to select elements and perform actions on them. Common uses include HTML/DOM manipulation, CSS manipulation, events, effects/animations, and AJAX.
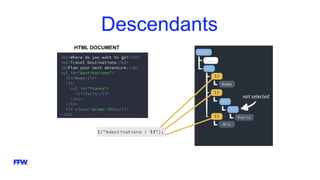
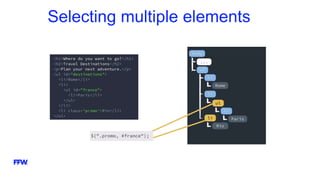
3) The document discusses jQuery selectors, events, traversing, chaining/stacking, and plugins to demonstrate jQuery's capabilities for interacting with web pages.